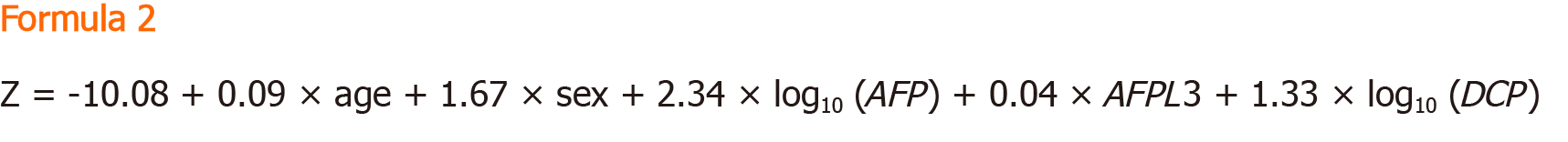Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2020; 12(9): 558-573
Published online Sep 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i9.558
Published online Sep 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i9.558
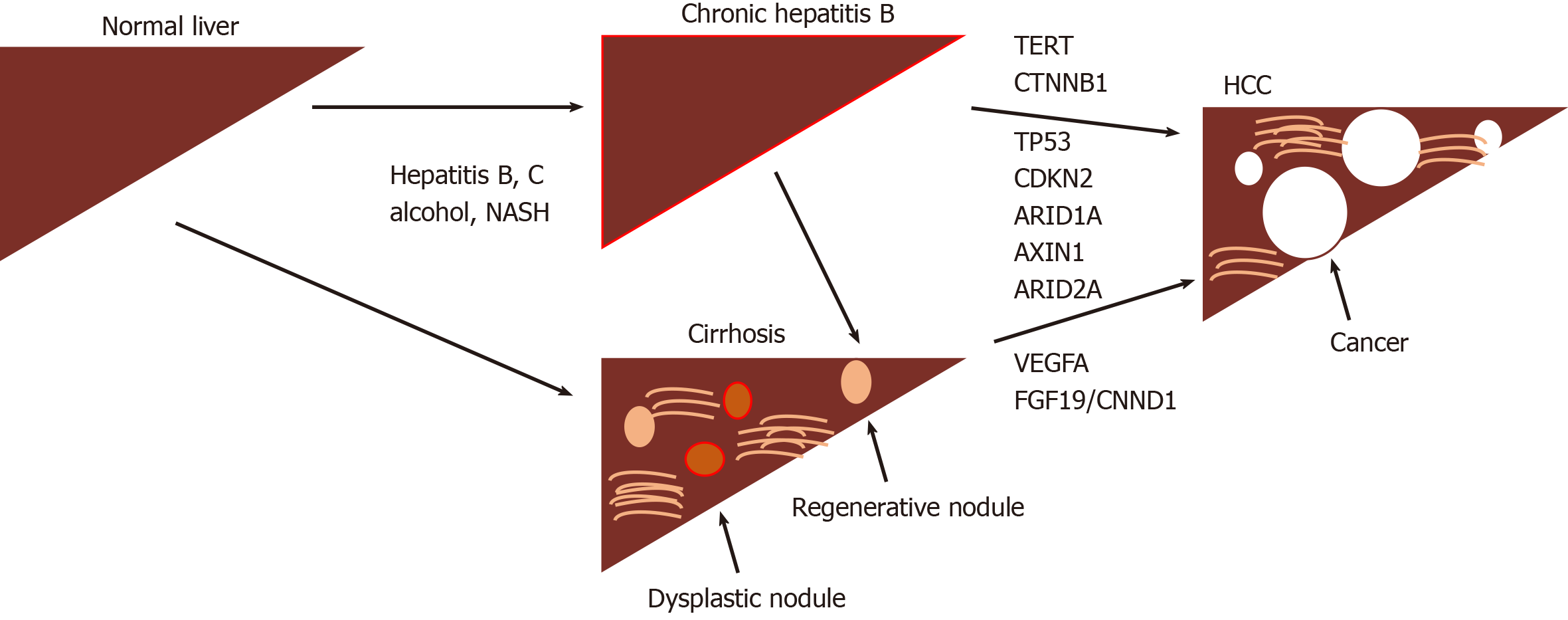
Figure 1 The development of hepatocellular carcinoma is recognized to occur through intermediate steps involving inflammation or fibrosis (cirrhosis) via a variety of mechanisms.
NASH: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; TERT: Telomerase reverse transcriptase; CTNNB1: Catenin beta 1; TP53: Tumor protein 53; CDKN2: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A; ARID1A: AT-Rich Interaction Domain 1A; ARID2A: AT-Rich Interaction Domain 2A; VEGFA: Vascular endothelial growth factor A; FGF19: Fibroblast growth factor 19; CNND1: Cyclin D1; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
Formula 1
Formula 2
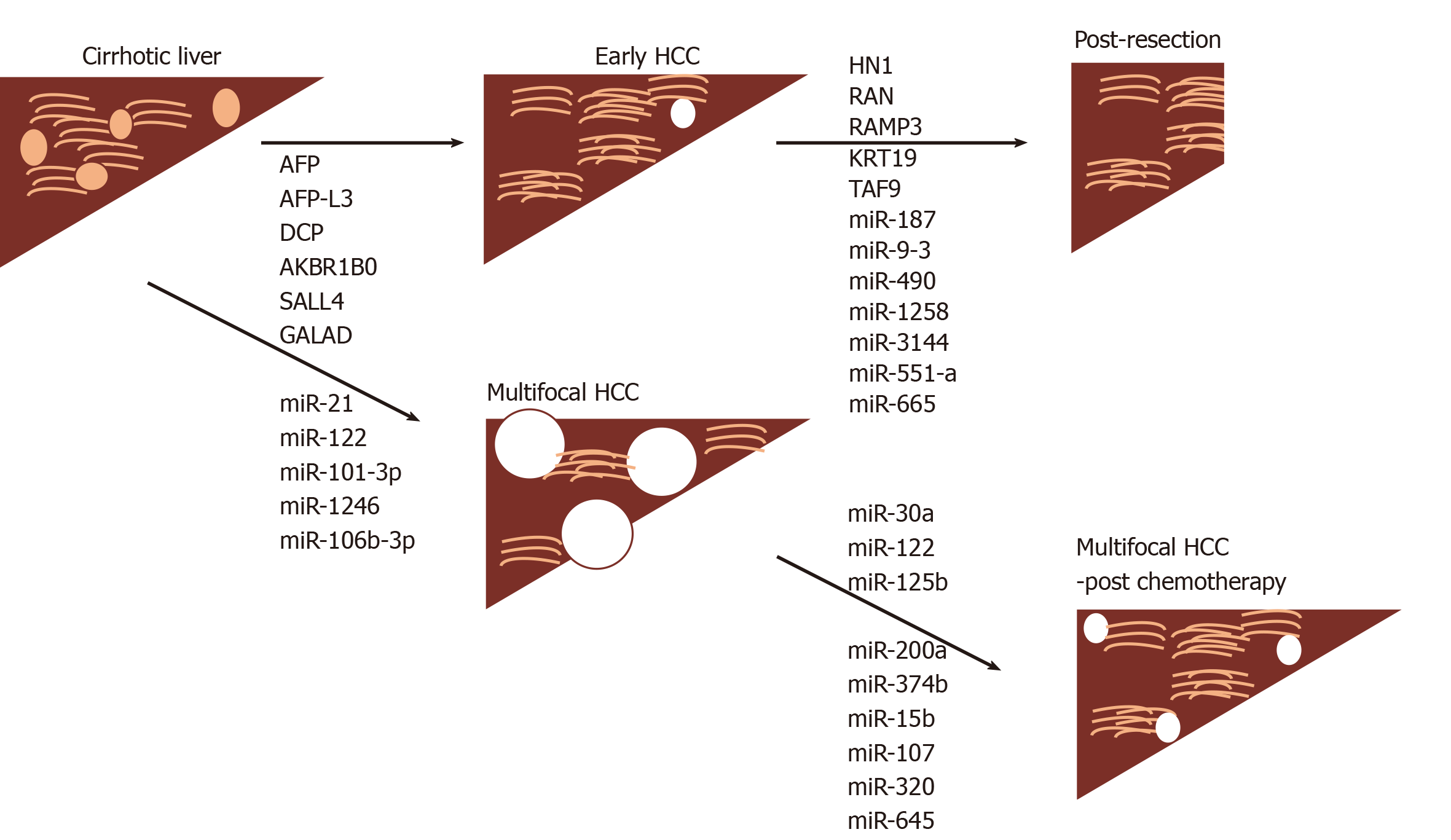
Figure 2 Markers associated with cancer development and those associated with response to surgical intervention or chemotherapy.
HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; AFP-L3: Isoform of AFP binding lectin L3; DCP: Des-gamma carboxyprothrombin; AKBR1B0: Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member 10; SALL4: Sal-like protein 4; GALAD: Gender, Age: Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive of alpha-fetoprotein, Alpha-fetoprotein, and Des-γ-carboxy prothrombin.
- Citation: Singh G, Yoshida EM, Rathi S, Marquez V, Kim P, Erb SR, Salh BS. Biomarkers for hepatocellular cancer. World J Hepatol 2020; 12(9): 558-573
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v12/i9/558.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v12.i9.558