Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2021; 13(4): 260-280
Published online Apr 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i4.260
Published online Apr 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i4.260
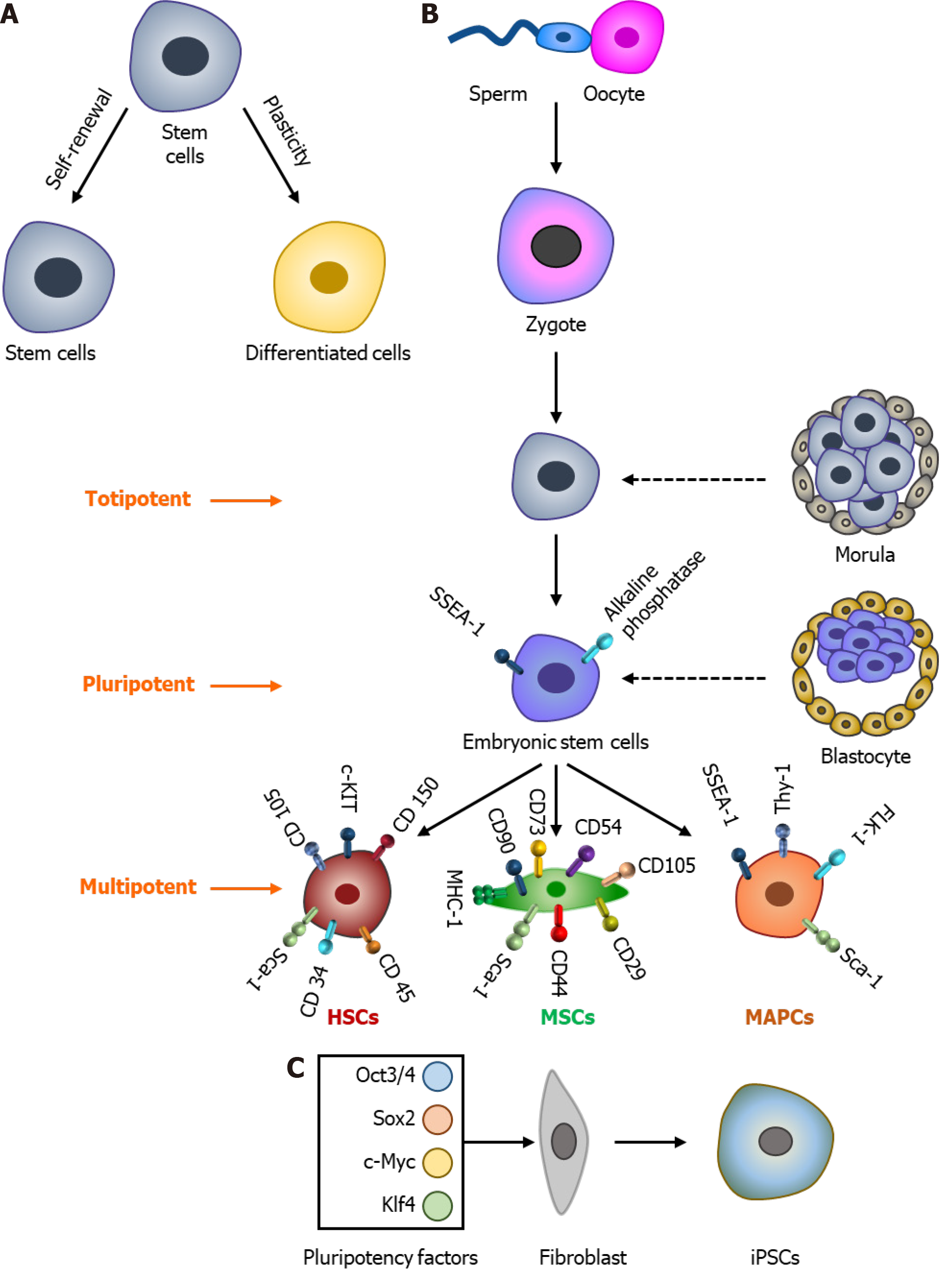
Figure 1 Stem cell properties and their types.
A: Stem cells have two unique fundamental properties, self-renewal, and differentiation potential; B: Showing the development of different stem cells such as embryonic stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and multipotent adult progenitor stem cells (MAPCs); C: Showing the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from mouse fibroblast cells using four factors (octamer-binding transcription factor 3/4, SRY-box transcription factor 2, c-Myc, Kruppel-like factor 4). SSEAs: Stage-specific embryonic antigens.
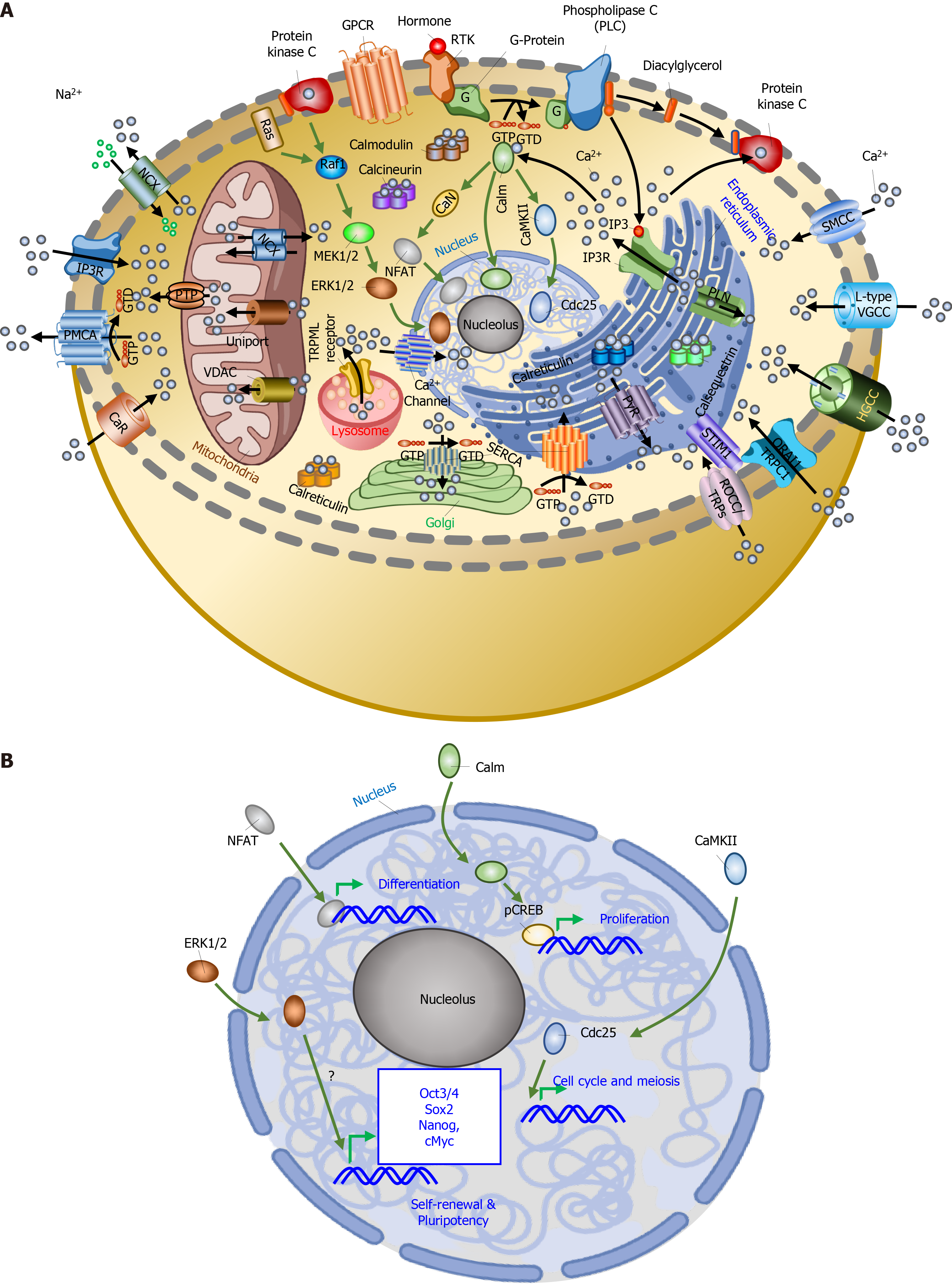
Figure 2 Calcium toolkit and calcium signaling.
A: Calcium (Ca2+) signaling toolkit components include cell-surface receptors (G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and protein tyrosine kinase receptors), Ca2+ channels (voltage-gated channels and two-pore channels, voltage-gated K+ channel, Ca2+-activated K+ channel, ATP-sensitive K+ channels, TRPC1-7 ORAI1-3, IP3R, RyR2), Ca2+ pumps and exchangers (Na+/Ca2+ exchangers (NCX), Na+/Ca2+-K+ exchangers, plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase (PMCA) and sarco-endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+ ATPase), Ca2+ buffers (parvalbumin, calbindin, and calretinin [cytoplasmic buffers] and Ca2+ buffers of the ER lumen, calsequestrin, calreticulin, glucose-regulated protein [GRP] 78 and GRP94), Ca2+ sensors (EF-hand [CaM, TnC, calpains, NCS-1, hippocalcin, neurocalcin, recoverin, MICU1, etc.] or C2 Ca2+-binding domains [annexin 1-13, otoferin, protein kinase C, RASAL, etc.], ER Ca2+ sensors STIM1 and STIM2), and Ca2+-sensitive cellular process. In a typical Ca2+-sensitive cellular process, the hormone binds to a specific receptor. This binding causes GDP-GTP exchange on the G protein. G protein (GTP-bound) activates phospholipase C (PLC). Activated PLC breaks phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to inositol trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol. IP3 moves to a specific receptor on the ER, binds with the receptor, and triggers the release of sequestered Ca2+. Released Ca2+ and diacylglycerol activate protein kinase C enzyme. Activated protein kinase C phosphorylates cellular proteins and activates downstream proteins (Raf1 and other proteins). Activated Raf1 binds and activates MEK1/2 and MEK1/2, which phosphorylate extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2. ERK1/2 enters the nucleus and on/off the genes against the hormone response. The released Ca2+ decreases ER calcium level. Low Ca2+ of ER sense by ER Ca2+ sensor (STIM) and activate it. An activated Ca2+ sensor binds the Ca2+ channel protein (ORAI) on the plasma membrane, opens the Ca2+ channel, and allows the Ca2+ entry into the cytoplasm from extracellular space. This process is called store-operated Ca2+ entry; B: Activated transcription factors and other proteins bind to DNA and increase the gene expression for self-renewal, proliferation, and differentiation processes in the stem cells. CaR: Ca2+ receptor; CREB: cAMP response element-binding protein; IP3R: Inositol trisphosphate receptor; NFAT: Nuclear factor of activated T-cells; VDAC: Voltage-dependent anion channel; VGCC: Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel.
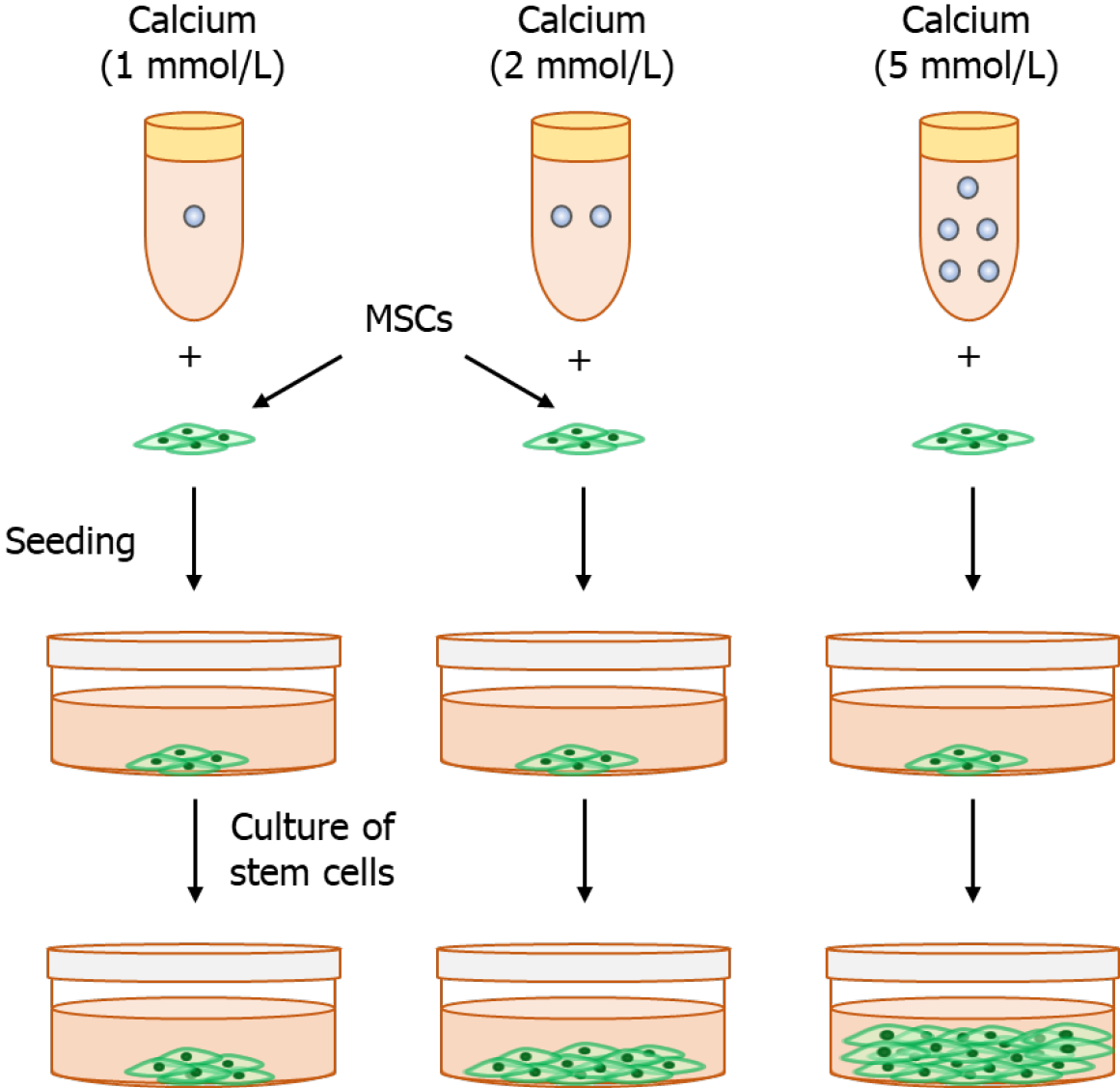
Figure 3 Calcium-dependent stem cell proliferation.
Stem cells cultured in 1, 2, and 5 mmol/L calcium. Our results (not published) reveal that higher calcium-treated stem cells show a high proliferation rate. MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells.
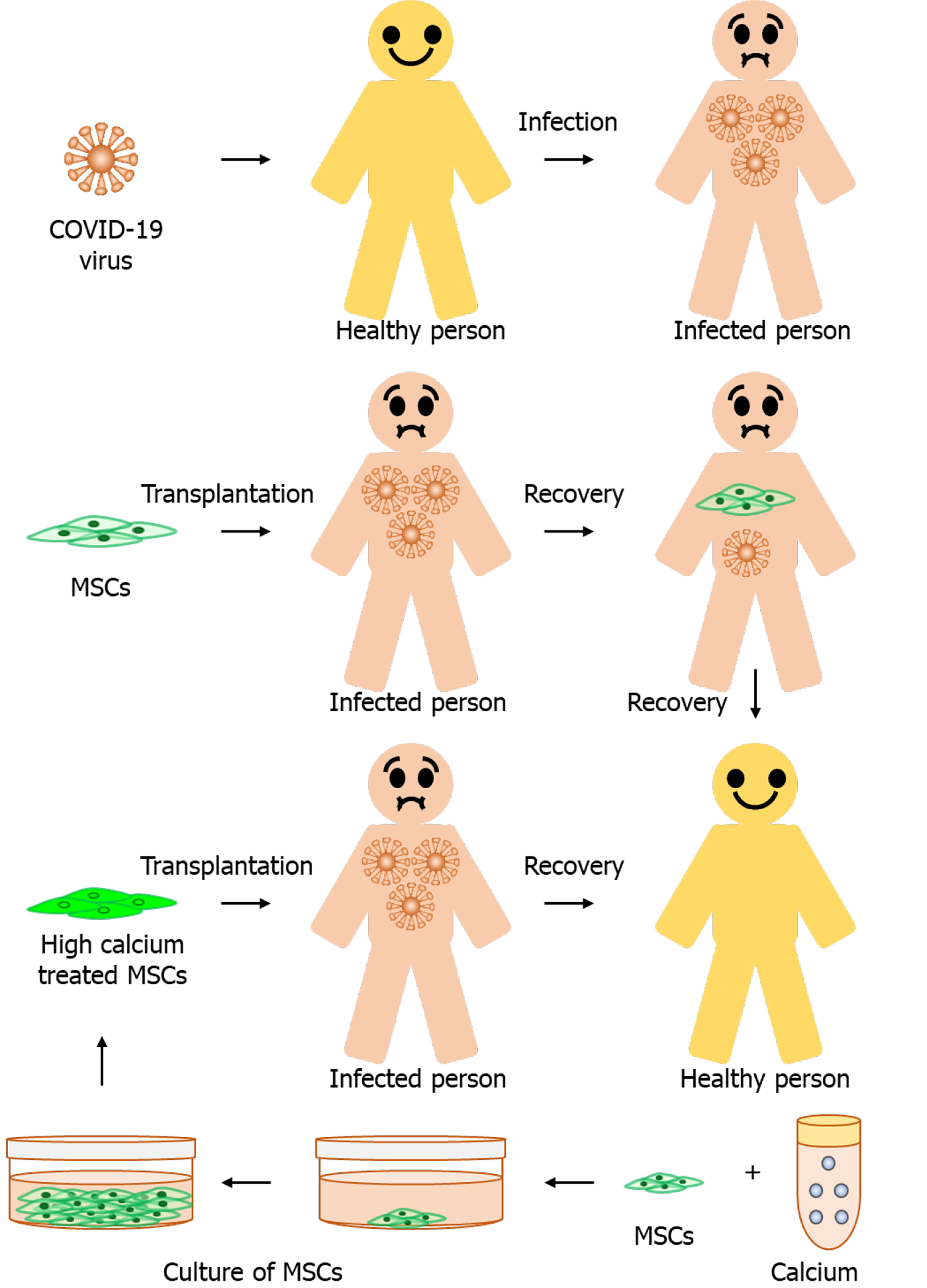
Figure 4 Treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 patient.
We hypothesize that calcium-treated mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a better option to counter the coronavirus’s inflammatory storm response, treat the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patient, and other deadly diseases.
- Citation: Ahamad N, Singh BB. Calcium channels and their role in regenerative medicine. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(4): 260-280
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i4/260.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i4.260