Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
肝细胞癌中XIAP mRNA及蛋白表达的意义
陶璐薇, 林菊生, 陈孝平, 周鹤俊, 蔡晓坤, 李超
陶璐薇, 林菊生, 周鹤俊, 蔡晓坤, 李超, 华中科技大学同济医学院附属同济医院肝病研究所
陈孝平, 华中科技大学同济医学院附属同济医院肝脏外科中心 湖北省武汉市 430030
ORCID number: $[AuthorORCIDs]
陶璐薇, 女, 1978-12-02生, 广西桂林市人, 汉族, 2002年华中科技大学同济医学院硕士生, 主要从事肝脏疾病的研究.
电话: 027-83663595
收稿日期: 2004-09-07
修回日期: 2004-09-13
接受日期: 2004-09-19
在线出版日期: 2004-12-15
目的: 通过检测XIAP mRNA及蛋白在肝细胞癌中的表达程度, 探讨XIAP在原发性肝细胞癌发生中的作用.
方法: 应用RT-PCR技术检测正常肝细胞株L-02, 肝癌细胞株SMMC7721, HepG2和30例肝癌及其相应癌旁组织中XIAP mRNA的水平, 同时应用免疫组织化学方法检测了上述细胞株及组织中XIAP蛋白的表达.
结果: 三株细胞株均有XIAP mRNA的表达, XIAP/β-actin均值分别为L-02: 0.418±0.045, SMMC7721: 0.719±0.069, HepG2: 0.654±0.055. 其中L-02细胞株的XIAP mRNA水平显著低于SMMC7721及HepG2(P<0.05), 两株肝癌细胞株的XIAP mRNA表达无显著性差异(P>0.05). 三株细胞亦均有XIAP蛋白的表达, 其细胞爬片平均光度分别为0.158±0.016, 0.291±0.022, 0.238±0.011, 三株细胞的XIAP蛋白水平存在显著性差异(P<0.05). 肝癌组织XIAP mRNA表达较癌旁组织显著升高, XIAP/β-actin均值分别为: 0.587±0.064, 0.313±0.059(P<0.05). 免疫组化染色显示: XIAP蛋白表达主要集中在肝细胞胞质中, 其在肝癌组织中的表达显著高于癌旁组织, 平均光度分别为: 0.276±0.054, 0.095±0.014(P<0.05).
结论: XIAP mRNA及其蛋白在肝癌组织及肝癌细胞系中表达水平明显升高, 提示他可能是促进肝细胞恶变的一个重要因素.
关键词: N/A
引文著录: 陶璐薇, 林菊生, 陈孝平, 周鹤俊, 蔡晓坤, 李超. 肝细胞癌中XIAP mRNA及蛋白表达的意义. 世界华人消化杂志 2004; 12(12): 2788-2791
Expression of XIAP mRNA and protein in human hepatocellular carcinoma
Lu-Wei Tao, Ju-Sheng Lin, Xiao-Ping Chen, He-Jun Zhou, Xiao-Kun Cai, Chao Li
Lu-Wei Tao, Ju-Sheng Lin, He-Jun Zhou, Xiao-Kun Cai, Chao Li, Institute of Liver Diseases, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China
Xiao-Ping Chen, Hepatic Surgery Center, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China
Correspondence to: Dr. Ju-Sheng Lin, Institute of Liver Diseases, Tongji hospital, Tongji medical colloge of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430030, Hubei province, China. linjusheng2001@163.net
Received: September 7, 2004
Revised: September 13, 2004
Accepted: September 19, 2004
Published online: December 15, 2004
AIM: To study the expression of XIAP mRNA and protein in tissues of hepatocellar carcinoma (HCC), and to investigate the role of XIAP in the development of primary HCC.
METHODS: The expression of XIAP mRNA in normal liver cell line L-02, hepatoma cell lines, SMMC7721 and HepG2, and tissues of primary HCC (n = 30)as well as the corresponding adjacent tissues of HCC was detected by semi-quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The expression of XIAP protein was observed in preceding cell lines and tissues by immunohistochemical staining.
RESULTS: The expression level of XIAP mRNA in L-02 was lower than that in SMMC7721 and HepG2 (mean XIAP/β-actin: 0.418 ± 0.045 vs 0.719 ± 0.069, P < 0.05; 0.418 ± 0.045 vs 0.654 ± 0.055, P < 0.05 respectively). No significant difference existed in the XIAP mRNA expression between SMMC7721 and HepG2 cells. The expression of XIAP protein was significantly different among three cell lines (0.158 ± 0.016 vs 0.291 ± 0.022 vs 0.238 ± 0.011, P < 0.05). The expression of XIAP mRNA and protein in HCC tissues was higher than those in thecorresponding cancer-adjacent tissues (mRNA: 0.587 ± 0.064 vs 0.313 ± 0.059, P < 0.05; protein: 0.276 ± 0.054 vs 0.095 ± 0.014, P < 0.05). XIAP protein was mainly distributed in cytoplasm.
CONCLUSION: Overexpression of XIAP mRNA and protein may play an important role in the carcinogenesis of primary HCC.
Key Words: N/A
0 引言
肿瘤的发生是一个多因素多基因多步骤的过程, 而促凋亡和抗凋亡因素间的失衡是其中的一个重要事件. 半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶(caspase), 又被称死亡蛋白酶, 是凋亡过程的执行者. 多种凋亡相关蛋白, 如Bcl-2, Fas等均通过调控凋亡级联反应的上游间接调控caspase的活性, 从而调节细胞的凋亡过程. X染色体连锁的凋亡抑制蛋白(X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein, XIAP)是凋亡抑制蛋白(inhibitor of apoptosis protein, IAP)家族的新成员, 是一新发现的强烈的凋亡抑制蛋白, 可以通过抑制caspase-3, caspase-7及caspase-9阻断凋亡过程. 我们以β-actin mRNA为内参, 采用RT-PCR技术及免疫组织化学SP方法检测正常肝细胞株L-02, 肝癌细胞株SMMC7721, HepG2和肝癌及癌旁组织中XIAP mRNA和蛋白水平, 从而探讨XIAP与肝细胞恶变的关系.
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
正常肝癌细胞株L-02, 人肝癌细胞株SMMC7721, HepG2均由同济医院肝病研究所传代培养, 为贴壁生长细胞. 所有肝癌组织及癌旁组织标本均由同济医院肝脏外科中心手术切除(2003-04/2003-08), 并经病理证实. 逆转录试剂, 包括MMLV及Oligo dT购自Promega公司; PCR扩增试剂, 包括Taq酶、dNTP购自北京天为时代公司; Trizol购自上海华舜生物工程公司; 鼠抗人XIAP mAB购自BD Bioscience Parmingen公司; 免疫组织化学sp试剂盒及DAB试剂盒购自北京中山生物技术公司; 目的基因XIAP和内参β-actin引物使用引物设计软件primer 2.0设计, 扩增片断分别为335 bp和159 bp, 两对引物均由上海生物工程研究所合成XIAP上游引物序列: 5'-tcagcagttggaagacacag-3'; β-actin下游引物序列5'-agtccagcacttgctaactc-3'; β-actin上游引物序列: 5'-tggcaccacaccttctacaa-3; β-actin下游引物序列5'-agcctggatagcaacgtaca-3'.
1.2 方法
所有细胞均用含100 mL/L胎牛血清(FBS)和100 kU/L青霉素及链霉素的DMEM(dulbeccos modified engle medium)培养基, 在37 ℃ 5 mL/L CO2条件下培养. 按Trizol说明书中步骤提取细胞总RNA, 以紫外分光光度仪测定RNA浓度及纯度, 其余于-75 ℃中冻存, 近期使用. 组织每次约剪取50 mg, 用预冷的PBS漂洗干净后, 冰上充分匀浆, 其余提取过程同细胞总RNA. 逆转录反应取RNA 1 μg, 5×RT Buffer 4 μL, 10 mmol/L dNTP 1 μL, 50 mU/L RNasin 0.5 μL, 0.5 g/L Oligo dT 1 μL, 200 MU/L MMLV 1μL, DEPC水定容至20 μL, 充分混匀, 42 ℃反应60 min, 94 ℃灭活5 min. 阴性对照为不加RNA的反应体系. 取上述反应产物cDNA2 μL, 10 mmol/L dNTP 2 μL, 10×Buffer 2.5 μL, 25 mmol/L MgCl2 2 μL, 12.5 pmol/L XIAP及β-actin引物1 μL, 去离子水定容至24.5 μL, 充分混匀后94 ℃热启动5 min, 加入2.5 mU/L Taq酶0.5 μL. 扩增条件: 94 ℃热变性1 min, 52 ℃退火1 min, 72 ℃延伸45 s, 30个循环, 72 ℃补偿5 min, 同时扩增XIAP及β-actin. 空白对照为不加入cDNA模板的反应体系. 取PCR反应产物3 μL, 与6×PCR上样缓冲液0.5 μL混合后, 于20 g/L琼脂糖凝胶(含0.5 mg/L溴化乙锭)中电泳, 75 V, 40 min, 于紫外光灯下观察结果, 以UVP凝胶分析系统拍照并分析结果.
免疫组化石蜡切片常规脱蜡至水, 滴加30 mL/L H2O2甲醇孵育30 min, 置0.01 mol/L枸橼酸钠缓冲液中加热92 ℃以上, 15 min抗原修复, PBS振洗后加正常羊血清封闭30 min, 滴加一抗(1:300)4 ℃孵育过夜. 次日室温复温1 h, 加生物素化二抗孵育30 min, 辣根过氧化物酶标记链霉卵白素孵育30 min, PBS洗后DAB显色, 中性树胶封片. 细胞爬片将预先处理的载波片置于六孔板中, 再将对数生长期细胞以5×105每孔接种于六孔板中. 待细胞贴壁后, 以40 g/L多聚甲醛固定30 min, 后续步骤除无需抗原修复外同石蜡切片.
统计学处理 试验数据以mean±SD表示, 率的显著性差异分析采用SPSS10.0软件.
2 结果
2.1 正常肝细胞株及肝癌细胞株中XIAP mRNA及蛋白的表达
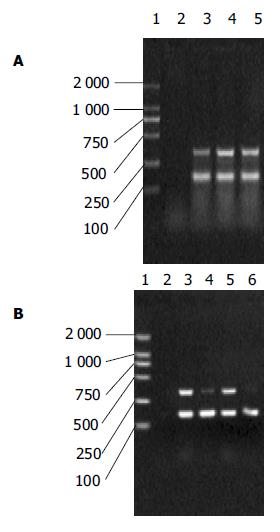
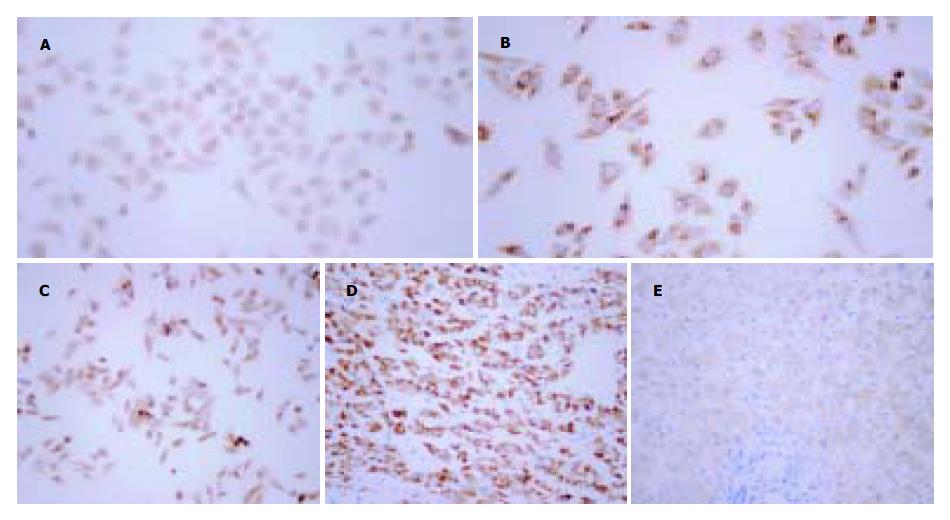
正常肝细胞株L-02 XIAP/β-actin为0.418±0.045, SMMC7721: 0.719±0.069, HepG2: 0.654±0.055. 其中L-02 XIAP mRNA的表达水平较SMMC7721和HepG2低(P<0.05, t检验), 但在两肝癌细胞株XIAP mRNA水平无明显差异(P>0.05, t检验, 图1A). 细胞爬片免疫组化显示三株细胞中均有XIAP蛋白的表达, 其阳性产物呈棕黄色, 主要分布于胞质中. 图像分析示免疫组化细胞爬片平均光度L-02为0.158±0.016, SMMC7721: 0.291±0.022, HepG2: 0.238±0.011. 三者的平均光度经统计学分析均有显著性差异(P<0.05, t检验), 以SMMC7721表达水平最高, L-02最低(图2A-C).
图1 XIAP mRNA在肝癌中的表达.
A: 1: marker; 2: 不加cDNA的PCR反应体系; 3: L-02正常肝细胞株; 4: SMMC7721肝癌细胞株; 5:HepG2肝癌细胞株; B: 1: marker; 2: 不加cDNA的反应体系; 3: 肝癌组织1; 4: 相应癌旁组织1; 5: 肝癌组织2; 相应癌旁组织2.
图2 XIAP蛋白在肝癌中的表达SP×400.
A: L-02细胞中XIAP蛋白表达; B: SMMC7721细胞中XIAP蛋白表达; C: HepG2细胞中XIAP蛋白表达; D: 肝癌组织中XIAP蛋白表达; E: 癌旁组织中XIAP蛋白表达.
2.2 肝癌组织及癌旁组织中XIAP mRNA及蛋白的表达
肝癌组织XIAP/β-actin为0.587±0.064, 癌旁组织为0.313±0.059, 二者间有显著的统计学差异(P<0.05, t test, 图1B). 免疫组化阳性染色为棕黄色颗粒, 主要集中于胞质中. 肝癌组织切片免疫组化染色平均光度为0.276±0.054, 癌旁组织为0.095±0.014. 两组均值间有统计学差异(P<0.05, t test, 图2D-E).
3 讨论
caspase是细胞凋亡过程的最终执行者. 死亡相关受体分子(Fas等)及多种应激因子(如紫外线照射等)分别通过不同途径激活caspase-8或caspase-9, 诱发一系列级联链锁反应, 激活下游的caspase-7及caspase-3, 最终导致细胞正常结构的崩解和细胞凋亡. IAP家族是近年新发现的具有强烈凋亡抑制作用的蛋白质家族, 其结构的共同特点是名为杆状病毒IAP重复序列(baculoviral inhibitory repeat, BIR)的结构域. 在现发现的IAP家族的成员, 如survivin、Livin、 ILP-2中均存在BIR结构域, 并能通过BIR与相应的caspase的结合达到抑制caspase活性从而抑制凋亡的作用[1-6]. XIAP的主要结构包括3个BIR结构域, 一个功能不明的两性分子结构区, 羟基端一个富含半胱氨酸的锌指结构以及以上结构间的连接区域(linker). 通过竞争性结合及非竞争性机制, XIAP的BIR结构域及linker区域能够分别抑制caspase-3, caspase-7及caspase-9, 从而起到抑制细胞凋亡, 促进细胞生存的作用[7-15]. 此外, XIAP还能通过激活丝裂原激活蛋白激酶(MAPK)家族的另一个成员C-JUN N末端激酶1[JNK1], 从而抑制由TNFα及ICE[即caspase1]介导的细胞凋亡[16-22]. 现有研究表明, 当细胞处于不利条件, 如缺氧、缺乏血清时, XIAP表达升高, 同时XIAP在多种肿瘤中均有异常表达[23]. 故许多学者均认为: XIAP基因的异常表达可能是肿瘤细胞失去正常凋亡调控并能在不良条件中生存的重要条件. Ingo et al检测了包括血液、中枢神经、肾脏、肺等多个系统的60个肿瘤细胞系, 发现XIAP在所有的细胞系中均有普遍表达[24]. Ramp et al运用免疫组化检测了145例肾脏透明细胞癌标本, 发现其中95%的肿瘤组织表达XIAP, 其中低分化肿瘤的XIAP表达远高于高分化肿瘤, 而晚期肿瘤则明显高于早期肿瘤[25]. Amantana et al对顺铂耐药的前列腺癌细胞株DU145的研究发现, XIAP的高表达及其对caspase-3的抑制作用是DU145对顺铂耐药的原因之一. 他们同时证实, 使用XIAP的反义核酸治疗能明显增强顺铂的疗效, 减弱细胞耐药性[26].
本研究结果显示XIAP mRNA及蛋白在三株细胞中均有表达. 其中, 在正常肝细胞株L-02中的表达量较肝癌细胞株SMMC7721及HepG2中为低, 而两株肝癌细胞株的XIAP mRNA及蛋白的表达水平没有显著性差异. XIAP的普遍表达可能与细胞株建株时为达到永生化的反复筛选, 从而使得XIAP高表达而具有强抗凋亡能力的细胞得以存活有关. 值得关注的是, 在mRNA水平, 肝癌细胞株SMMC7721及HepG2的XIAP表达相近, 而在蛋白水平SMMC7721则高于HepG2, 其机制可能与XIAP mRNA5'端的核糖体进入序列(internal ribosome entry site, IRES)的活性及细胞内的泛素化水平相关. IRES能帮助细胞在不利条件下翻译出XIAP, 而XIAP的降解则是由泛素化过程介导的[27-29]. 因此, 可能由于SMMC7721和HepG2在肿瘤起源、细胞特性上存在诸多差异, 导致其胞内IRES活性及泛素化水平的不一致, 从而导致了XIAP蛋白水平的变化. 研究同时发现在癌旁组织中即存在XIAP的表达, 在肝癌组织中XIAP及蛋白则明显升高. 其机制可能为在良性基础肝病, 如肝炎、肝硬化的基础上, 肝脏细胞发生修复性增生, 抗凋亡机制作用增强, XIAP相应表达上调. 而其中少数XIAP表达明显上调的细胞克隆具有极强抗凋亡能力, 失去了正常的凋亡调控并在多种不利条件下存活下来而发展为恶性肿瘤. 总之, 本研究表明XIAP可能通过细胞的凋亡调控参与了肝细胞癌的发生和发展, 他的过表达与肝细胞癌发生发展相关. 这为肝癌的发生预测和早期诊断寻求新的指标, 为肝癌的预防和治疗提供新的靶点.