Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2014; 6(5): 511-525
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.511
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.511
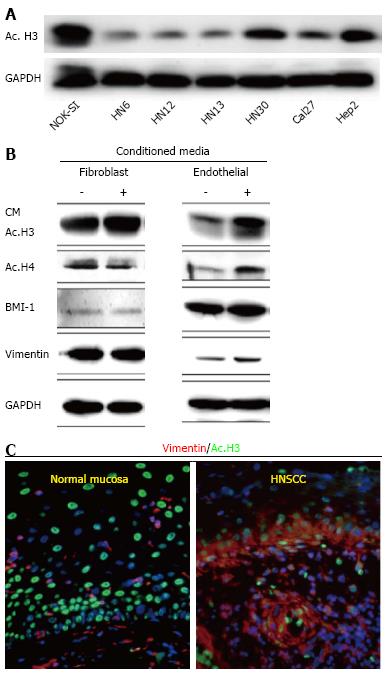
Figure 1 Data represents acetylation status of histone 3 in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Giudice et al[151].
A: Tumor cells present hypoacetylation of histone 3 (ac.H3) in a panel of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) compared to control cells (NOK-SI); B: Endothelial cell-secreted factors are capable of inducing ac.H3 while fibroblast cell-secreted factors cannot. Also, endothelial cell-secreted factors induce increased expression of BMI-1 and vimentin compared to the fibroblast counterpart; C: Representative examples of human samples of normal oral mucosa and HNSCC. Note acetylated tumor cells (Ac. H3-FITC) with high levels of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition marker vimentin (TRICT) are localized at the invasion front of HNSCC (arrow). Normal mucosa display acetylated cells distributed throughout the epidermis but do not express vimentin. ac. H3: Acetyl histone 3; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; CM: Conditioned Media; BMI-1: B lymphoma Mo-MLV insertion region 1 homolog; NOK-SI: Normal oral epithelial keratinocytes.
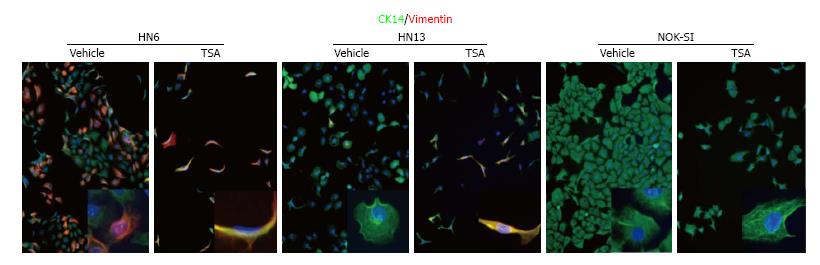
Figure 2 Figure from Giudice et al[151] depicting chemically-induced chromatin acetylation leading to activation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype.
Inhibition of HDAC induces vimentin expression in HNSCC cells and EMT. Vehicle treated HNSCC cells (HN6 and HN13) present an epithelioid shape and express CK14. Administration of TSA result in acquisition of a fusiform morphology and expression of vimentin. Normal keratinocytes (NOK-SI) are not sensitive to EMT upon administration of TSA. TSA: Trichostatin A; CK14: Cytokeratin 14; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; HDAC: Histone deacteylases; HNSCC: Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma; NOK-SI: Normal oral epithelial keratinocytes.
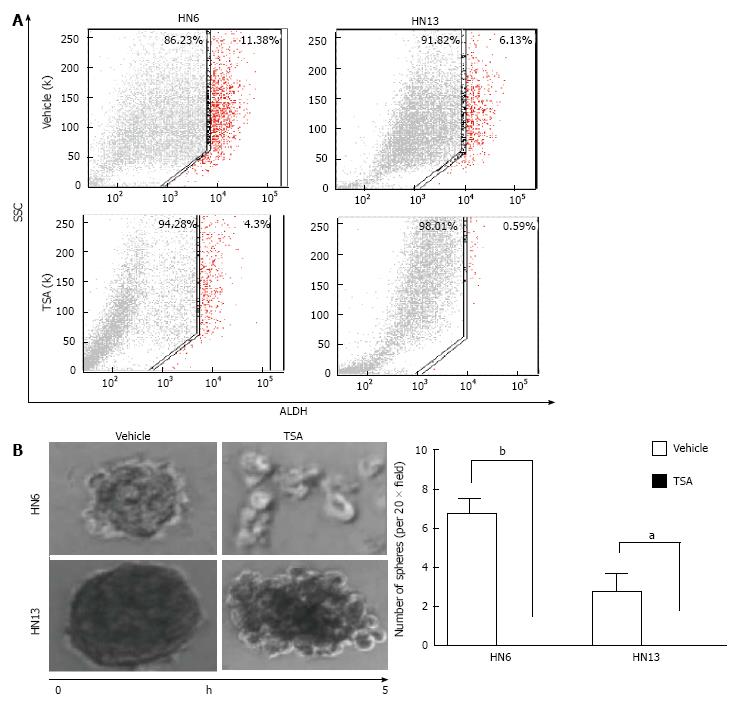
Figure 3 Data from Giudice et al[151] showing the impact of histone deacetylases inhibitor on the population of CICs.
A: Fluorescence-activated cell sorting of ALDH+ cells demonstrates that HNSCC cell lines have a high number CICs, and that administration of TSA reduced total number of ALDH+ cells; B: HDACi (TSA) disrupts tumor spheres as depicted in representative images of tumor spheres and by quantification of spheres (HN6 bP < 0.01, HN13 aP < 0.05). TSA: Trichostatin A; ALDH: Aldehyde dehydrogenase; SCC: Side scatter of light; HDACi: Histone deacteylases inhibitors; HNSCC: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
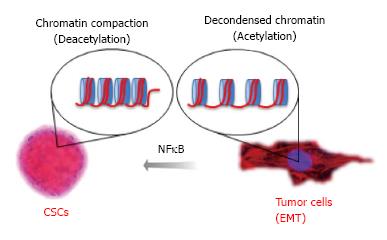
Figure 4 Data from Almeida et al proposing the mechanism for nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells driven resistance to chemotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Chromatin undergo normal compaction and decondensation through the acetylation of core histones organized in nucleosomes. Acetylation of tumor histones driven by expression of NFκB influences tumor behavior and plasticity of Cancer Stem Cells. NFκB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; EMT: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition.
- Citation: Le JM, Squarize CH, Castilho RM. Histone modifications: Targeting head and neck cancer stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2014; 6(5): 511-525
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v6/i5/511.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.511