Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2017; 9(2): 26-36
Published online Feb 26, 2017. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v9.i2.26
Published online Feb 26, 2017. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v9.i2.26
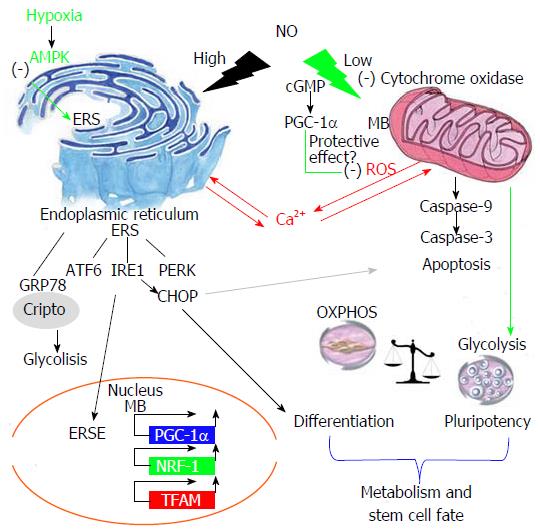
Figure 1 Nitric oxide dose effect on mitochondrial function and endoplasmic reticulum stress.
High NO activates an ER stress response that induces apoptosis, at least in some types of cells, such as β-cells and macrophages. Depletion of ER Ca2+ and activation of the ERS pathway, including ATF6 activation and CHOP induction, was also detected in these cell types after treatment with NO. The soluble protein CRIPTO (also known as TDGF1) and its cell-surface receptor, 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78), have crucial roles in promoting quiescence and in the maintenance of many cell types, including haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Under hypoxic conditions, HIF1α binds to hypoxia responsive elements (HREs) in the promoter region of CRIPTO and activates its expression. CRIPTO then binds to GRP78 and stimulates glycolytic metabolism-related proteins. This acts as a link between the ERS response and cell metabolism that finally controls stem cell fate. In addition, a low concentration of NO inhibits CcO and induces AMPK, which activates glycolysis. This can help to maintain pluripotency and cell proliferation. NO could have a protective effect under hypoxic conditions because the activation of AMPK inhibits CHOP expression and prevents apoptosis. This figure shows the relationship between NO, mitochondrial function and ERS and its impact on stem cell development. ERSE: Endoplasmic reticulum stress element; MB: Mitochondrial biogenesis; OXPHOS: Oxidative phosphorylation. AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; ATF 6: Transcription factor 6; CcO: Cytochrome c oxidase; CREB: cAMP response element binding protein; ERS: Endoplasmic reticulum stress; ESCs: Embryonic stem cells; Sgc: Soluble guanylate cyclase; cGMP: Cyclic guanosine monophosphate; HIF: Hypoxia inducible factor; HSP70: Heat shock protein 70; JNK: c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MB: Mitochondrial biogenesis; MD: Mitochondrial dynamics; NO: Nitric Oxide; NOS: Nitric oxide synthase; NRF-1: Nuclear respiratory factor 1; OXPHOS: Oxidative phosphorylation; PERK: Protein kinase-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; PSCs: Pluripotent stem cells; PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ coactivator 1α; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; Tfam: Mitochondrial transcription factor A; UPR: Unfolded protein response.
- Citation: Caballano-Infantes E, Terron-Bautista J, Beltrán-Povea A, Cahuana GM, Soria B, Nabil H, Bedoya FJ, Tejedo JR. Regulation of mitochondrial function and endoplasmic reticulum stress by nitric oxide in pluripotent stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2017; 9(2): 26-36
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v9/i2/26.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v9.i2.26