Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Apr 27, 2021; 13(4): 393-410
Published online Apr 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i4.393
Published online Apr 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i4.393
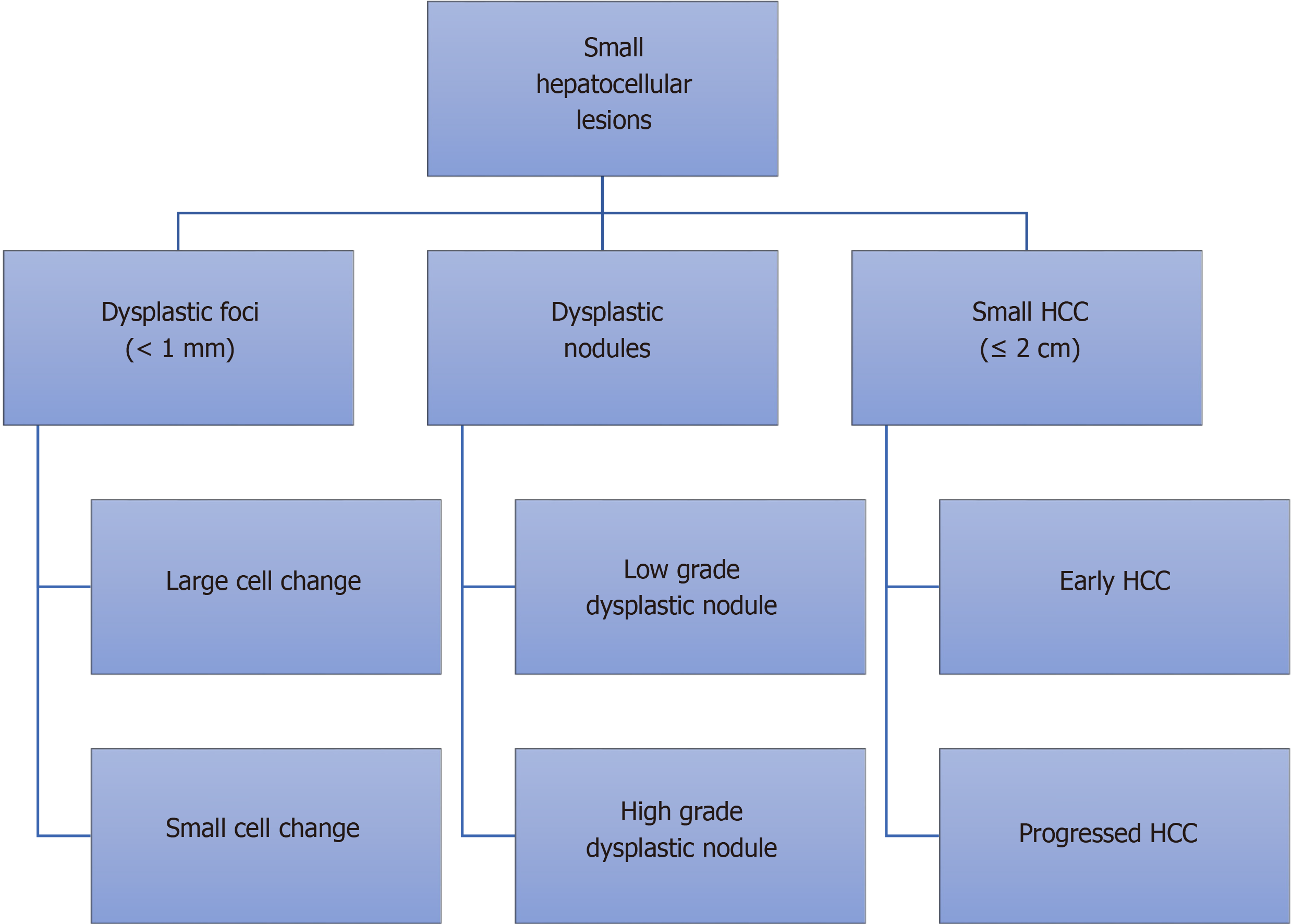
Figure 1 International consensus group for hepatocellular neoplasia classification of small hepatocellular lesions.
HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
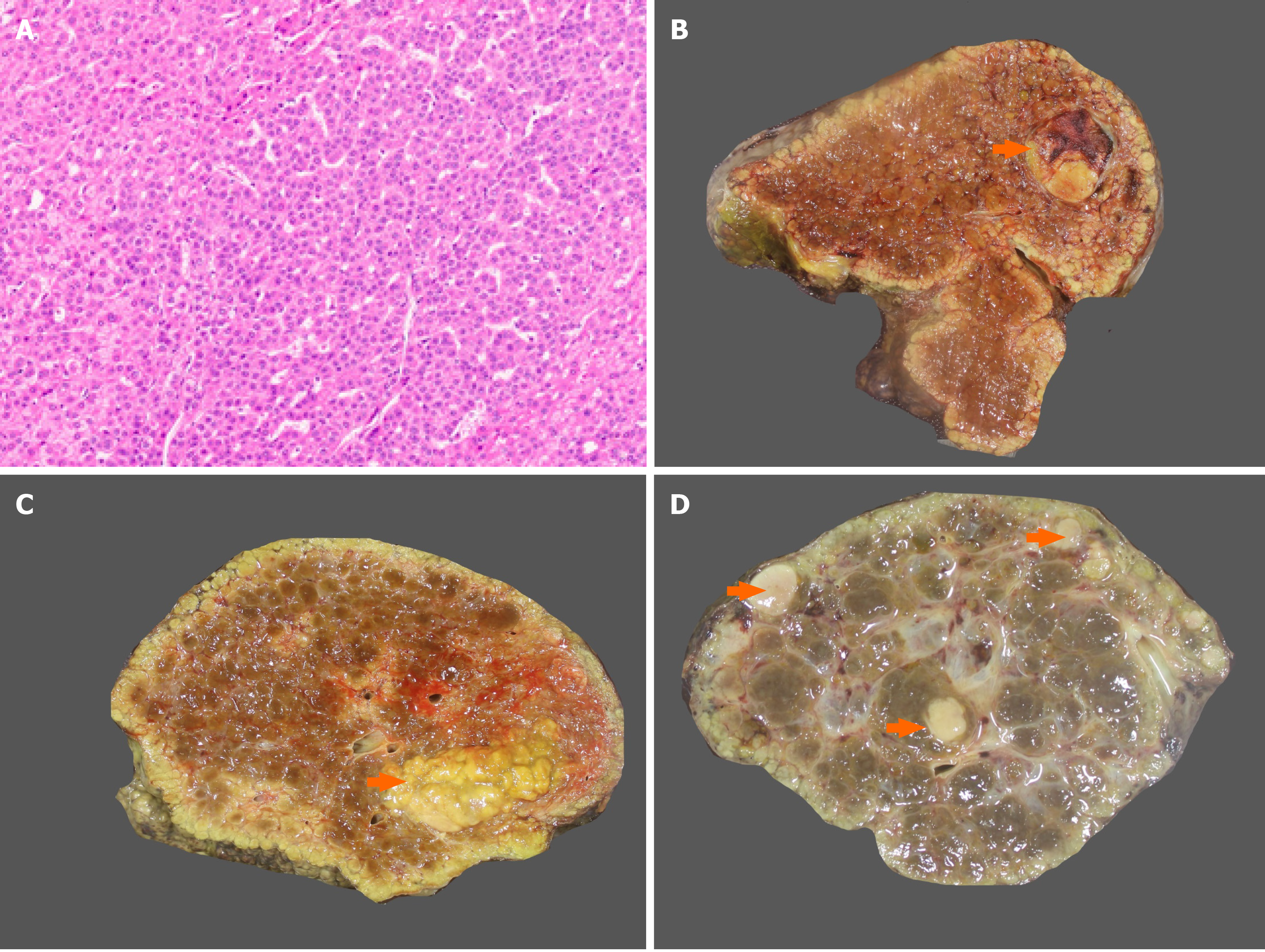
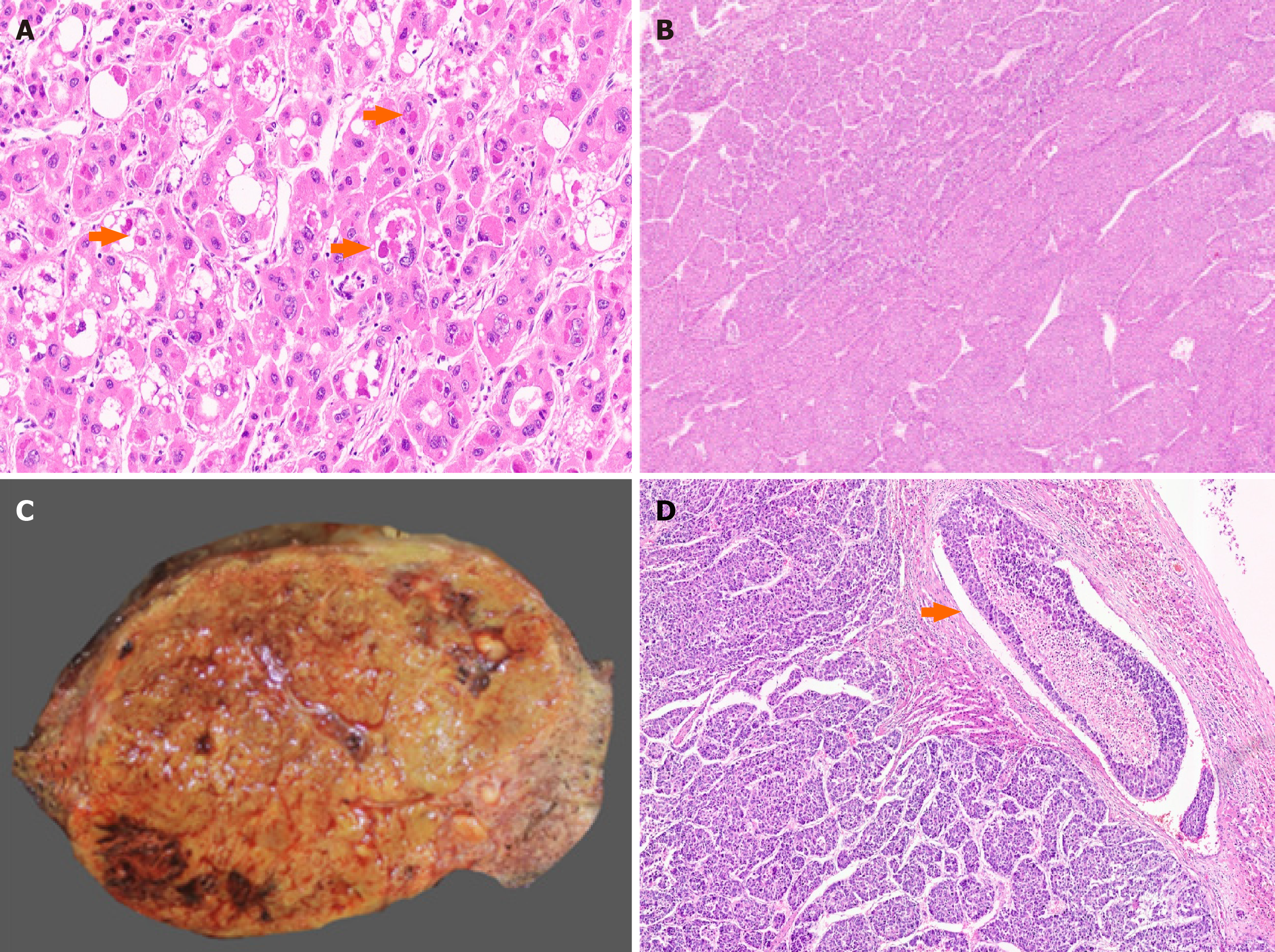
Figure 2 Dysplasia and gross morphology of hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Dysplastic foci with small cell change (hematoxylin and eosin); B: Nodular hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in a cirrhotic liver (arrow); C: Multinodular HCC in a cirrhotic liver (arrow); D: Multicentric HCC (arrow).
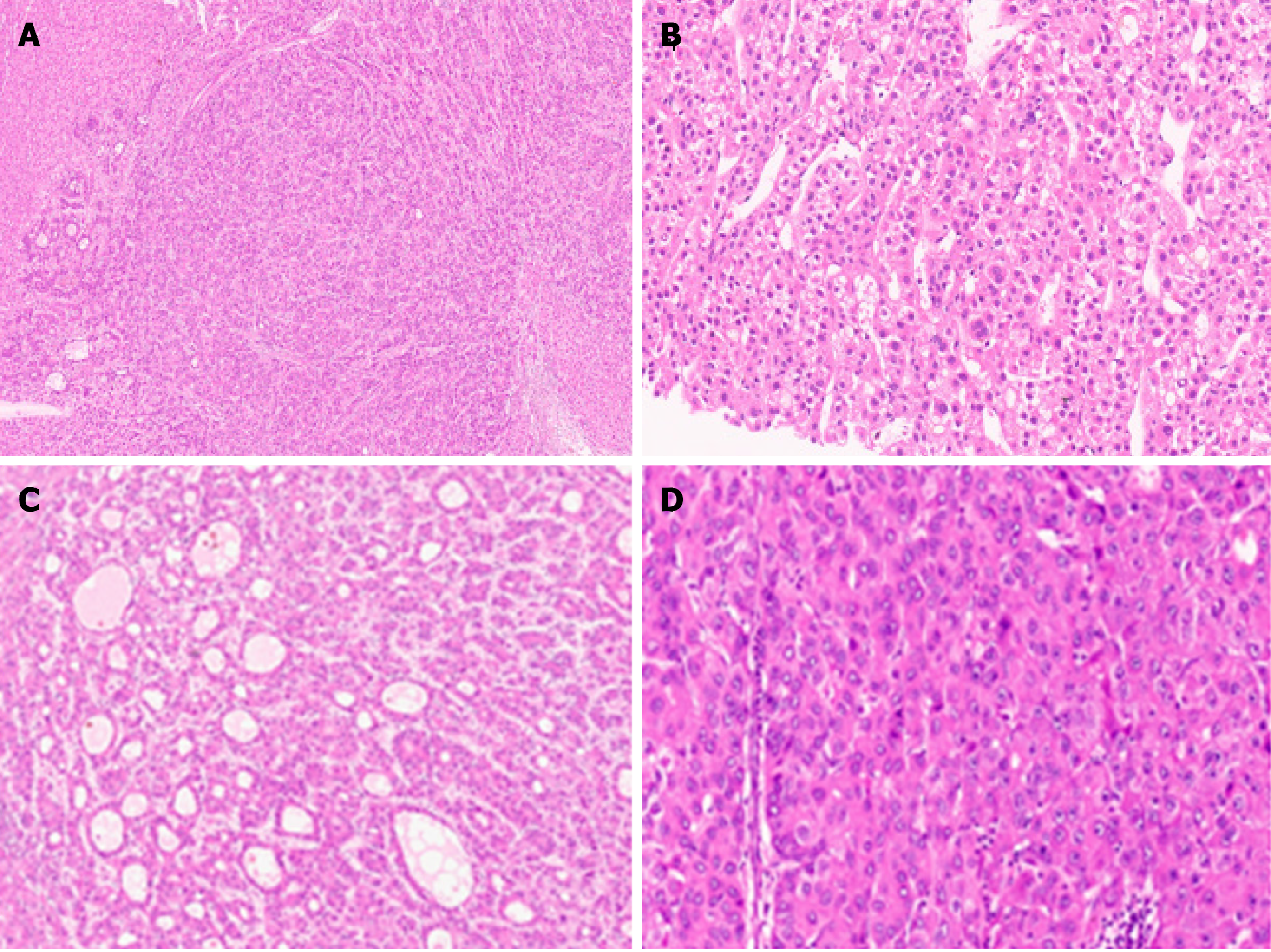
Figure 3 Well differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Early hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with pseudoacinar pattern [hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)]; B: Well differentiated HCC with thin trabeculae (H&E); C: Well differentiated HCC with pseudoacini (H&E); D: HCC with solid sheet growth pattern (H&E).
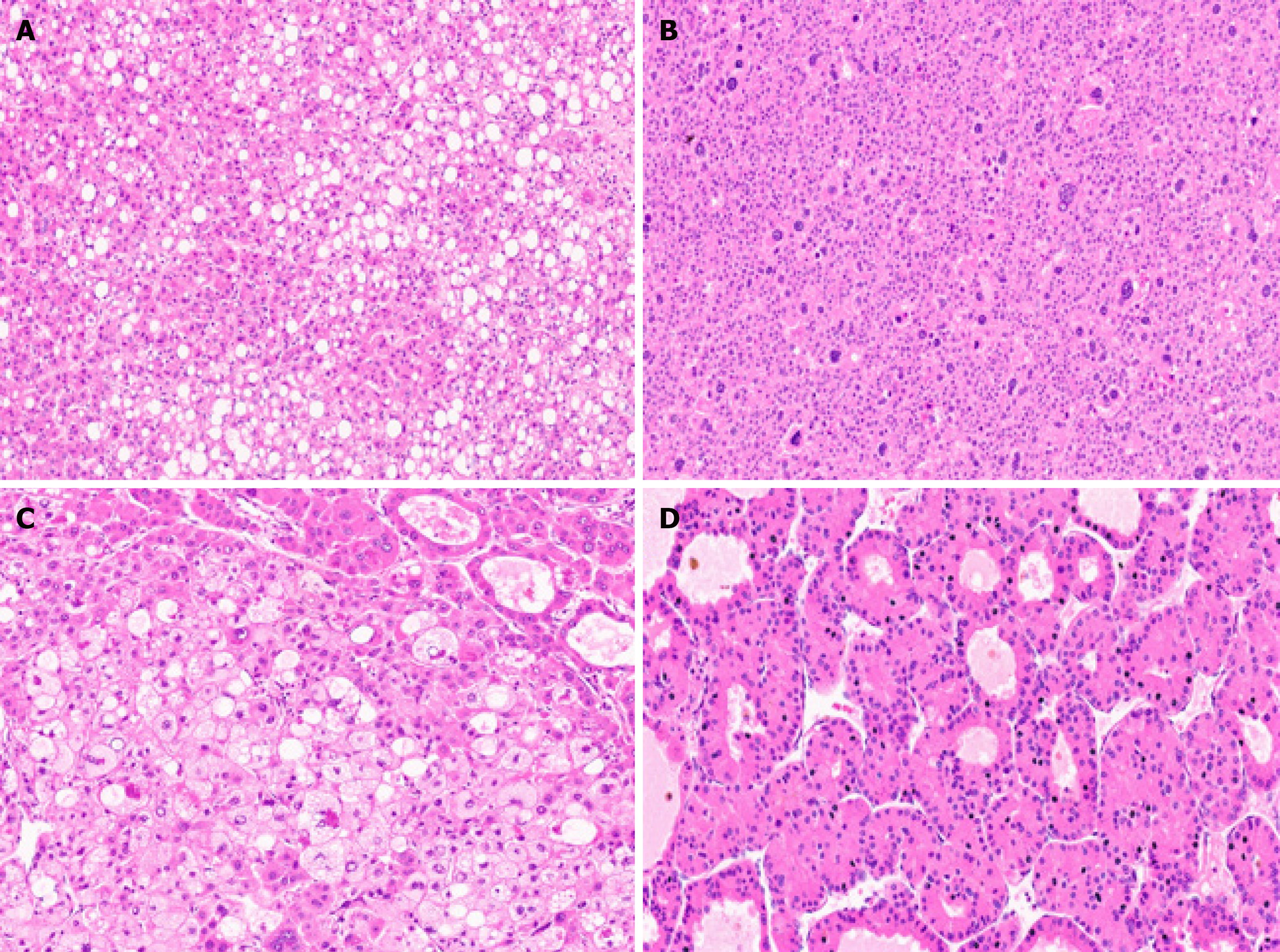
Figure 4 Hepatocellular carcinoma cytological features.
A: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with fatty change [hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)]; B: Marked pleomorphism in an HCC (H&E); C: Foamy cell cytoplasm in an HCC (H&E); D: HCC with oncocytic cells (H&E).
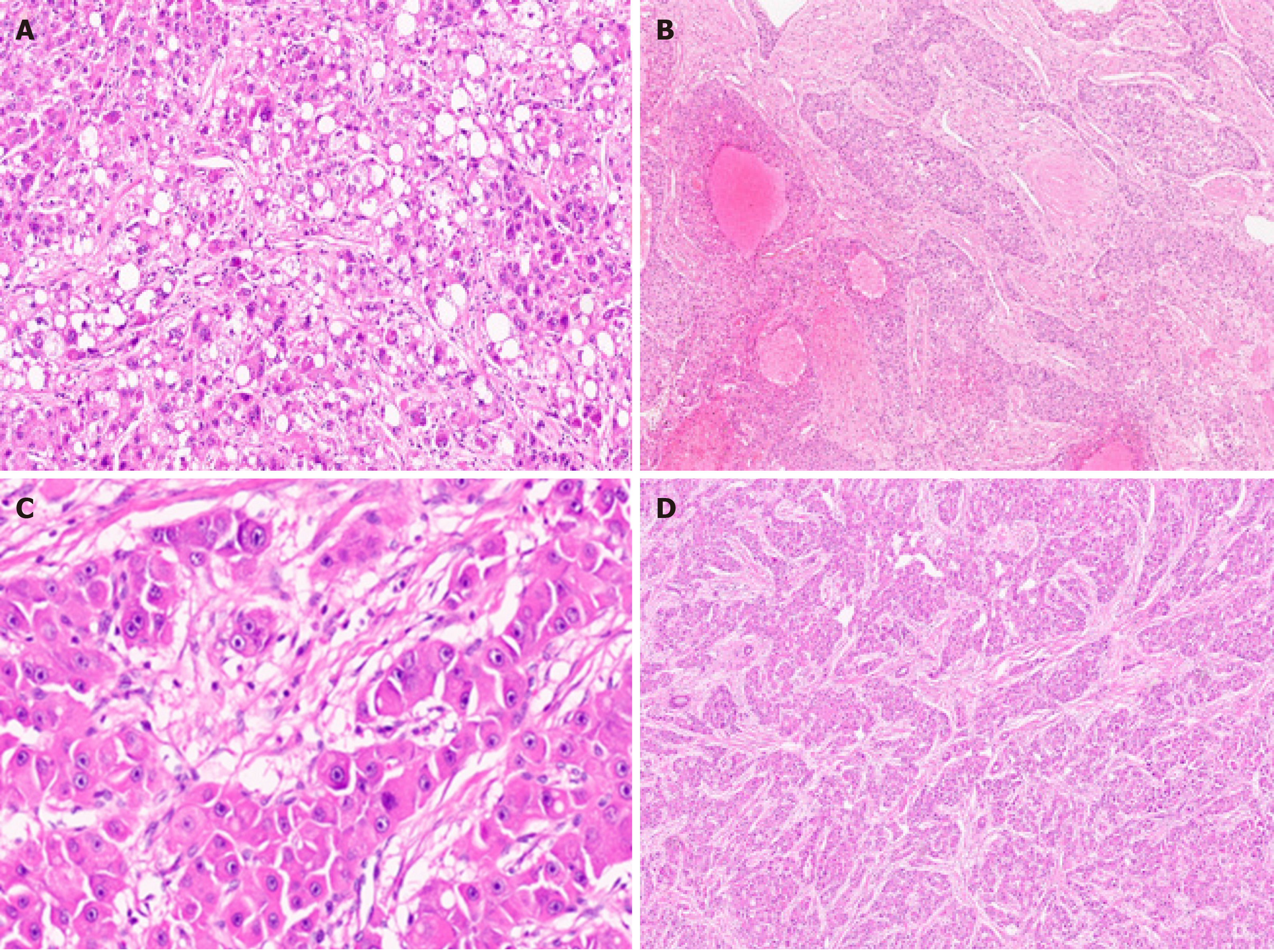
Figure 5 Conventional and macrotrabecular massive hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Hyaline globules in a conventional hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [arrow, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)]; B: Macrotrabecular massive HCC (H&E); C: Large macrotrabecular massive HCC with satellite nodule; D: Macrotrabecular massive HCC with vascular invasion (arrow, H&E).
Figure 6 Hepatocellular carcinoma subtypes.
A: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with steatohepatitic pattern [hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)]; B: Sclerotic HCC (H&E); C: Fibrolamellar HCC with large cells and prominent nucleoli (H&E); D: Fibrolamellar HCC with lamellar fibrosis (H&E).
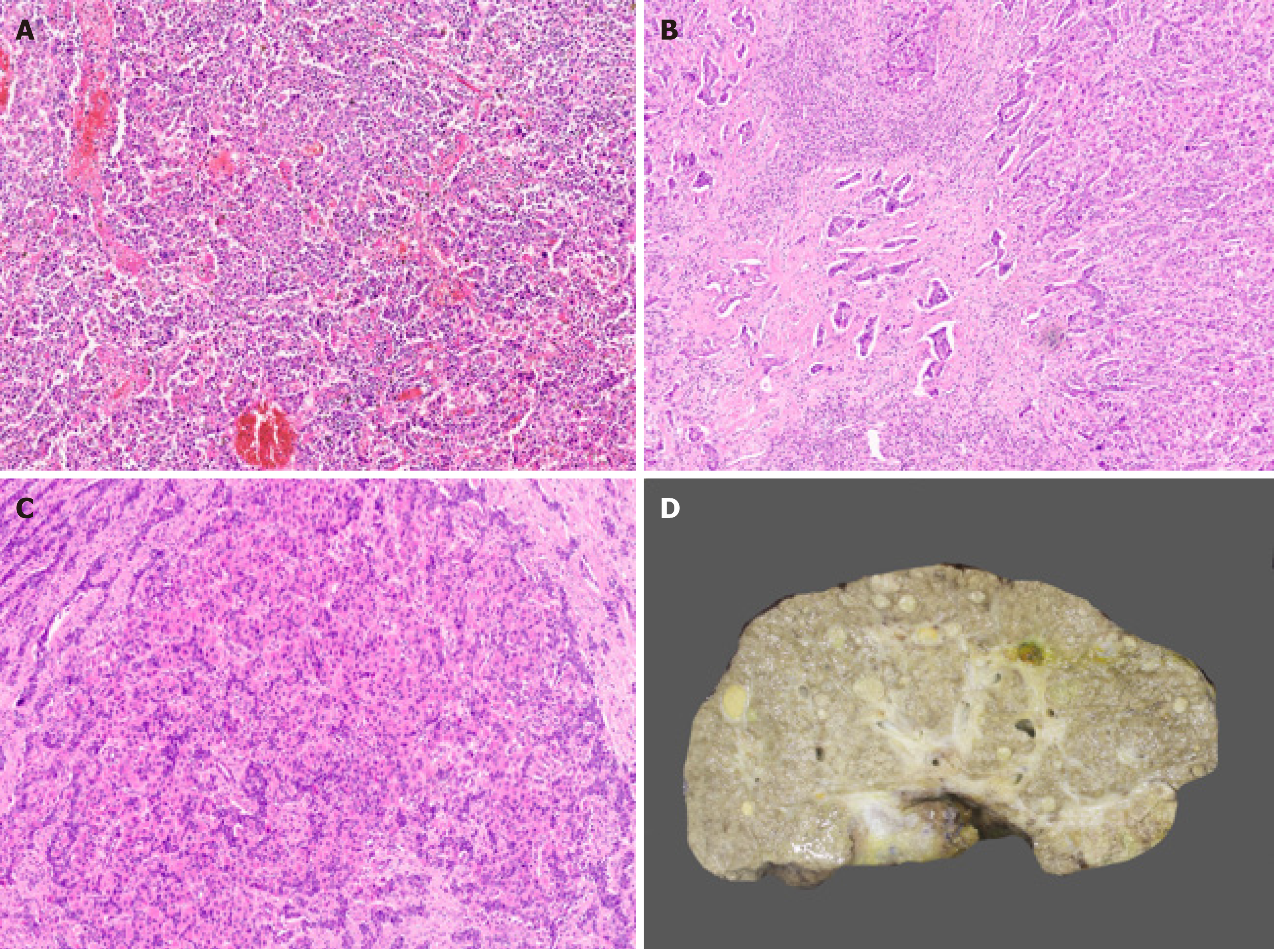
Figure 7 Hepatocellular carcinoma subtypes.
A: Lymphoepithelioma like hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [hematoxylin and eosin H&E)]; B: Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma (cHCC-CCA) with hepatocytic and cholangiocytic component (H&E); C: cHCC-CCA with stem/progenitor cell features (H&E); D: Cirrhotomimetic HCC with numerous tumor nodules.
- Citation: Vij M, Calderaro J. Pathologic and molecular features of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(4): 393-410
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i4/393.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i4.393