Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Aug 27, 2010; 2(8): 311-317
Published online Aug 27, 2010. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v2.i8.311
Published online Aug 27, 2010. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v2.i8.311
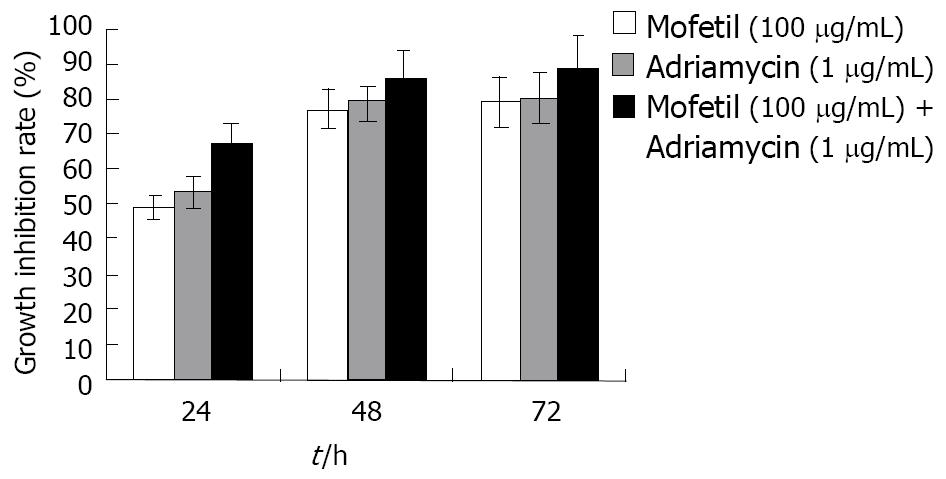
Figure 1 The inhibitory effects of mofetil + adriamycin treatment on the growth of HepG-2 cells.
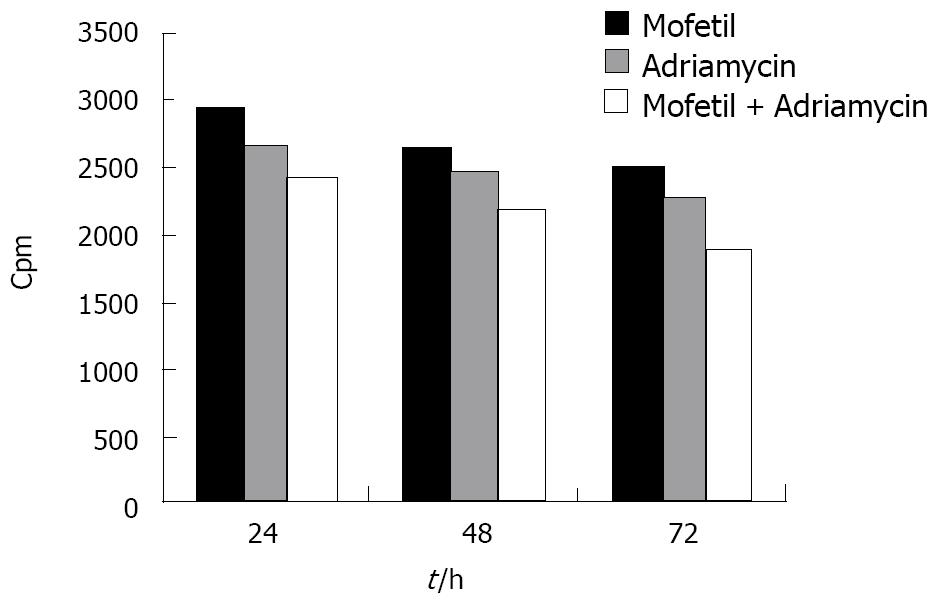
Figure 2 Effects of mofetil + adriamycin treatment on the proliferation of HepG-2 cells.
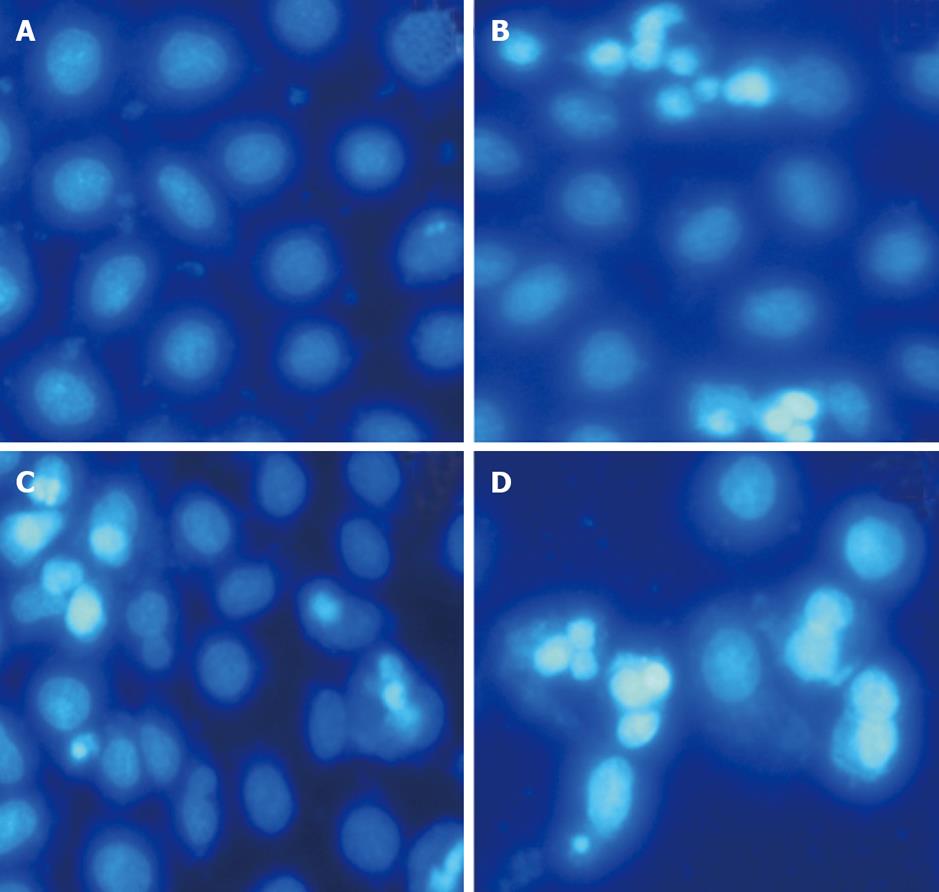
Figure 3 Morphological changes in the apoptotic cells after Hoechst 33258 staining (×200).
A: Untreated HepG-2 cells; B: HepG-2 cells treated with 100 μg/mL mofetil (MMF) for 48 h; C: HepG-2 cells treated with 1 μg/mL adriamycin (ADM) for 48 h; D: HepG-2 cells treated with MMF + ADM for 48 h.
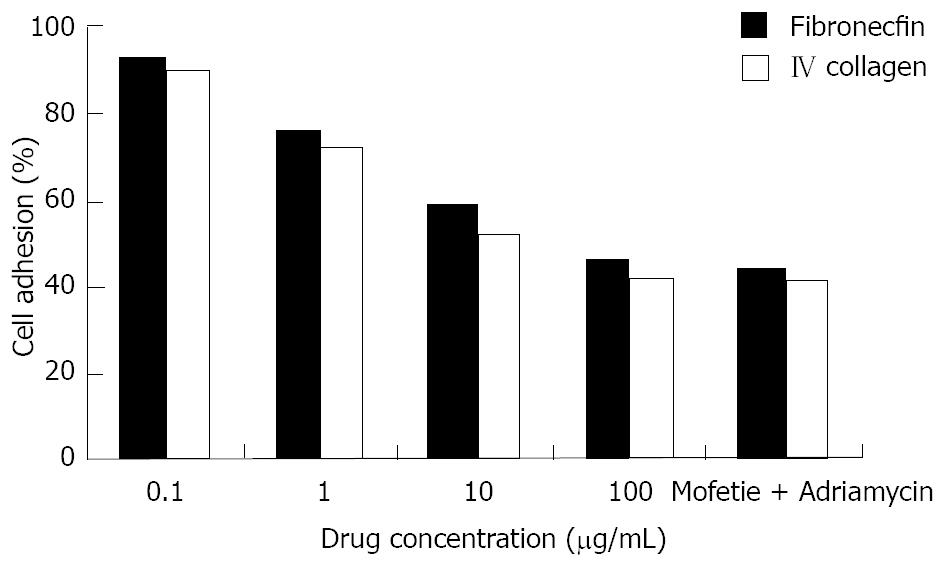
Figure 4 Effect of mofetil + adriamycin treatment on the adhesion properties of HepG-2 cells.
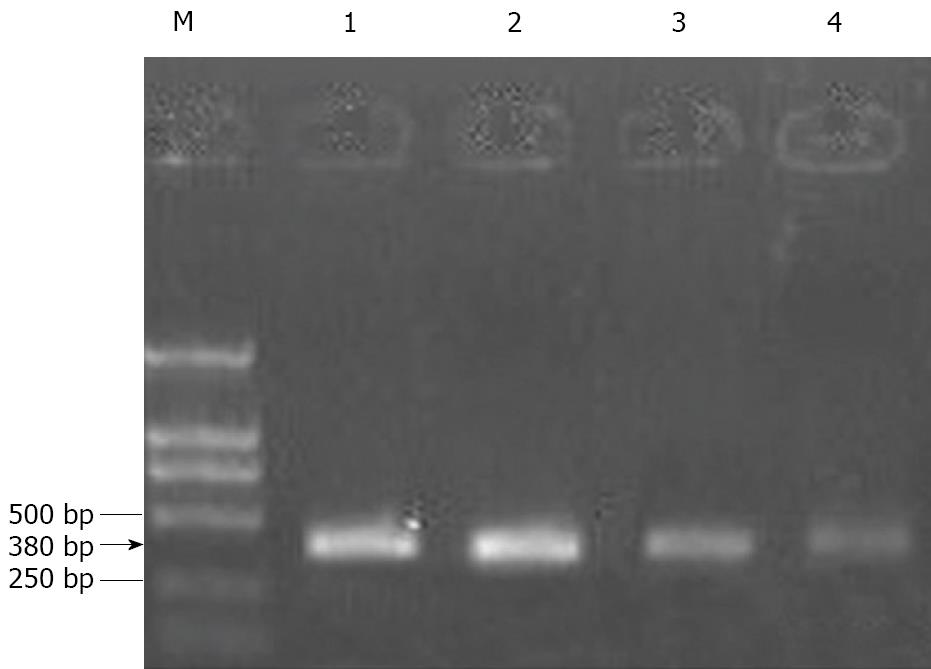
Figure 5 Effect of mofetil + adriamycin treatment on Bcl-2 gene expression in HepG-2 cells.
M: Standard reference; 1: Untreated HepG-2 cells; 2: HepG-2 cells treated with 100 μg/mL mofetil (MMF) for 72 h; 3: HepG-2 cells treated with 1 μg/mL adriamycin (ADM) for 72 h; 4:HepG-2 cells treated with MMF (100 μg/mL) + ADM (1 μg/mL) for 72 h.
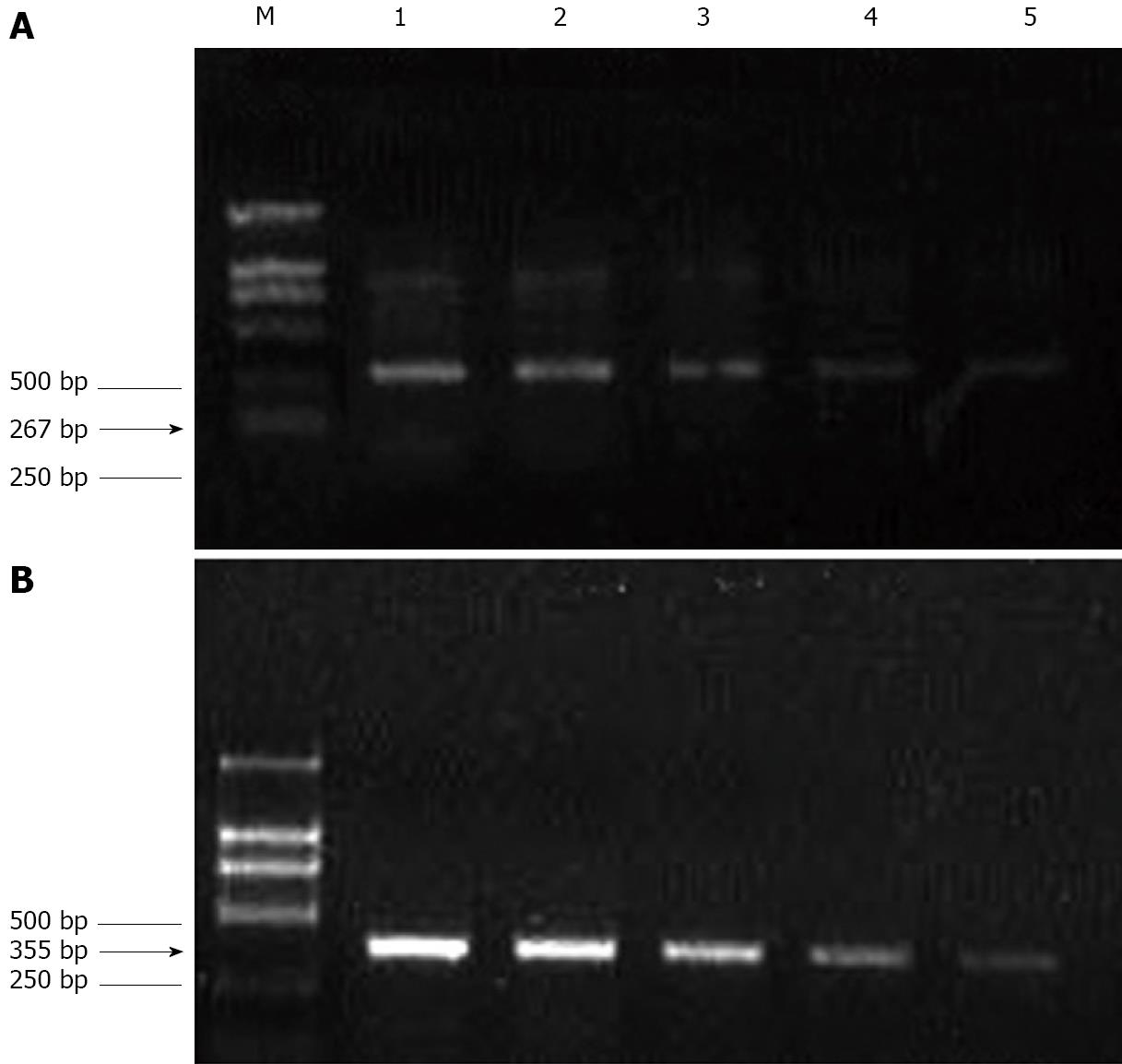
Figure 6 Effect of mofetil + adriamycin treatment on gene expression in HepG-2 cells.
A: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1; B: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; M: Standard reference; 1: Untreated HepG-2 cells; 2: HepG-2 cells treated with 0.1 μg/mL mofetil (MMF) for 72 h; 3: HepG-2 cells treated with 1 μg/mL MMF for 72 h; 4: HepG-2 cells treated with 10 μg/mL MMF for 72 h; 5: HepG-2 cells treated with 100 μg/mL MMF for 72 h.
- Citation: Chu YK, Liu Y, Yin JK, Wang N, Cai L, Lu JG. Effect of mycophenolate mofetil plus adriamycin on HepG-2 cells. World J Hepatol 2010; 2(8): 311-317
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v2/i8/311.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v2.i8.311