Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Jan 27, 2023; 15(1): 116-122
Published online Jan 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i1.116
Published online Jan 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i1.116
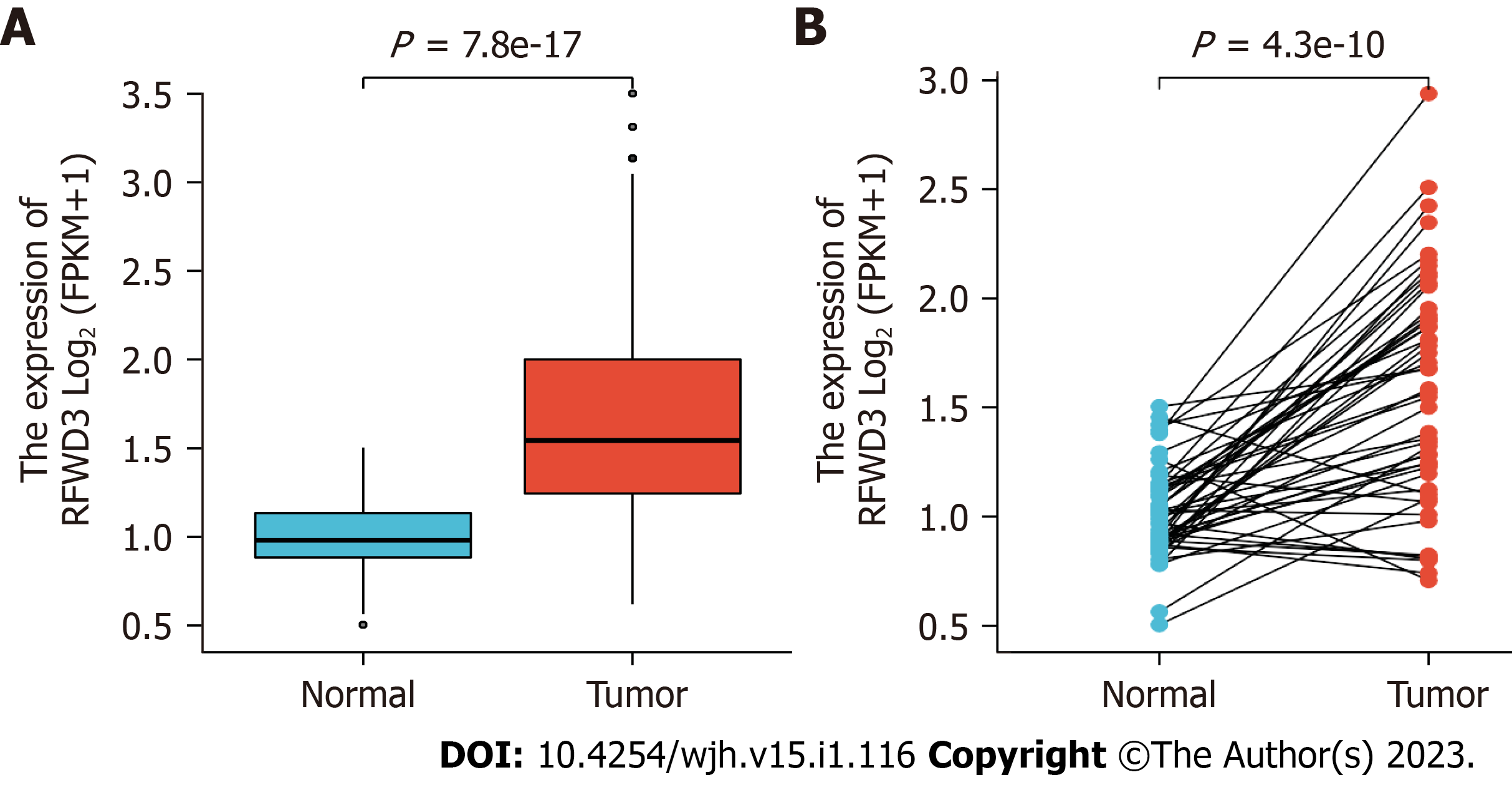
Figure 1 Differential expression levels of ring finger and WD repeat domain 3 in hepatocellular carcinoma and normal tissues.
A: Non-paired hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and normal samples; B: Paired HCC and normal samples. Data source: mRNA-Seq data from the Genotype-Tissue Expression project (GTEx) of The Cancer Genome Atlas processed through the Toil process in the UCSC Xena database. (https://xenabrowser.net/datapages/)[2].
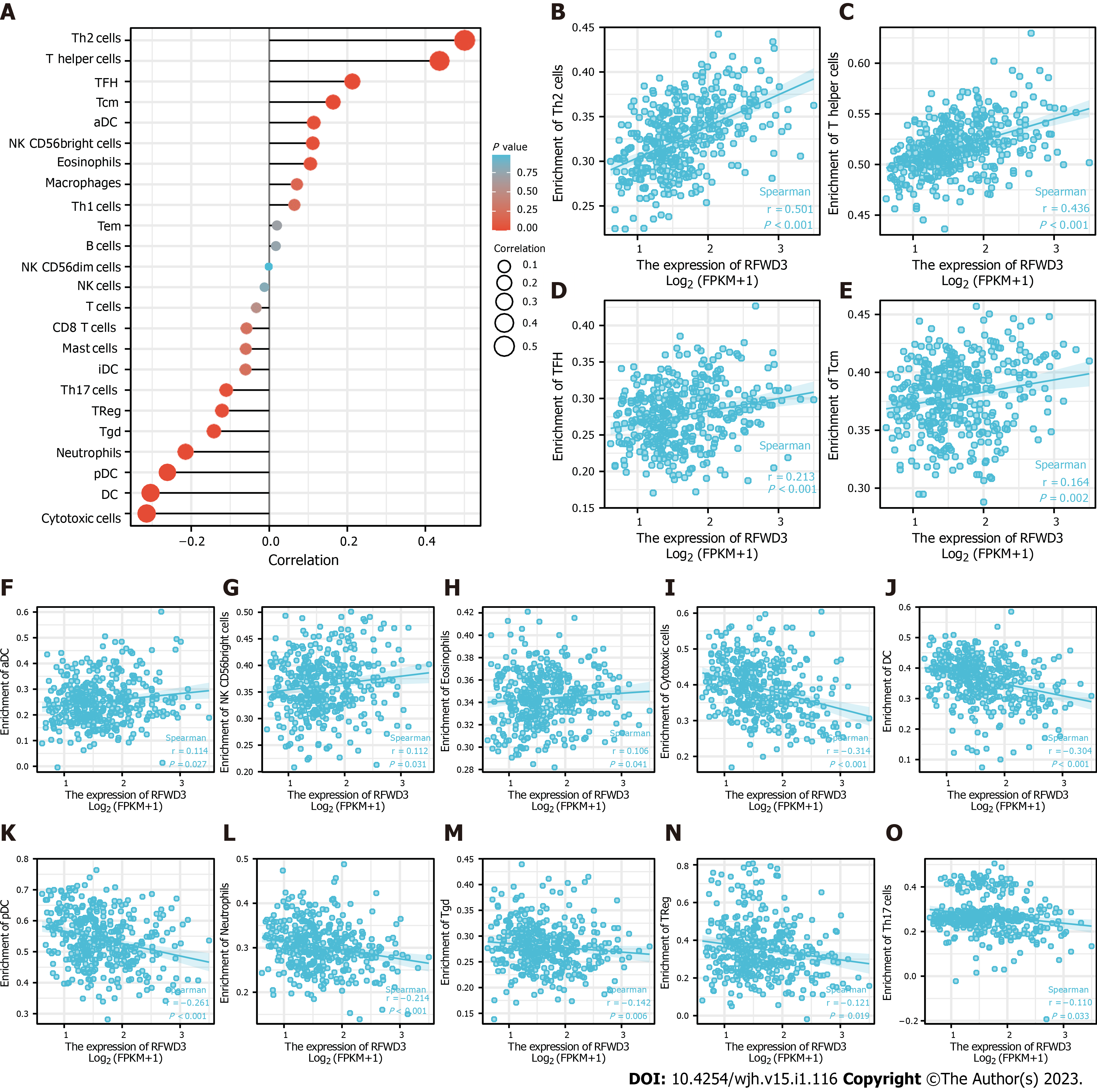
Figure 2 Correlation analysis of ring finger and WD repeat domain 3 expression and immune cell infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Lollipop plot manifesting the correlation between ring finger and WD repeat domain 3 (RFWD3) expression and the infiltration level of 24 immune cell types; B-H: The infiltration levels of 7 immune cell types have significant positive correlation with RFWD3 expression; B: T helper (Th)2 cells; C: Th cells; D: T follicular helper (TFH) cells; E: T central memory (Tcm) cells; F: Activated dendritic cells (aDCs); G: Natural killer (NK) CD56bright cells; H: Eosinophils; I-O: The infiltration levels of 7 immune cell types have significant negative correlation with RFWD3 expression; I: Cytotoxic cells; J: Dendritic cells (DCs); K: Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs); L: Neutrophils; M: T gamma delta (Tgd) cells; N: T regulatory cells (Tregs); O: Th17 cells.
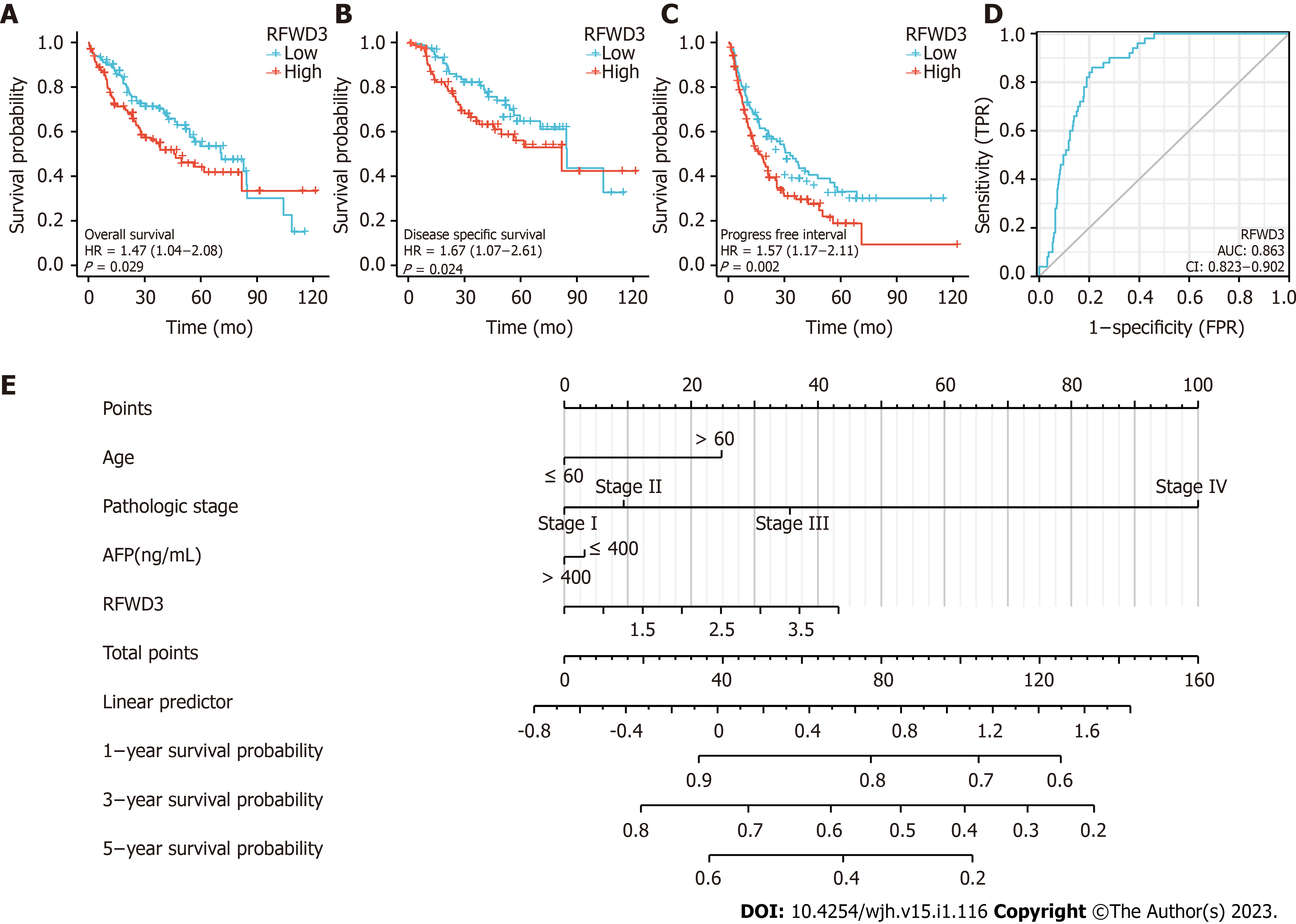
Figure 3 Survival analysis of ring finger and WD repeat domain 3 in hepatocellular carcinoma and the nomogram for prognosis.
A-C: Ring finger and WD repeat domain 3 (RFWD3) expression is related to overall survival, disease-specific survival (B) and progression-free interval (C)[9] in the The Cancer Genome Atlas-liver hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) data; D: Receiver operating characteristic curves for the RFWD3 gene’s prognosis predictive ability. The nomogram can predict 1-, 3- and 5-year overall survival of HCC based on clinicopathological features and the expression of RFWD3.
- Citation: Miao YD, Quan WX, Wang JT, Gan J, Dong X, Zhang F. Prognostic role of ring finger and WD repeat domain 3 and immune cell infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2023; 15(1): 116-122
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i1/116.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i1.116