Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
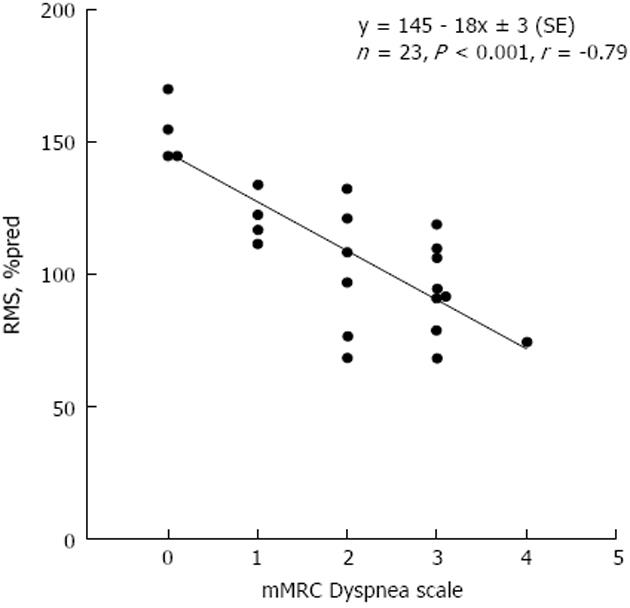
Figure 1 Relationship of respiratory muscle strength (percent of predicted) and modified medical research council dyspnea score in end-stage liver patients without ascites.
Solid line: Linear regression. Linear regression equation and corresponding Pearson’s correlation coefficient are shown. The slope of the line indicates that the dyspnea score increases, on average, by one modified medical research council score unit per approximately 20% decrease in respiratory muscle strength, percent of predicted (%pred). RMS: respiratory muscle strength; mMRC: modified medical research council.
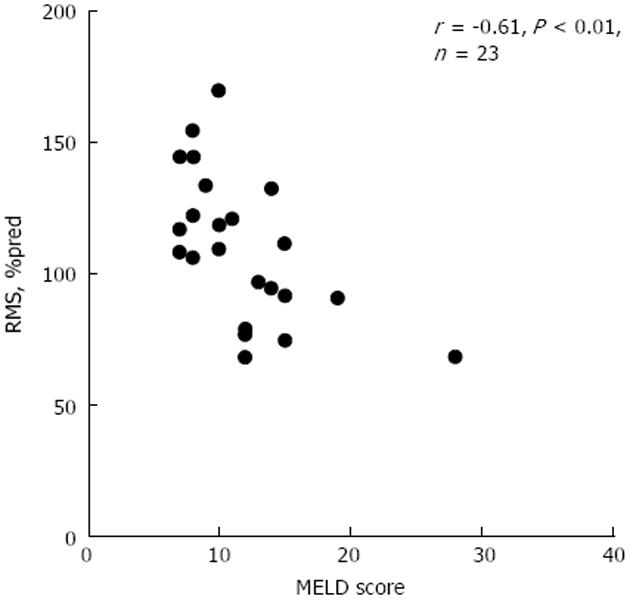
Figure 2 Relationship of respiratory muscle strength (percent of predicted) and end-stage liver disease score in end-stage liver patients without ascites.
RMS: respiratory muscle strength; MELD: model for end-stage liver disease; %pred: percent of predicted.
- Citation: Kaltsakas G, Antoniou E, Palamidas AF, Gennimata SA, Paraskeva P, Smyrnis A, Koutsoukou A, Milic-Emili J, Koulouris NG. Dyspnea and respiratory muscle strength in end-stage liver disease. World J Hepatol 2013; 5(2): 56-63
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v5/i2/56.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v5.i2.56