Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2021; 13(8): 1058-1071
Published online Aug 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i8.1058
Published online Aug 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i8.1058
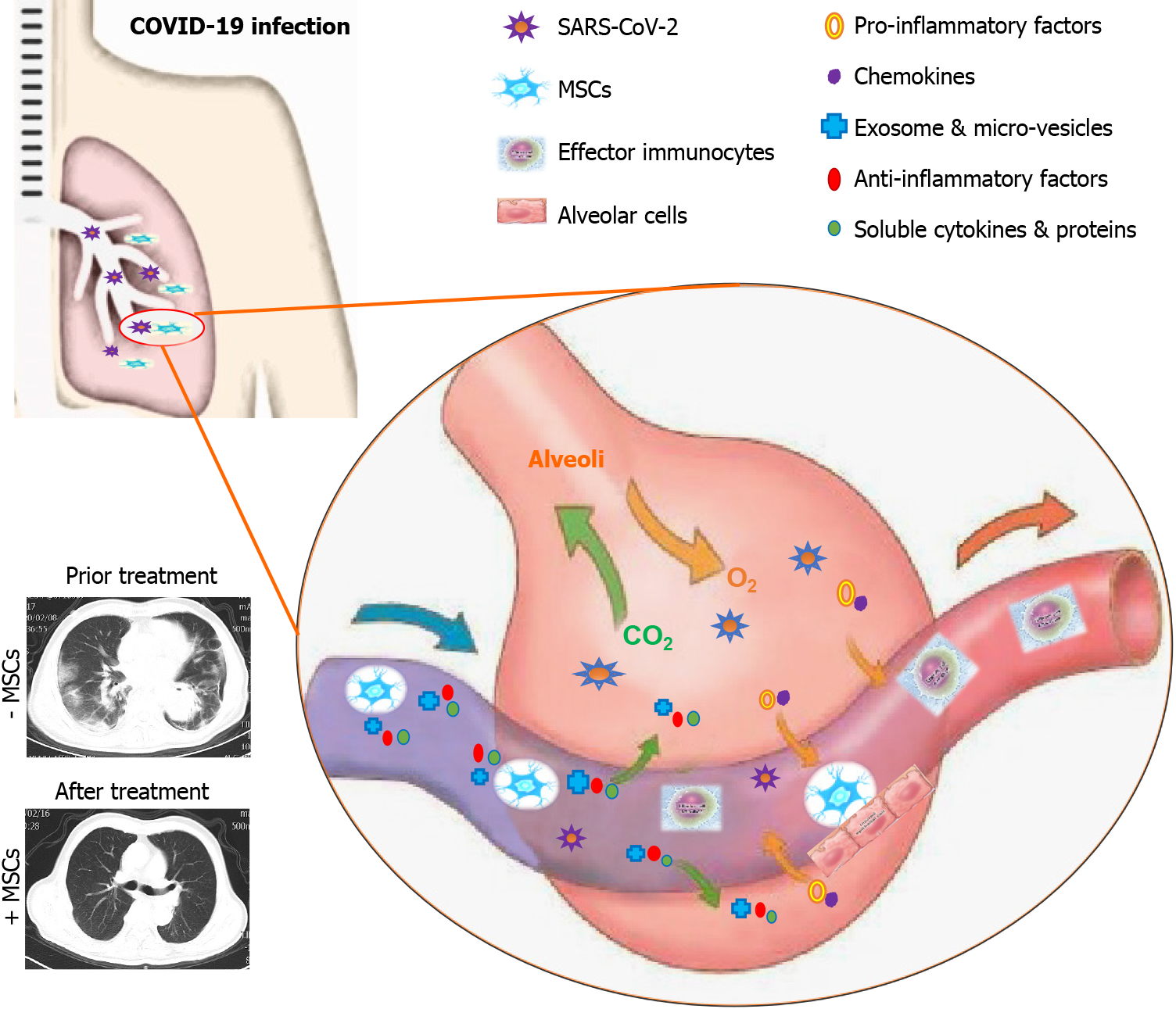
Figure 1 Schematic model for management of coronavirus disease 2019 associated pulmonary disease by mesenchymal stem/stromal cell application.
Coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) could result in multifaceted deteriorations of the infected lungs such as ground glass opacity, alveolar epithelial cell injury, inflammatory exudation, pro-inflammatory factor and chemokine accumulation, effector immunocyte abnormalities, and the accompanied cytokine storm. Systematic or partial infusion is adequate for the effective remission of the damaged lung tissues by simultaneously suppressing the abnormal immune response, secreting exosomes and micro-vesicles, and accelerating cell repair and the SARS-CoV-2 clearance. MSCs: Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019.
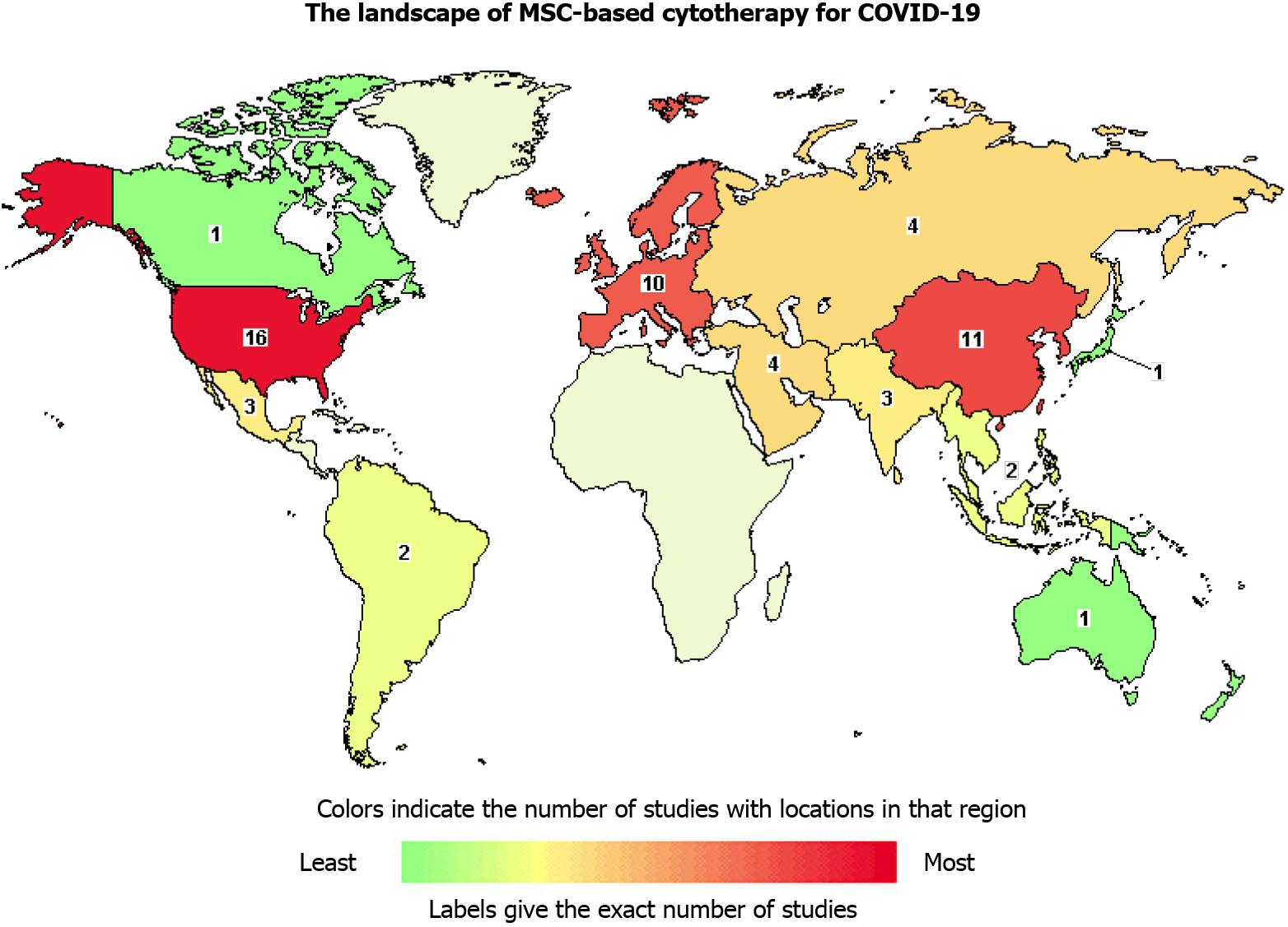
Figure 2 Landscape of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells-based cytotherapy for coronavirus disease 2019.
The map reveals the distribution of registered clinical trials on coronavirus disease 2019 treatment with mesenchymal stem/stromal cells with the aid of the Clinicaltrials.gov website.
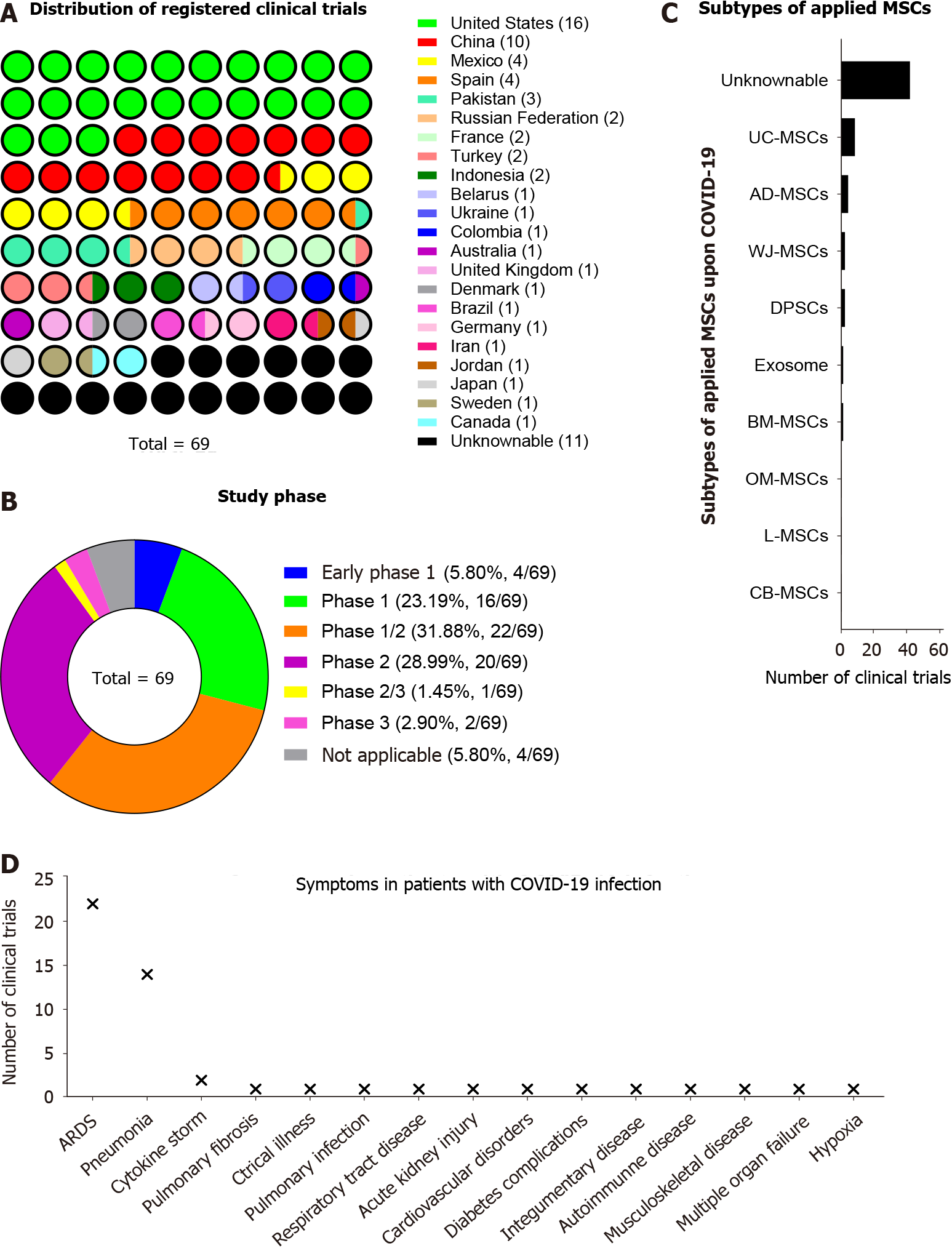
Figure 3 Detailed information of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-based cytotherapy for coronavirus disease 2019.
A: Distribution of registered clinical trials among the countries for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment by utilizing mesenchymal stem/stromal cell (MSC)-based cytotherapy; B: Study phase of registered clinical trials; C: Distribution of subtypes of applied MSCs for COVID-19 treatment; D: Distribution of symptoms in patients with COVID-19 before MSC-based cytotherapy. MSCs: Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells; COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019.
- Citation: Zhang LS, Yu Y, Yu H, Han ZC. Therapeutic prospects of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in COVID-19 associated pulmonary diseases: From bench to bedside. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(8): 1058-1071
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i8/1058.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i8.1058