Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2020; 12(9): 1032-1049
Published online Sep 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i9.1032
Published online Sep 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i9.1032
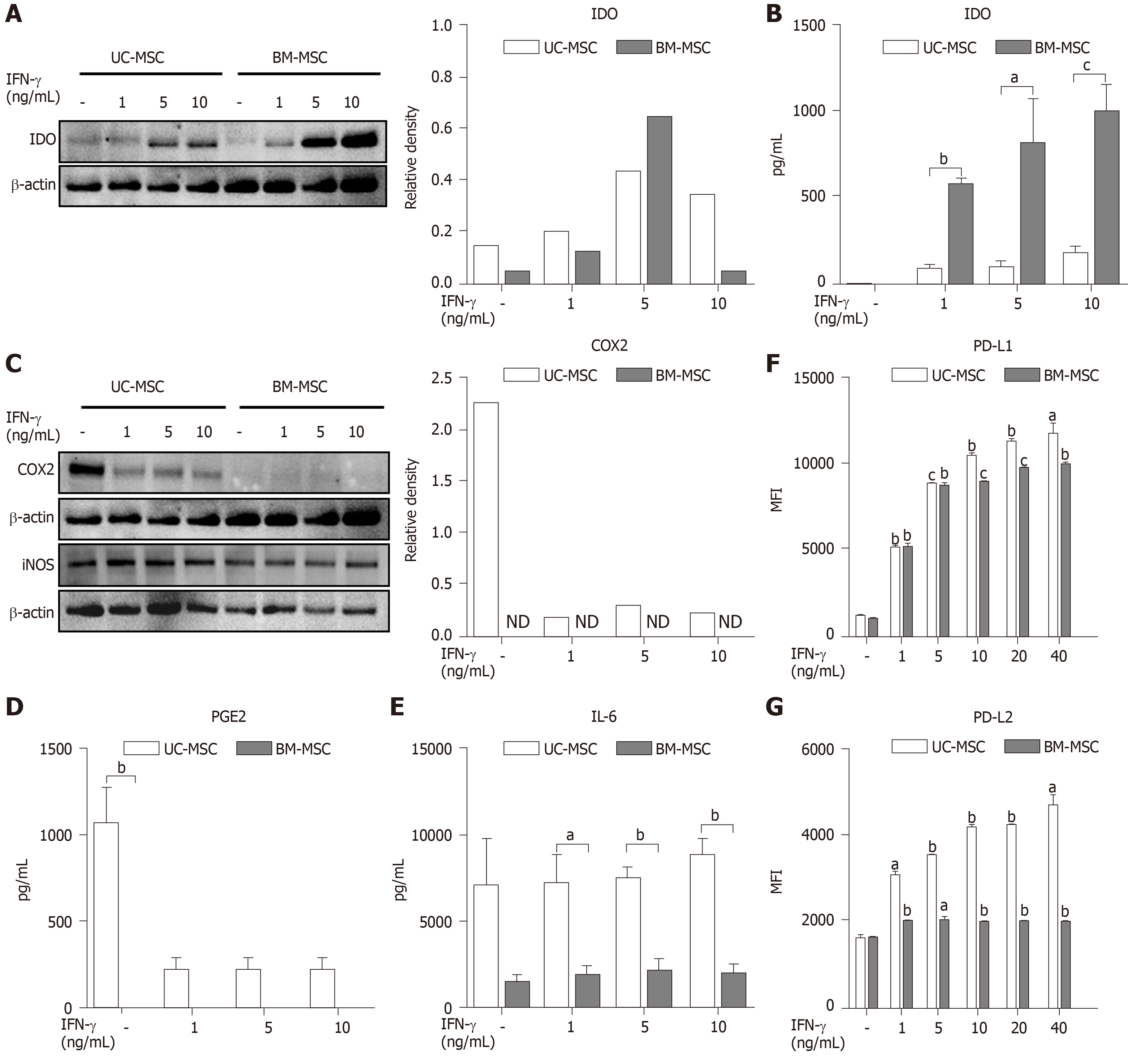
Figure 2 Immunomodulatory effects of interferon-gamma-stimulated mesenchymal stem cells.
Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells were stimulated with 0, 1, 5 or 10 ng/mL of interferon-gamma in culture for 72 h. A and C: Expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (A) and cyclooxygenase-2 (C) of interferon-gamma-stimulated mesenchymal stem cells measured by western blotting; B, D and E: Expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (B), prostaglandin E2 (D), and interleukin-6 (E) in cultured medium measured by ELISA; F and G: Expression of PD-L1 (F) and PD-L2 (G) after interferon-gamma stimulation analyzed by flow cytometry. Statistical analysis was performed by Student’s t-tests, aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.0001 vs indicated group. B, D and E: aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.0001 vs first bar of each group (F and G). BM-MSC: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells; IDO: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; IL-6: Interleukin 6; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; MFI: Mean fluorescence intensity; ND: Not detected; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; UC-MSC: Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
- Citation: Song Y, Lim JY, Lim T, Im KI, Kim N, Nam YS, Jeon YW, Shin JC, Ko HS, Park IY, Cho SG. Human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord and bone marrow exert immunomodulatory effects in different mechanisms. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(9): 1032-1049
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i9/1032.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i9.1032