Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. May 27, 2025; 17(5): 106892
Published online May 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i5.106892
Published online May 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i5.106892
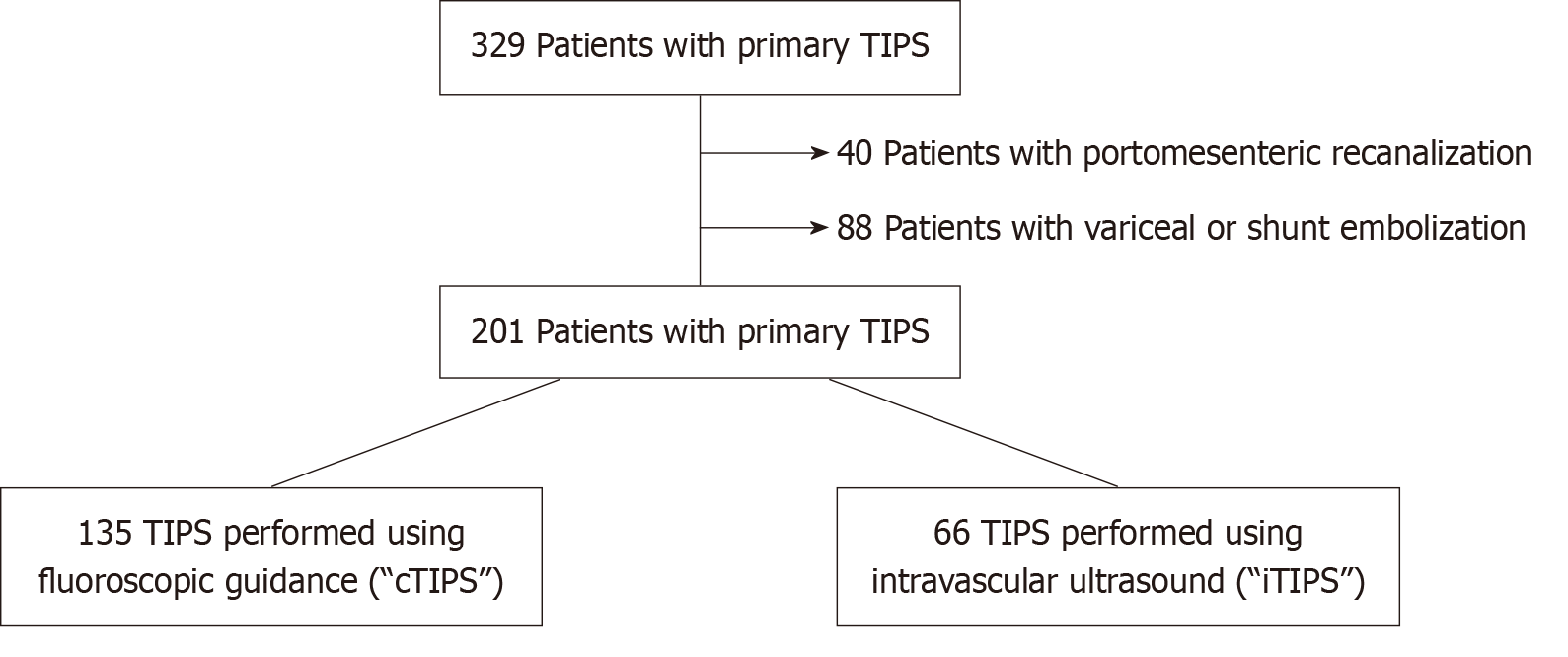
Figure 1 Study cohort derivation.
After identifying patients who underwent transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation, patients were excluded if portomesenteric recanalization or variceal/shunt embolization was required. Patients were then divided into cohorts based on the predominant imaging guidance modality used during transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation. TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; iTIPS: Intravascular ultrasound-guided transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; cTIPS: Conventional fluoroscopic-guided transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
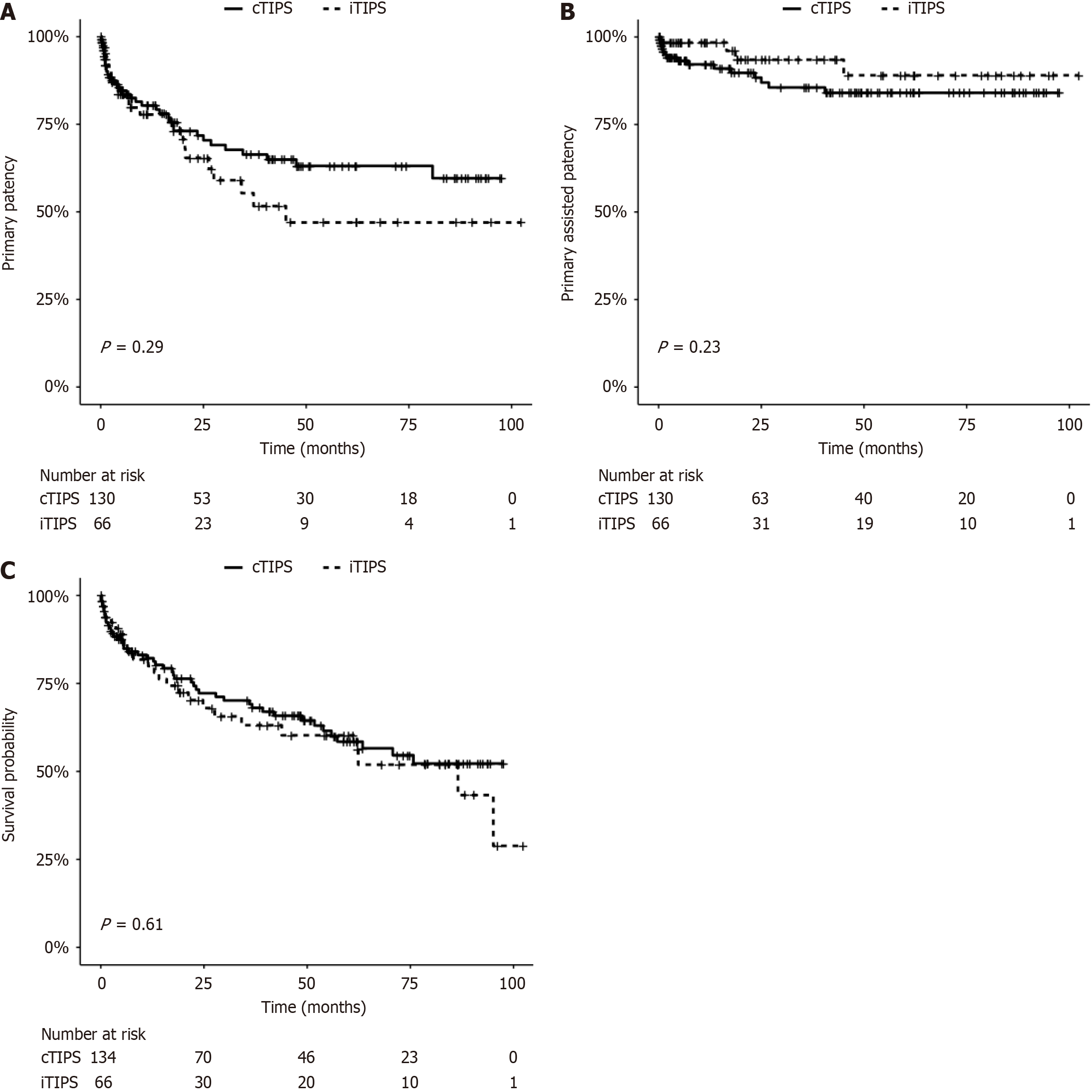
Figure 2 Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: a comparative analysis of patency and patient mortality between intravascular ultrasound guidance vs fluoroscopic guidance.
A log-rank test was used for statistical comparison. A: Kaplan-Meier survival curves are shown for intervention-free survival (e.g. primary patency); B: Kaplan-Meier survival curves are shown for thrombosis-free survival (e.g. primary assisted patency) comparing the conventional fluoroscopic-guided transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) and intravascular ultrasound-guided TIPS groups; C: Patient mortality following TIPS creation. Kaplan-Meier survival curves are shown for the conventional fluoroscopic-guided TIPS and intravascular ultrasound-guided TIPS groups following TIPS creation. iTIPS: Intravascular ultrasound-guided transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; cTIPS: Conventional fluoroscopic-guided transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
- Citation: Hung ML, Jairam A, Carr M, Berman ZT, Taddonio M, Minocha J, Aryafar H, Mondschein JI, Soulen MC, Nadolski GJ, Redmond J. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation using intravascular ultrasound vs fluoroscopic guidance: A dual-institution retrospective comparative study. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(5): 106892
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i5/106892.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i5.106892