Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2016; 8(2): 47-55
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i2.47
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i2.47
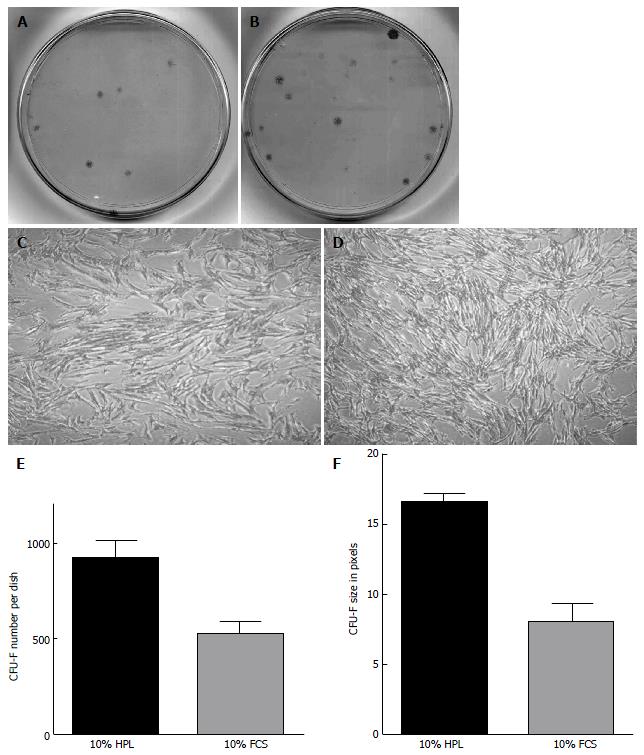
Figure 1 The enhancement of mesenchymal stem cell colony formation in platelet lysate-cultured bone marrow aspirates from a single patient.
Day-14 colonies formed from 200 μL of fresh BM aspirate seeded on plastic culture dish with either 100 mL/L FCS (A) or 100 mL/L PL (B). Higher magnification (40 ×) of individual colonies grown in 100 mL/L FCS (C) or 100 mL/L PL (D). Quantified analysis of the number of colonies (E). The average size of colonies in pixels (F). Colony number and size were analysed using NIS Elements BR Nikon software. BM: Bone marrow; PL: Platelet lysate; FCS: Fetal calf serum.
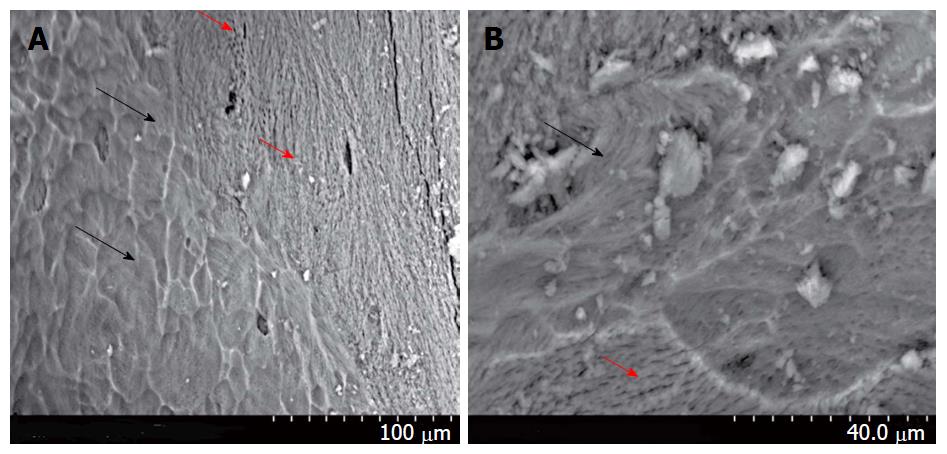
Figure 2 The attachment of platelet lysate-expanded bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on orthoss scaffold.
BM MSCs at passage 2 were incubated with the scaffold by continuous mixing at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for 3 h with DMEM + 50 mL/L PL. The scaffold was then washed and incubated for 10 d with DMEM + 50 mL/L PL. SEM image illustrate MSCs on the scaffold (A). Higher magnification demonstrates MSC morphology on the scaffold surface (B). Black arrow: MSC cells; Red arrow: Orthoss scaffold. BM: Bone marrow; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; PL: Platelet lysate.
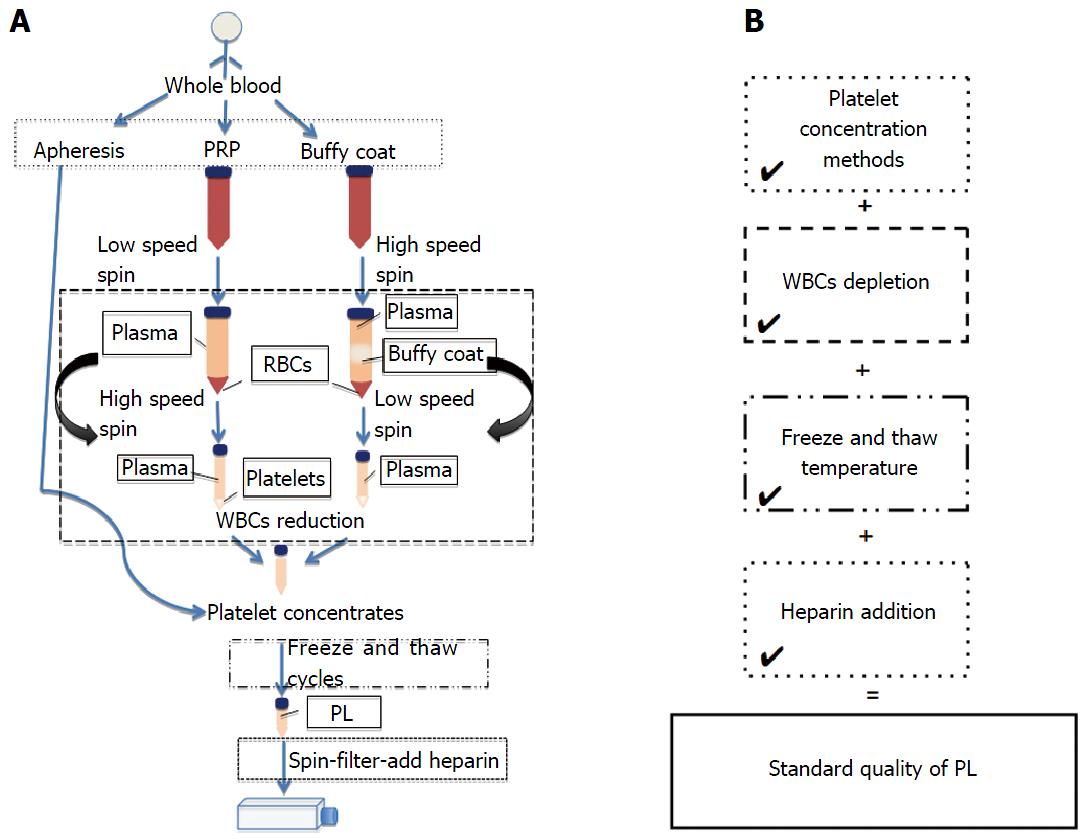
Figure 3 Summary of the current methods used for platelet lysate preparation.
A: Step by step guide of the PL preparation methods; B: Suggested stages to standardise in PL preparation. PRP: Platelet rich plasma; PL: Platelet lysate.
- Citation: Altaie A, Owston H, Jones E. Use of platelet lysate for bone regeneration - are we ready for clinical translation? World J Stem Cells 2016; 8(2): 47-55
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v8/i2/47.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v8.i2.47