Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2012; 4(12): 402-405
Published online Dec 27, 2012. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i12.402
Published online Dec 27, 2012. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i12.402
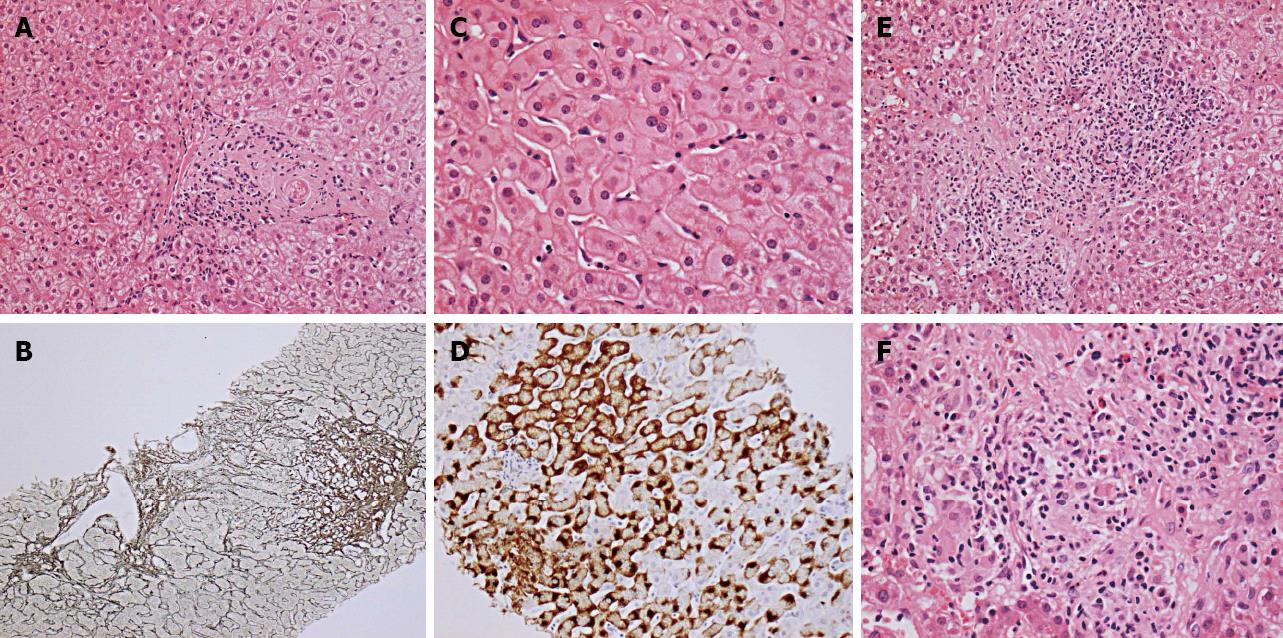
Figure 1 The histological features of hepatic sarcoidosis complicating chronic hepatitis B virus infection.
A: Portal tract showing minimal portal inflammation attributable to hepatitis B virus [haematoxylin eosin (HE) staining ×20]; B: Portal fibrosis (reticulin ×40); C: Ground glass hepatocytes (HE ×40); D: Hepatitis B surface antigen immunostain showing accumulation in cytoplasm (×20); E: Granulomatous portal tract inflammation with duct irregularity (HE ×20); F: High power portal granulomatous inflammation (HE ×40).
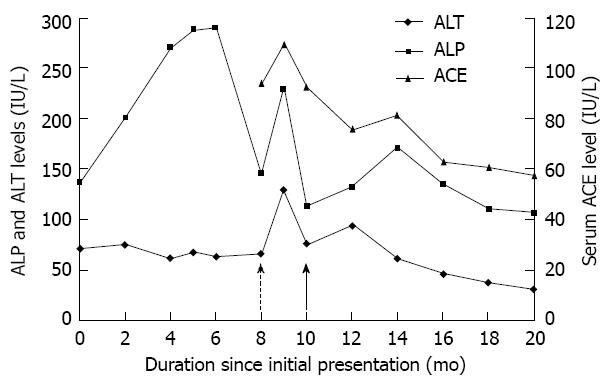
Figure 2 The changes in alanine transaminase, alkaline phosphatase and angiotensin converting enzyme levels in patient 1.
The dotted arrow and the solid arrow mark the commencement of antiviral treatment and steroid treatment respectively. ALT: Alanine transaminase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme.
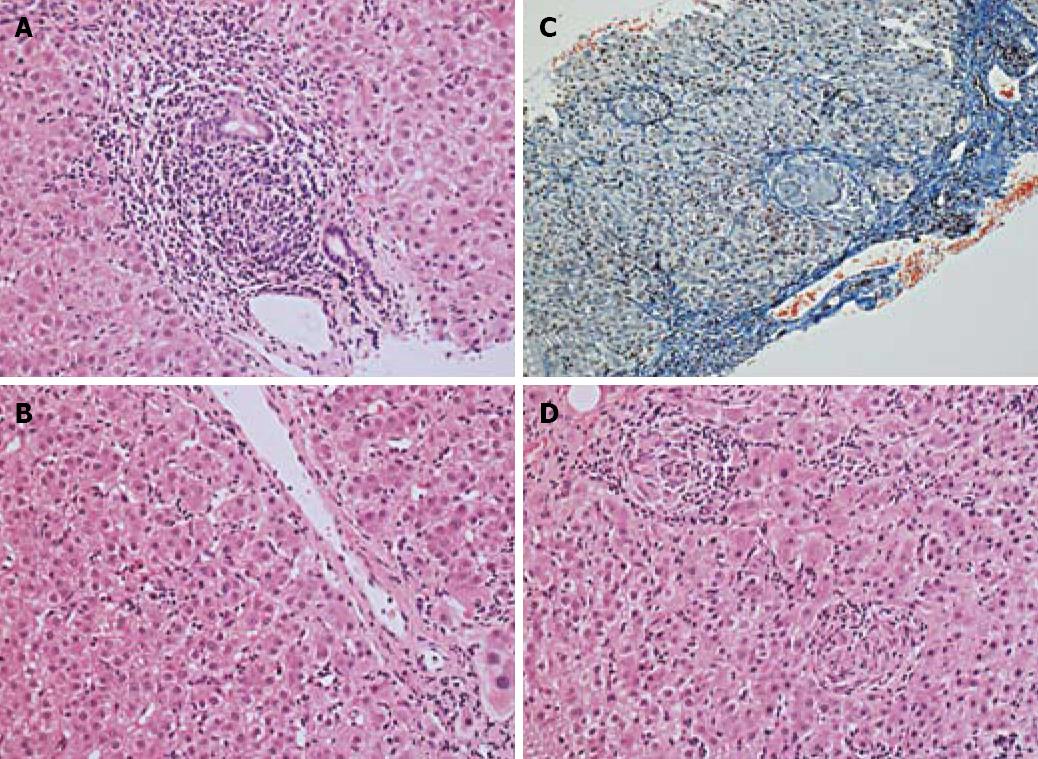
Figure 3 Histological features of hepatic sarcoidosis complicating chronic hepatitis C virus infection.
A: Portal inflammation including lymphoid follicle and interface activity [haematoxylin eosin (HE) staining ×20]; B: Parenchymal inflammation and necroinflammation with acidophil bodies (HE ×20); C: Architectural stain showing parenchymal granulomatous inflammation and fibrosis (Chromotrope-Aniline Blue ×10); D: Parenchymal granulomatous hepatitis (HE ×20).
Figure 4 The changes in alanine transaminase, alkaline phosphatase and angiotensin converting enzyme levels in patient 2.
The arrow marks the commencement of steroid treatment. ALT: Alanine transaminase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme.
- Citation: Aravinthan A, Gelson W, Limbu A, Brais R, Richardson P. Hepatic sarcoidosis complicating treatment-naive viral hepatitis. World J Hepatol 2012; 4(12): 402-405
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v4/i12/402.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v4.i12.402