修回日期: 2007-07-23
接受日期: 2007-07-28
在线出版日期: 2007-07-28
目的: 探讨肝细胞癌(HCC)患者血清和组织中Glypican-3(GPC3)蛋白的表达及临床意义.
方法: 收集HCC患者27例和肝良性病变患者28例的术前1 d空腹血清及组织标本, 采用Western blot检测血清中GPC3蛋白, 同时采用免疫组织化学SP法检测组织标本中GPC3的表达情况.
结果: 27例HCC患者HCC组织、癌旁组织和远癌肝组织中GPC3蛋白阳性的表达率分别为81.5%, 0%和0%(HC: 23.4689, P<0.001), 术前血清中GPC3蛋白阳性率分别为55.6%; 28例肝良性病变患者组织和血清中阳性率均为0%; GPC3蛋白对HCC诊断的敏感性为55.6%, 特异性为100%, 误诊率为0%. HCC患者血清中GPC3蛋白表达与其瘤体大小和病理分级之间差异有显著性(P<0.05), 而与患者年龄、性别、HBsAg及AFP值之间差异无显著性(P>0.05).
结论: GPC3蛋白在HCC患者血清和组织中有较高的表达, 对诊断HCC有较高的敏感性和特异性, 可作为HCC早期诊断的标志物.
引文著录: 缪辉来, 谢贵林, 温继育, 陈念平, 陈明, 包仕廷. Glypican-3蛋白在肝细胞癌患者血清和组织中的表达及意义. 世界华人消化杂志 2007; 15(21): 2311-2315
Revised: July 23, 2007
Accepted: July 28, 2007
Published online: July 28, 2007
AIM: To investigate glypican-3 (GPC3) protein expression and its clinical significance in serum and tissues in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
METHODS: Serum and tissues from 27 patients with HCC and 28 with benign liver disease were collected the day before operation. Expression of GPC3 in serum was detected by Western blotting, and expression in tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry.
RESULTS: In the 27 patients with HCC, GPC3 expression in the HCC, paracarcinomatous and non-tumor liver tissues was 81.5, 0 and 0%, respectively (HC: 23.4689, P < 0.001), and that in the serum before operation was 55.6%. There was no expression of GPC3 in the tissue and serum of the 28 patients with benign liver disease. The sensitivity, specificity and false-positive rates were 55.6, 100 and 0%, respectively, with serum GPC3 protein standard alone in the diagnosis of HCC. GPC3 protein expression in serum had no correlation with patient age or sex, alfa feta protein and hepatitis B surface antigen of HCC (P > 0.05), but was correlated with tumor size and pathological grade (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSION: GPC3 protein expression in serum and tissue in HCC is higher than in non-HCC tissue. There is also greater sensitivity and specificity, and over-expression of GPC3 in HCC serum, which may be of value for the early diagnosis of HCC.
- Citation: Miao HL, Xie GL, Wen JY, Chen NP, Chen M, Bao ST. Glypican-3 protein expression in serum and tissues and its clinical significance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2007; 15(21): 2311-2315
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v15/i21/2311.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v15.i21.2311
肝细胞癌(hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC)目前仍是世界上最常见的实体肿瘤[1-2], AFP是目前筛选、检测和随访HCC最常用的肿瘤标记物, 但仍然面临在分化程度好的HCC或退行发育的HCC可能仅有轻度或没有AFP水平升高[3-4], 对于肿瘤直径小于1 cm的微小HCC的检出率仍不高, 约30%-40%早期、可切除性HCC患者中血清AFP可以没有明显升高, 而良性或特殊疾病等情况下AFP可为阳性[5-6]等诸多问题, 对于HCC的诊断、特别是早期诊断还没有可靠的血清学指标. Glypican-3(GPC3)蛋白是一种膜性硫酸乙酰肝素糖蛋白, 影响多种生物效应分子[3,7-10], 在HCC中的诊断价值评估成为当今热门研究课题之一[11-13], 本研究组发现GPC3在肝细胞癌中的表达比AFP基因更敏感, AFP表达阴性的HCC组织中表达阳性率也高[14-15]; 但Glypican-3的特异度、灵敏度等诊断试验价值究竟如何, 能否作为满意的肝癌肿瘤标记物值得进一步研究.
2002-12/2005-03术后病理证实为HCC患者27例, 男23例, 女4例, 年龄23-70(平均50.7±10.7)岁. HCC大体分型、组织学分类按1982年全国肝癌协作组制定的分类标准, 病理分级按Edmondson HCC分级标准, 肝硬化命名和分类按WHO标准. 另随机收集肝良性病变患者28例的组织和血清. 术前1 d空腹取血清标本, 立即放于4℃冰箱, 分离血清, -20℃保存待测. 组织标本均在手术中收集, 取材离体后速冻于液氮中, 并于-70℃超低温冰箱中贮存备用. 标本取材大小均约1 cm×1 cm×0.2 cm; 肿瘤组织均在原发灶取材, 避开坏死、炎症区域, 癌旁组织取自相应肿块旁2 cm, 远癌组织取自距肿块边缘5 cm以上的肝脏组织. 兔抗人GPC3多克隆抗体购自美国Santa Cruz公司, GAPDH、Anti-goat及anti-mouse IgG(H+L) 购自康成生物工程公司, 免疫组化试剂盒购自北京中山公司.
1.2.1 免疫组织化学染色: 采用链霉抗生物素蛋白-过氧化酶(S-P)法, GPC3一抗工作浓度1: 50. 均用PBS代替一抗作阴性对照. 采用双盲法, 观察切片至少5个具有代表性高倍视野, 不少于1000个细胞, 染色以胞质中染成淡黄或棕黄色为阳性, 对免疫组化结果进行评估.
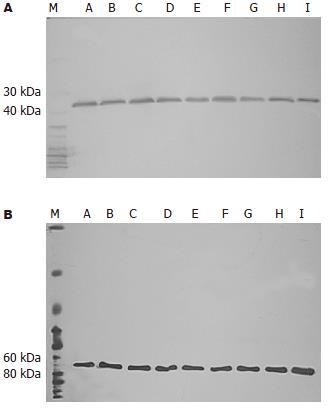
1.2.2 Western blot检测: 蛋白裂解液(Brij液) 1 mol/L Tris 1 mL, 0.5 mol/L EDTA, 0.5 mol/L 0.4 mL, 5 mol/L NaCl 3mL、10% Brij 96 8.75 mL、10% NP40 1.25 mL补水至总体积为100 mL; 蛋白酶抑制剂: Leupeptin 25 µmol/L, Aprotinin 25 µmol/L, AEBSF 25 µmol/L, Brij液100 mL需加入至少两种蛋白酶抑制剂共100 µL. BCA蛋白质定量: BCATM试剂A, BCATM试剂B, BSA标准溶液(2 g/L); 配制BSA标准浓度梯度并准备BCATM工作液, 96孔板测量(标准品或样品:工作液= 1:8)four-parameter法曲线拟合. 根据拟合标准曲线进行每个样品浓度的计算. 变性聚丙烯酰胺不连续凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE): 制备分离胶(pH8.8), 制备积层胶(pH6.8), 样品准备, 加入电泳缓冲液, 上样, 电泳. 蛋白质转移. 膜的封闭和抗体孵育: GPC3抗体稀释比例为1:400, Anti-goat稀释比例为1:1500. GAPDH稀释比例为1:10000 anti-mouse IgG(H+L)稀释比例为1:4000. 结果检测以X光胶片曝光, 图片扫描保存为电脑文件, 并用Tanon分析软件将图片上每个特异条带灰度值的数字化.
统计学处理 应用SAS8.0 for windows软件处理, 两组间计量资料比较采用t检验, 计数资料比较采用χ2检验, 以P<0.05认为有显著性差异.
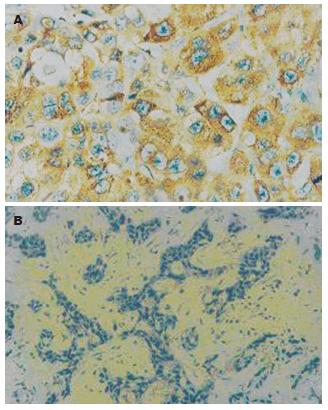
GPC3蛋白阳性细胞常簇集形成克隆样区域, 阳性细胞和阴性细胞有明显的不同形态, HCC组织(A组)、癌旁组织(B组)和远癌肝组织(C组)中的表达率分别为81.5%, 0%和0%(HC: 23.4689, P<0.001). HCC组织与非HCC组织(癌旁组织和正常组织)之间的GPC3蛋白表达阳性率差异有非常显著意义(P<0.01, 图1A-B). 以病理诊断为金标准血清中GPC3蛋白诊断HCC结果的有效性评价见表1.
| 研究试验结果 | 病理诊断结果 | 合计 | ||
| 肝细胞癌 | 肝良性病变 | |||
| GPC3蛋白 | (+) | 14 | 0 | 14 |
| (-) | 13 | 28 | 41 | |
| 合计 | 27 | 28 | 55 | |
GPC3蛋白作为一种膜性间质蛋白, 其表达方式与生长因子(如成纤维细胞生长因子等)及其受体表达方式一致[16-17], 能通过一系列细胞表面受体传导的信号来调节细胞形态和各种细胞行为如: 黏附、增殖、迁移、存活和分化[3,10,18]. Hsu et al[19]应用Northern blotting检测到胚胎期GPC3蛋白表达于发育中的小肠和中胚层来源组织中, 而在成人除在胎盘、卵巢、乳腺、间皮、肺及肾组织有弱表达之外, 其他正常分化组织中未发现有表达[20-24]. 同时, 有少量报道称GPC3C末端融合蛋白在HCC中有高表达[25-26]. 我们采用了免疫组织化学SP法显示阳性染色主要位于细胞质及细胞膜, 呈细颗粒状; 阳性细胞常簇集形成克隆样区域, 阳性细胞和阴性细胞有明显的不同形态[11], 发现81.5%的HCC组织不同程度地表达GPC3蛋白, 而正常肝细胞、胆管细胞、血管内皮细胞、Ito细胞及成纤维细胞均未见表达, 癌旁组织不表达GPC3蛋白; 我们还发现直径>5 cm HCC中GPC3蛋白的阳性表达率高于直径≤5 cm HCC中的阳性表达率(P<0.05), HCC组织与非HCC组织(癌旁组织和正常组织)之间的GPC3蛋白表达阳性率差异有非常显著意义(P<0.01), 这说明GPC3蛋白在HCC组织中有广泛而稳定的表达, 癌旁肝组织中未发现GPC3蛋白表达, 主要原因为GPC3蛋白作为靶基因被其他基因激活来发挥抑癌作用, 可在肝肿瘤的发生中起抑癌作用[27-28], 假如在癌旁组织中发现该蛋白表达, 可能已有转移性卫星灶了.
有研究提示GPC3在肝细胞癌的发生、发展中是较AFP更早期的事件[6,24,29-30], 本研究Western blot发现55.6% HCC患者血清中不同程度的表达GPC3蛋白, 而肝良性病变患者血清中不表达GPC3蛋白. 通过诊断实验的评价分析, Western bolt方法检测血清中GPC3蛋白有较高的敏感性(55.6%)和特异性(100%), 有很低的误诊率, 鉴别诊断价值较大. 我们还发现GPC3蛋白表达与患者的性别、年龄、肝功Child分级、HBsAg、临床分期、肿瘤有无包膜、瘤灶数等都无显著相关性, 而与肿块直径、病理分级等有显著相关性(P<0.05), GPC3蛋白在直径>5 cm HCC的阳性表达率明显高于直径≤5 cm HCC的阳性表达率; GPC3蛋白在低分化(Edmonson-SteinerⅢ和Ⅳ级)的阳性表达率明显高于在高分化(Edmonson-SteinerⅠ和Ⅱ级)的阳性表达率. 这提示检测HCC组织和/或血液中的GPC3蛋白的表达对于预测肿瘤的恶性程度、病情轻重及预后有重要价值. GPC3蛋白作为一个特异性的肿瘤标记物, 可能在细胞癌变的初始即有稳定的表达, 是HCC发生的一个较早期事件, 表达的质和量与HCC的直径、恶性程度大小和病程的进展有关. 由此可见检测GPC3蛋白可作为诊断HCC的肿瘤特异性标记物, 对区别肝脏肿瘤结节的良恶性、HCC的早期诊断上有重要意义.
α-甲胎蛋白(AFP)是临床诊断肝细胞癌的主要手段, 但我国肝细胞癌中有30%-40%属AFP阴性, 单凭AF P用于肝细胞癌的临床诊断和普查易造成漏诊和误诊. GPC-3(GPC3) 影响多种生物效应分子, 与这些肿瘤的发生、发展有密切关系. 有研究表明肝细胞癌血清中的GPC3蛋白阳性率高, GPC3能否作为满意的肝细胞癌肿瘤标记物令人关注.
本实验进行之初尚无GPC3蛋白的商品化的ELASA检测试剂盒, 我们采用 Western blot方法检测血清的 GPC3 蛋白水平.通过诊断试验来探讨GPC3对HCC早期诊断的敏感性、特异性、误诊率.
本研究发现GPC3 蛋白在HCC患者血清和组织中有较高的表达, 对诊断HCC有较高的敏感性和特异性, 可作为HCC早期诊断的标志物.
目前研究发现肿瘤相关纤维母细胞能分泌多种生长因子和酶类, 从而促进肿瘤侵袭转移, 但纤维母细胞与上皮细胞相互作用是许多因子共同参与的复杂过程, 其中许多环节的作用机制还不清楚.
本文研究了CPC3 蛋白在肝细胞癌患者血清和组织中有较高的表达, 诊断肝癌的灵敏性, 和特异性较 高. 论证有据, 层次清楚, 对基础和临床的肝癌研究有一定的指导意义.
编辑: 何燕 电编:郭海丽
| 1. | Tsuda M, Kamimura K, Nakato H, Archer M, Staatz W, Fox B, Humphrey M, Olson S, Futch T, Kaluza V. The cell-surface proteoglycan Dally regulates Wingless signalling in Drosophila. Nature. 1999;400:276-280. [PubMed] |
| 2. | Lin X, Perrimon N. Dally cooperates with Drosophila Frizzled 2 to transduce Wingless signalling. Nature. 1999;400:281-284. [PubMed] |
| 3. | Xiang YY, Ladeda V, Filmus J. Glypican-3 expression is silenced in human breast cancer. Oncogene. 2001;20:7408-7412. [PubMed] |
| 4. | Tangkijvanich P, Anukulkarnkusol N, Suwangool P, Lertmaharit S, Hanvivatvong O, Kullavanijaya P, Poovorawan Y. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis based on serum alpha-fetoprotein levels. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2000;31:302-308. [PubMed] |
| 5. | Peters MG, Farias E, Colombo L, Filmus J, Puricelli L, Bal de Kier Joffe E. Inhibition of invasion and metastasis by glypican-3 in a syngeneic breast cancer model. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003;80:221-232. [PubMed] |
| 6. | Kwack MH, Choi BY, Sung YK. Cellular changes resulting from forced expression of glypican-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Cells. 2006;21:224-228. [PubMed] |
| 7. | Zhou L, Liu J, Luo F. Serum tumor markers for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:1175-1181. [PubMed] |
| 8. | Li M, Choo B, Wong ZM, Filmus J, Buick RN. Expression of OCI-5/glypican 3 during intestinal morphogenesis: regulation by cell shape in intestinal epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1997;235:3-12. [PubMed] |
| 9. | Veugelers M, Cat BD, Muyldermans SY, Reekmans G, Delande N, Frints S, Legius E, Fryns JP, Schrander-Stumpel C, Weidle B. Mutational analysis of the GPC3/GPC4 glypican gene cluster on Xq26 in patients with Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome: identification of loss-of-function mutations in the GPC3 gene. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:1321-1328. [PubMed] |
| 10. | Kim H, Xu GL, Borczuk AC, Busch S, Filmus J, Capurro M, Brody JS, Lange J, D'Armiento JM, Rothman PB. The heparan sulfate proteoglycan GPC3 is a potential lung tumor suppressor. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003;29:694-701. [PubMed] |
| 11. | Zhu ZW, Friess H, Wang L, Abou-Shady M, Zimmermann A, Lander AD, Korc M, Kleeff J, Buchler MW. Enhanced glypican-3 expression differentiates the majority of hepatocellular carcinomas from benign hepatic disorders. Gut. 2001;48:558-564. [PubMed] |
| 12. | Capurro M, Wanless IR, Sherman M, Deboer G, Shi W, Miyoshi E, Filmus J. Glypican-3: a novel serum and histochemical marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:89-97. [PubMed] |
| 13. | Nakatsura T, Yoshitake Y, Senju S, Monji M, Komori H, Motomura Y, Hosaka S, Beppu T, Ishiko T, Kamohara H. Glypican-3, overexpressed specifically in human hepatocellular carcinoma, is a novel tumor marker. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;306:16-25. [PubMed] |
| 15. | Hippo Y, Watanabe K, Watanabe A, Midorikawa Y, Yamamoto S, Ihara S, Tokita S, Iwanari H, Ito Y, Nakano K. Identification of soluble NH2-terminal fragment of glypican-3 as a serological marker for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2004;64:2418-2423. [PubMed] |
| 16. | Grisaru S, Cano-Gauci D, Tee J, Filmus J, Rosenblum ND. Glypican-3 modulates BMP- and FGF-mediated effects during renal branching morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 2001;231:31-46. [PubMed] |
| 17. | Midorikawa Y, Ishikawa S, Iwanari H, Imamura T, Sakamoto H, Miyazono K, Kodama T, Makuuchi M, Aburatani H. Glypican-3, overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma, modulates FGF2 and BMP-7 signaling. Int J Cancer. 2003;103:455-465. [PubMed] |
| 18. | Powell CA, Xu G, Filmus J, Busch S, Brody JS, Rothman PB. Oligonucleotide microarray analysis of lung adenocarcinoma in smokers and nonsmokers identifies GPC3 as a potential lung tumor suppressor. Chest. 2002;121:6S-7S. [PubMed] |
| 19. | Hsu HC, Cheng W, Lai PL. Cloning and expression of a developmentally regulated transcript MXR7 in hepatocellular carcinoma: biological significance and temporospatial distribution. Cancer Res. 1997;57:5179-5184. [PubMed] |
| 20. | Gonzalez AD, Kaya M, Shi W, Song H, Testa JR, Penn LZ, Filmus J. OCI-5/GPC3, a glypican encoded by a gene that is mutated in the Simpson-Golabi-Behmel overgrowth syndrome, induces apoptosis in a cell line-specific manner. J Cell Biol. 1998;141:1407-1414. [PubMed] |
| 21. | Pellegrini M, Pilia G, Pantano S, Lucchini F, Uda M, Fumi M, Cao A, Schlessinger D, Forabosco A. Gpc3 expression correlates with the phenotype of the Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome. Dev Dyn. 1998;213:431-439. [PubMed] |
| 22. | Lin H, Huber R, Schlessinger D, Morin PJ. Frequent silencing of the GPC3 gene in ovarian cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1999;59:807-810. [PubMed] |
| 23. | Murthy SS, Shen T, De Rienzo A, Lee WC, Ferriola PC, Jhanwar SC, Mossman BT, Filmus J, Testa JR. Expression of GPC3, an X-linked recessive overgrowth gene, is silenced in malignant mesothelioma. Oncogene. 2000;19:410-416. [PubMed] |
| 24. | Toretsky JA, Zitomersky NL, Eskenazi AE, Voigt RW, Strauch ED, Sun CC, Huber R, Meltzer SJ, Schlessinger D. Glypican-3 expression in Wilms tumor and hepatoblastoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2001;23:496-499. [PubMed] |
| 26. | Lu ZL, Luo DZ, Wen JM. Expression and significance of tumor-related genes in HCC. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:3850-3854. [PubMed] |
| 27. | Sung YK, Hwang SY, Park MK, Farooq M, Han IS, Bae HI, Kim JC, Kim M. Glypican-3 is overexpressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2003;94:259-262. [PubMed] |
| 28. | Sung YK, Hwang SY, Farooq M, Kim JC, Kim MK. Growth promotion of HepG2 hepatoma cells by antisense-mediated knockdown of glypican-3 is independent of insulin-like growth factor 2 signaling. Exp Mol Med. 2003;35:257-262. [PubMed] |
| 29. | Fujioka M, Nakashima Y, Nakashima O, Kojiro M. Immunohistologic study on the expressions of alpha-fetoprotein and protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist II in surgically resected small hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2001;34:1128-1134. [PubMed] |
| 30. | Libbrecht L, Severi T, Cassiman D, Vander Borght S, Pirenne J, Nevens F, Verslype C, van Pelt J, Roskams T. Glypican-3 expression distinguishes small hepatocellular carcinomas from cirrhosis, dysplastic nodules, and focal nodular hyperplasia-like nodules. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30:1405-1411. [PubMed] |