Copyright
©2012 Baishideng.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2012; 4(7): 62-70
Published online Jul 26, 2012. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v4.i7.62
Published online Jul 26, 2012. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v4.i7.62
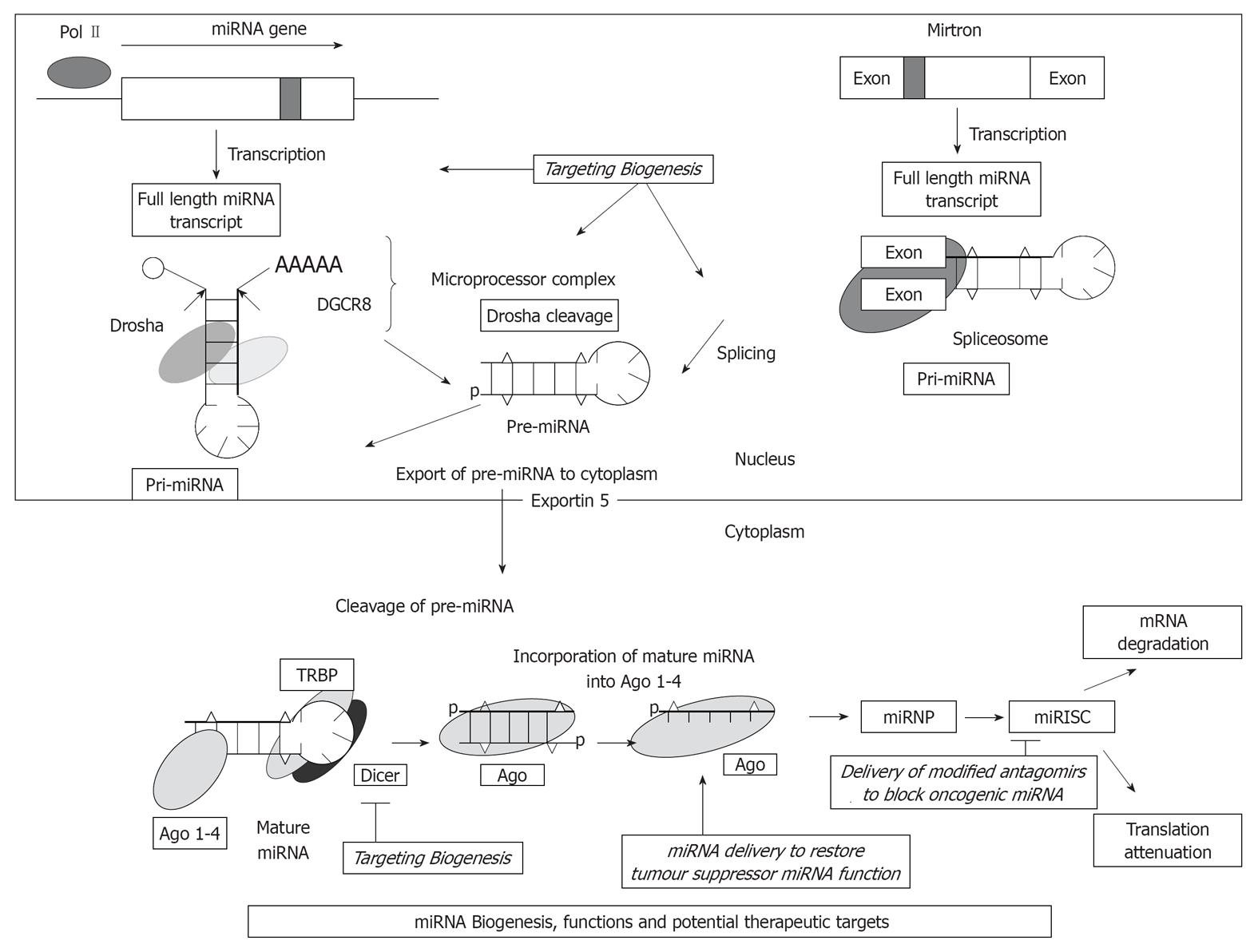
Figure 1 MiRNA biogenesis, functions and potential therapeutic targets.
miRNA transcript excised to form pri-miRNA, gets cleaved by Drosha and exported from nucleus to cytoplasm by Exportin-5. 70 n hairpin-loop precursor-miRNA (pre-miRNA) then processed by Dicer into mature RNA. The figure also explains the various potential miRNA therapeutic targets including biogenic pathways, restoring the tumor suppressor functions of miRNAs and blocking the oncogenic properties of miRNAs. miRNA mediated silencing involves either inhibition of translation or degradation of their target mRNA transcripts depending on the degree of complementarity. TRBP: Transactivating response RNA binding protein; miRISC: miRNA-induced silencing complex; miRNP: MicroRNA ribonucleoprotein complex; DGCR8: DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8.
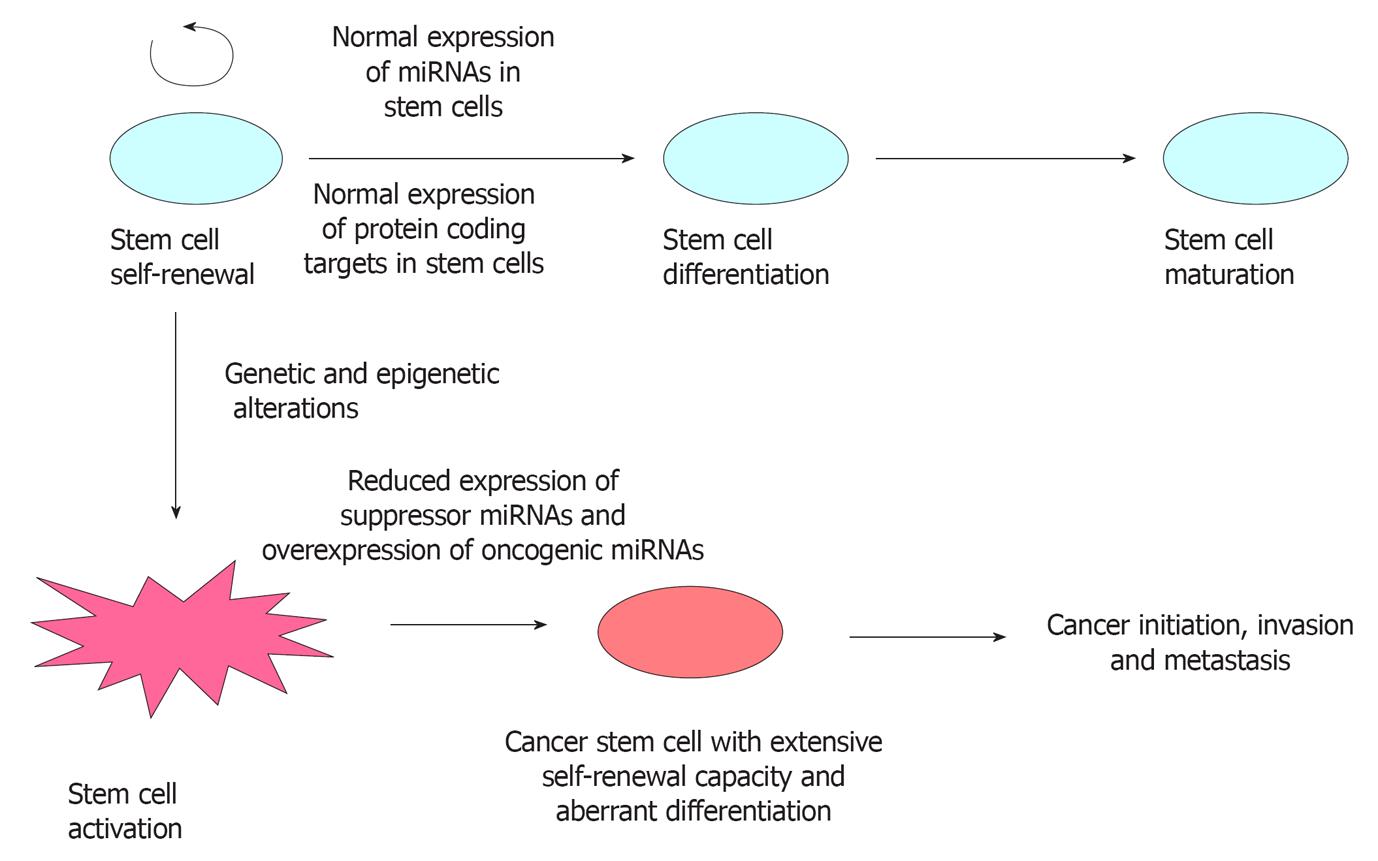
Figure 2 Stem cells express a unique set of miRNAs that maintain self-renewal, promote differentiation and maturation through various regulatory mechanisms.
Distinct small sub population of cells arises from stem cells due to accumulation of genetic and epigenetic abnormalities that might function as cancer stem cells. These cells display differential expression of miRNAs which regulate the fundamental properties that contribute to enhanced tumor initiation and metastatic potential.
- Citation: Garg M. MicroRNAs, stem cells and cancer stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2012; 4(7): 62-70
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v4/i7/62.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v4.i7.62