Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2020; 12(2): 110-122
Published online Feb 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i2.110
Published online Feb 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i2.110
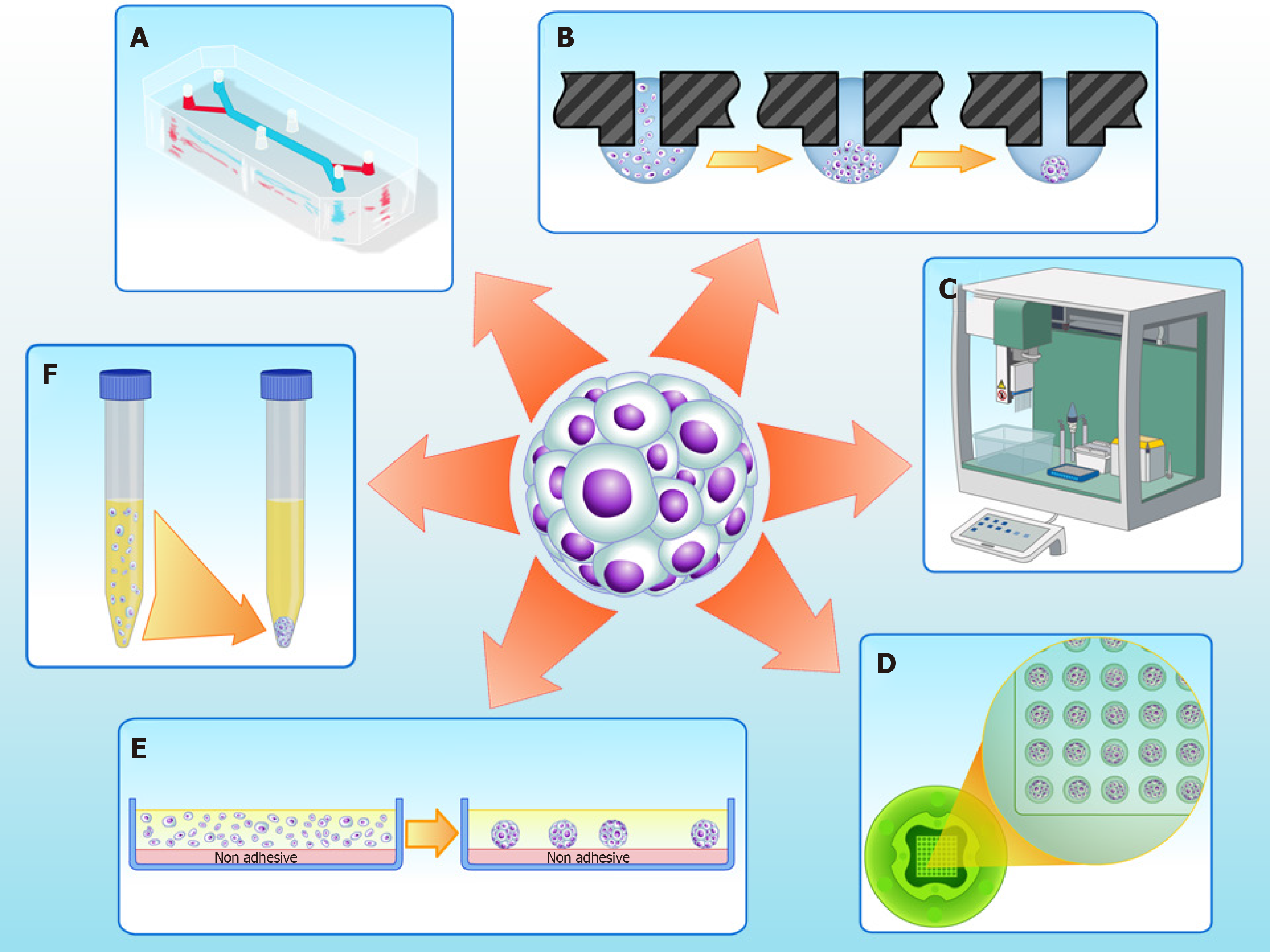
Figure 1 Three-dimensional cell culture techniques to fabricate spheroids in vitro.
A: Microfluidics; B: Hanging drop; C: Automatic platforms; D: Non-adherent agarose micromolded hydrogel produced from a silicone mold (3D Petri dish®, Microtissues); E: Non adhesive surfaces; F: Pellet culture.
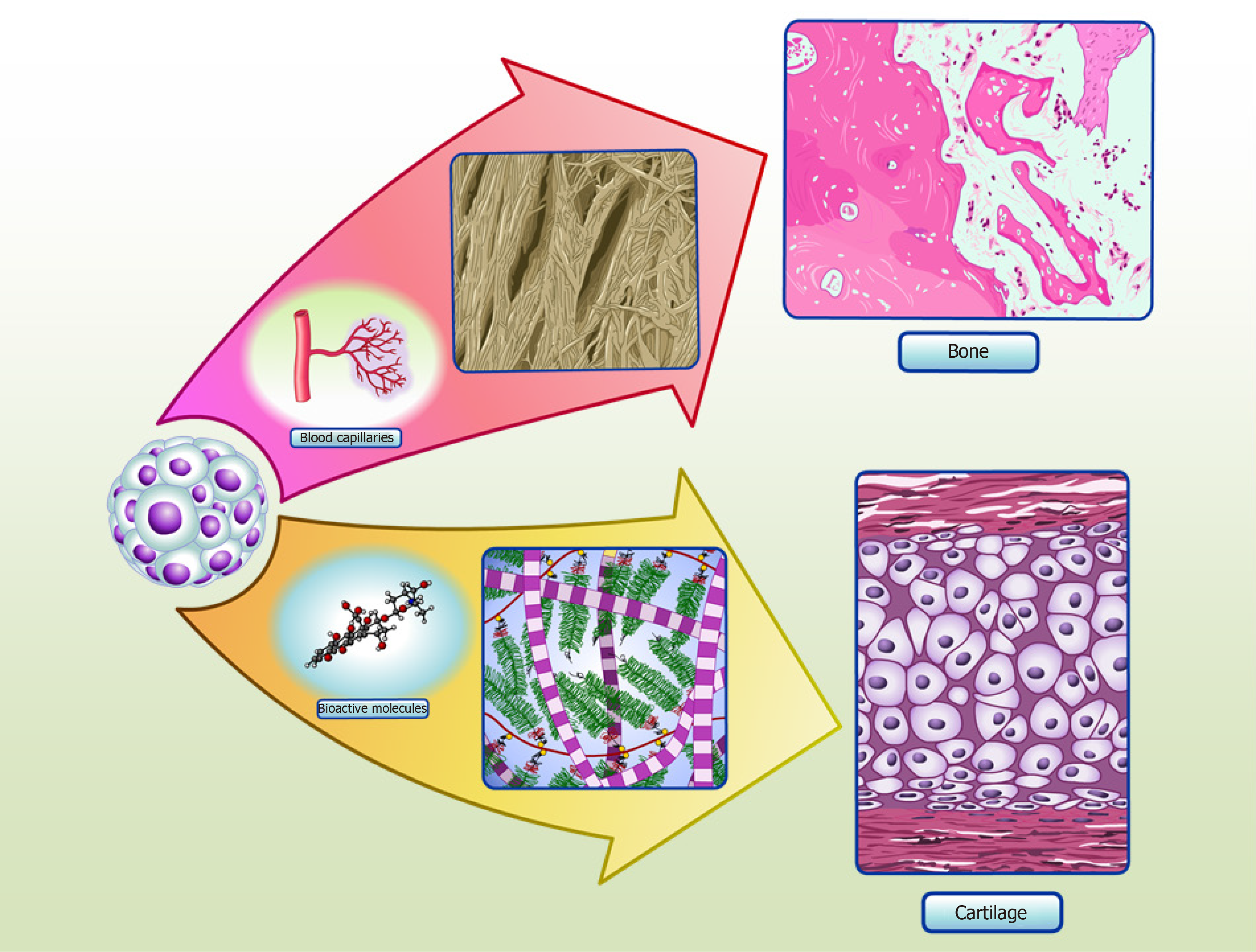
Figure 2 Spheroids in cartilage and bone tissue microenvironments.
Adipose stem/stromal cells (ASCs) spheroids delivered to defect area in vivo can secrete bioactive molecules and synthetize typical extracellular matrix proteins of cartilage, promoting regeneration. Our group have detected collagen type II and COMP in the secretome of in vitro ASCs spheroids, as the production of typical extracellular matrix proteins of cartilage in situ[35]. ASCs spheroids delivered to critical-size bone defects can stimulate angiogenesis by secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and synthesize bone typical extracellular matrix proteins, promoting regeneration. Our group have detected higher levels of VEGF secreted in ASCs spheroids induced to form a hypertrophic cartilage in vitro, as the production of typical extracellular matrix proteins of bone in situ (manuscript submitted).
- Citation: Kronemberger GS, Matsui RAM, Miranda GASCE, Granjeiro JM, Baptista LS. Cartilage and bone tissue engineering using adipose stromal/stem cells spheroids as building blocks. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(2): 110-122
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i2/110.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i2.110