Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2016; 8(1): 1-12
Published online Jan 26, 2016. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i1.1
Published online Jan 26, 2016. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i1.1
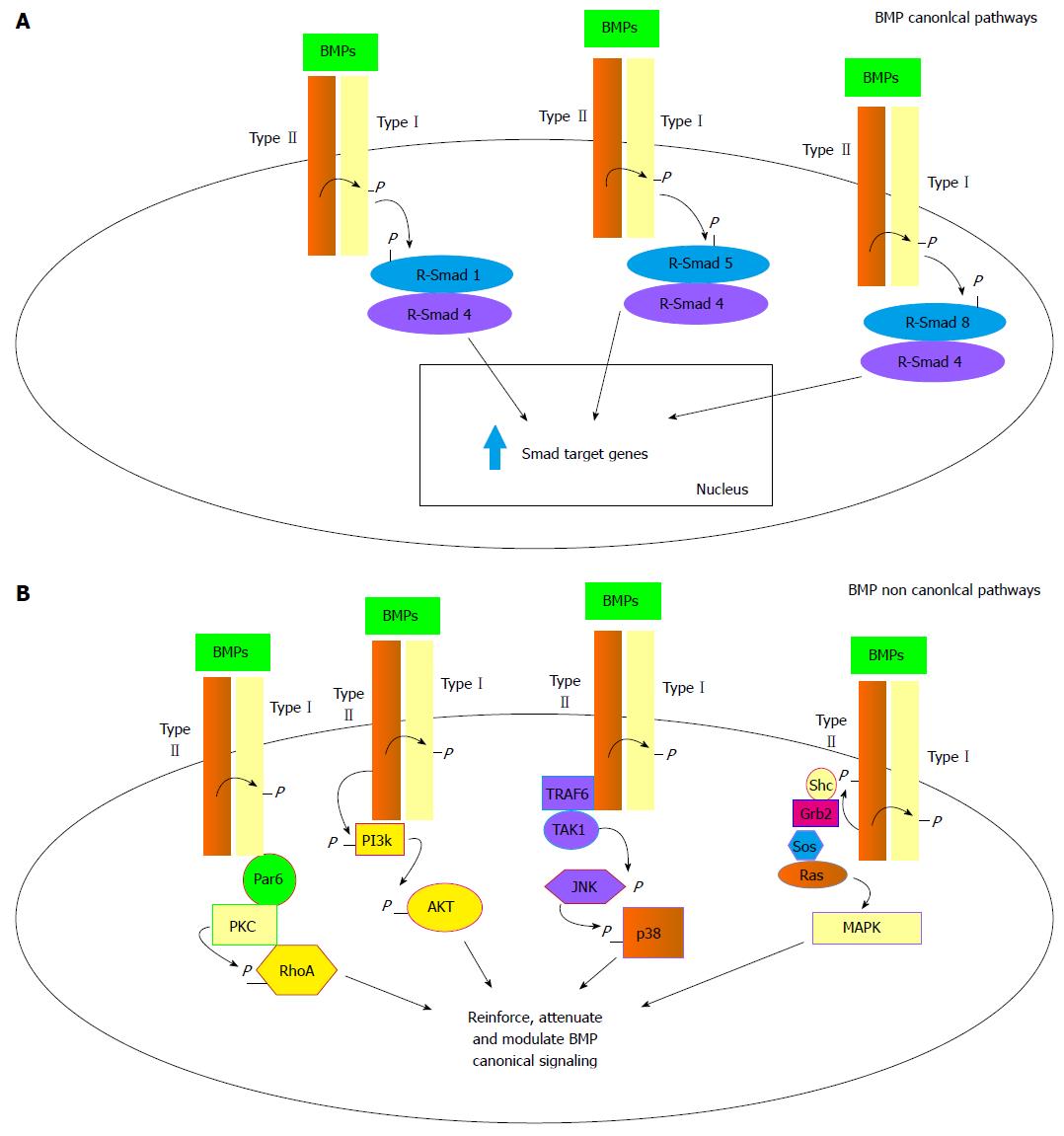
Figure 1 Canonical and non-canonical bone morphogenetic protein signal transduction.
A: BMP canonical pathway: Upon type I and type II receptor dimerization the R-Smads 1, 5 and 8 can be phosphorylated by activated type I receptor leading to coupling with the common R-Smad4 coactivator. The heterodimers then translocate to the nucleus promoting expression of target genes; B: BMP non canonical pathways: activation of type I and type II receptors after dimerization can lead to stimulation of various intracellular transduction signals other than the R-Smads dependent ones. From left to right: Activation of the PKC/RhoA pathway through par6 recruitment by type I activated receptor; activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway through direct PI3K phosphorylation by activated type II receptor; activation of JNK/p38 pathway through TRAF6/TAK1 recruitment by activated type II receptor and finally activation of the MAPK/ERK pathway through Shc/Grb2/Sos/Ras recruitment by type II activated receptor. BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein; Par6: Partitioning defective protein 6; PKC: Protein kinase C; PI3K: Phosphoinositide-3 kinase; AKT: V-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1; TRAF6: TNF receptor associated factor 6; TAK1: TGF-beta activated kinase 1; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase; Shc: Src homology 2 domain containing; Grb2: Growth factor receptor bound protein 2; Sos: Son-of-sevenless; RAS: Rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinase.
- Citation: Scarfì S. Use of bone morphogenetic proteins in mesenchymal stem cell stimulation of cartilage and bone repair. World J Stem Cells 2016; 8(1): 1-12
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v8/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v8.i1.1