修回日期: 2002-07-20
接受日期: 2002-07-22
在线出版日期: 2003-06-15
了解胸腺肽α1(Tα1)对慢性乙型肝炎患者免疫系统的影响, 评价Tα1对慢性乙型病毒性肝炎的疗效.
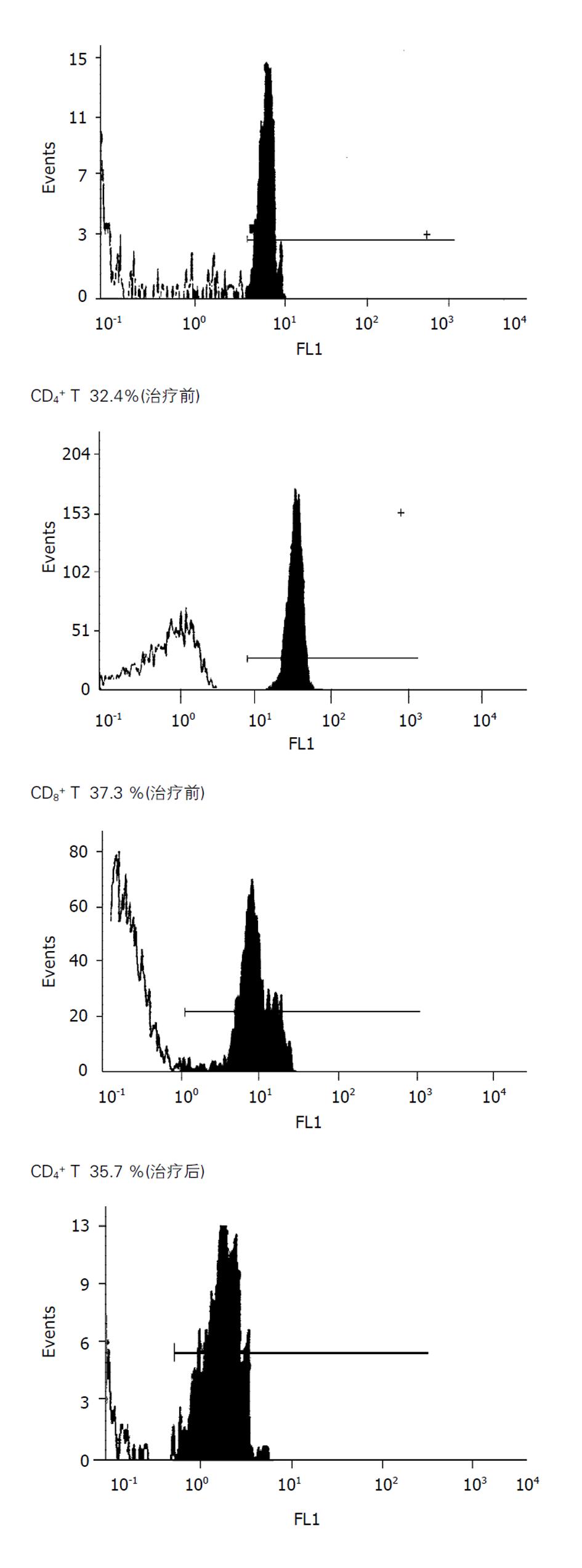
选择60例慢性乙型肝炎患者, 其中Tα1组25例, 给予Tα1(1.6mg, sc, 2次/wk, 3-6 mo)治疗, 联合组35例, 给予Tα1联合贺普丁(0.1 g, po, 1次/d, 3-6 mo)治疗, 另选60例作为对照组, 仅给予保肝治疗. 应用双抗体酶联分析法检测治疗前后血清中IFN-γ和IL-4的浓度, 以IFN-γ代表Th1, IL-4代表Th2, 从而计算Th1/Th2比值; 采用流式细胞仪观察外周血CD4+T, CD8+T细胞亚群.
联合组与对照组比, 治疗后肝功能改善显著(P<0.01) ; 联合组乙型肝炎病毒标志物HBsAg或HBeAg阴转(9例)及HBV-DNA定量指标降低(14例), 与对照组比, 均具有统计学差异(P<0.01; P<0.05). 但Tα1组分别与对照组、联合组比, 无统计学差异(P>0.05). Tα1组治疗后CD4+T细胞增高(由31.3±2.4增高到36.1±2.5)具有统计学意义(P<0.01), CD8+T细胞稍高且CD4+/CD8+无明显变化, 相差无统计学意义(P>0.05); IFN-γ浓度(由71.3±21.0增高到83.7±21.4)及Th1/Th2比值升高(由0.79±0.2增高到0.98±0.3)均有统计学意义(P均<0.05), 但IL-4表达水平变化无统计学意义.
Tα1能提高机体的细胞免疫功能, 有利于病毒清除和疾病的恢复.
引文著录: 段国荣, 聂青和, 周永兴, 王全楚, 田长印, 刘拉羊, 薛红安. 胸腺肽α1对慢性乙型肝炎患者免疫系统的影响. 世界华人消化杂志 2003; 11(6): 701-704
Revised: July 20, 2002
Accepted: July 22, 2002
Published online: June 15, 2003
To realize effect of thymosin-α1 (Tα1) on immune function with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) and to evaluate the efficacy of Tα1 in the treatment of CHB.
Sixty patients with CHB were randomly chosen. Twenty-five cases were received Tα1 (1.6 mg, sc, twice a week, 3-6mo) and thirty-five were received Tα1 combined with Lamivudine (0.1 g, po, once a day, 3-6 mo). Hepatic function, virological analyses (HBeAg, HBsAg, HBV-DNA) and immunological analyses (periperal blood T lymphocytes subset, IFN-α and IL-4 levels) from patients in pretreatment and posttreatment were observed.
At the end of treatment, ALT and T-Bil were decreased in the group of Tα1 combined with Lamivudine (P<0.01), HBeAg/HBsAg remained negative (n = 9) and HBV-DNA levels were also low (n = 14) in the group of Tα1 combined with Lamivudine (P<0.01 and P<0.05, respectively) as compared with healthy individuals. CD4+ T Cell (from 31.3±2.4 to 36.1±2.5), the level of IFN-α(from 71.3±21.0 to 83.7±21.4) and Th1/Th2 (from 0.79±0.2 to 0.98±0.3) increased in the group of Tα1 (P<0.01, P<0.05 and P<0.05, respectively).
Tα1 is efficient to treat patients with CHB because it can elevate the level of cellular immunity, which is beneficial to viral clearance.
- Citation: Duan GR, Nie QH, Zhou YX, Wang QC, Tian CY, Liu LY, Xue HA. Effect of thymosin-α1 on immune function with chronic hepatitis B. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2003; 11(6): 701-704
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v11/i6/701.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v11.i6.701
我国是病毒性肝炎的高发区, 乙型肝炎居首位, 目前尚缺乏特效治疗. 目前抗病毒药物效果不尽人意. 因此, 寻找更有效的治疗措施, 一直为临床医师及科研人员所关注[1-17]. 化学合成的胸腺肽α1(thymosin-α1, 日达仙, Tα1)对病毒性肝炎的治疗虽已有报道, 但多在于观察肝功能、病毒复制指标等. 而对于细胞免疫指标的检测报道较少, 尤其是Th1/Th2及外周血T淋巴细胞亚群的变化. 为此, 我们旨在观察患者外周血Th1/Th2及T淋巴细胞亚群的变化, 同时对患者肝功能生化指标及病毒复制指标进行观察分析, 从而评价Tα1对CHB的疗效.
慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)患者60例来自第四军医大学唐都医院, 西安交通大学第二医院及西安市中心医院. 其中Tα1组25例, 联合组35例, 另选60例作为对照组. 男21例, 女14例. 年龄21-60(平均40)岁. 诊断符合1995年(北京)第五次全国传染病与寄生虫病学术会议修订的标准. IFN-γ和IL-4双单克隆抗体ELISA检测试剂盒, 均购自深圳晶美生物工程有限公司, 批号991225. HBV-DNA PCR 检测试剂盒购自广州市中山医科大学达安基因股份有限公司, 批号S19990003. CD4-FITC和 CD8-PE 产地法国马赛(immunotech france). Epics-Profile二型流式细胞仪, 美国Coulter公司生产.
Tα1(日达仙, 美国赛生公司) 1.6 mg, 皮下注射, 2次/wk, 其中35例患者加用抗病毒药物(贺普丁)0.1 g, 口服, 1次/d, 同时配合多种维生素, 肌苷等常规保肝治疗. 疗程3-6 mo. 随机选择60例CHB患者作为对照, 仅给予保肝等对症处理. 患者于治疗前后抽血检测肝功能. 血清病毒学指标: HBsAg, 抗-HBs, HBeAg, 抗-HBe, 抗-HBc, PCR-HBV-DNA. 细胞免疫指标: CD4+T, CD8+T, CD4+/CD8+及细胞因子IFN-γ, IL-4浓度. 药物毒副作用观察. 外周血T细胞亚群检测步骤: 先加20 μL双标抗体于小试管底, 再加抗凝血100 μL, 混匀, 放置室温(18-25 °C)孵育30min; 加RBC溶解液1 mL, 待RBC溶解后上流式细胞仪检测; 波长488 nm时FITC(异硫氰酸荧光素)呈蓝-绿荧光, PE(藻红蛋白)呈红色荧光, 计数3000个细胞, 记录分析直方图, 数据经ELITE软件处理. 血清IFN-γ检测步骤: 从已平衡至室温的密封袋中取出所需板条, 分别将标本及不同浓度标准品(100 μL/孔)加入相应孔中, 然后再加入生物素化抗体工作液(50 μL/孔)和酶结合物(20-25 °C)共同孵育120 min. 洗板3次. 先后加入底物A, B各100 μL/孔, 避光置室温10-30 min. 加入终止液50 μL/ 孔, 混匀后即刻在ELISA读数仪上测量A450值, 绘制标准曲线, 并测定各血清标本中IFN-γ的浓度(ng/L). 血清IL-4检测步骤同上.
统计学处理 结果数据采用mean±SD, 方差分析, x2检验
联合组与对照组比, T-Bil和ALT相差有统计学意义(P<0.01, 表1); Tα1组与对照组比及Tα1组与联合组比, 均无统计学差异(P>0.05). 在Tα1组未见药物副反应; 在联合组治疗过程中2例发生轻度恶心, 1例出现白细胞轻微下降, 治疗结束后自行恢复.
检测病毒学标志, 在Tα1组和联合组HBeAg或HBsAg阴转共13例(13/60), HBV-DNA定量指标下降20例(20/60). 13例HBeAg或HBsAg阴转同时伴随HBV-DNA定量指标降低. 在肝功能复常方面: 联合组与对照组比, 有统计学差异(x2 = 8.681, P = 0.0032) ; 在阴转方面: 联合组与对照组比, 相差有统计学意义(x2 = 7.518, P = 0.0 061) ; 在HBV-DNA定量指标下降方面: 联合组与对照组比, 相差有统计学意义(x2 = 4.448, P = 0.035, 表2, 3)Tα1组与对照组比及Tα1组与联合组比, 均无统计学差异(P>0.05).
| 分组 | n | <104 | 104 | 105 | 106 | 107 | >107 |
| 对照组 | 60 | 0 | 7 | 13 | 24 | 12 | 4 |
| Tα1组 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 3 |
| 联合组 | 35 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 11 | 7 | 3 |
Tα1组治疗前后CD4+T细胞增高具有统计学意义(t = 6.93, P = 0.000), CD8+T细胞略高且CD4+/CD8+相差无统计学意义(t = 1.50, P=0.141; t = 1.41, P = 0.1 638); 治疗前后IFN-γ表达水平及Th1/Th2比值变化有统计学差异(t = 2.07, P = 0.0 441; t = 2.63, P = 0.0 117), IL-4表达水平变化无统计学意义(t = 0.41, P = 0.6 856, 表4, 图1).
病毒性肝炎是我国常见病多发病, 目前尚缺乏特效治疗, 其主要原因是发病机制较为复杂, 尚未完全阐明[18-41]. 多数资料表明, CHB患者细胞免疫功能低下[42,43]. Tα1能促进T细胞成熟和影响免疫调节细胞的功能, 还能增强IFN-γ及IL-2等细胞因子的生成, 促进免疫缺陷的重建. 这也是Tα1用于CHB治疗的理论依据. 本研究显示, 联合组与对照组比, 治疗前后肝功能显著改善, Tα1组分别与对照组、联合组比, 肝功能改善无统计学意义; 联合组与对照组相比, 治疗前后病毒学标志, 包括HBeAg或HBsAg阴转, HBV-DNA定量指标降低均具有统计学差异, 但Tα1组分别与对照组、联合组比差异无统计学意义. 可见, 无论在肝功能改善方面, 还是在病毒学标志方面, Tα1联合抗病毒药物(贺普丁)均显示良好的治疗效果. 本研究还显示, 在Tα1组, 治疗前后CD4+相差具有统计学意义, 治疗后CD8+稍高, CD4+/CD8+无明显变化, 相差无统计学意义. 这表明Tα1能提高机体的细胞免疫功能, CD4+增高可促使机体分泌IFN-γ、IL-2等细胞因子, 有利于病毒清除. 治疗后IFN-γ水平较治疗前高, 这可能与Tα1能增强IFN-γ的生成有关, 但仍低于正常血清IFN-γ水平(结合血清细胞因子检测结果). 可能原因是: (1)患者血清中可能存在诱生IFN的抑制因子; (2)产生IFN的活性细胞功能降低; (3)药物剂量不足或疗程不够长. 因此, 加用IFN-γ治疗或Tα1疗程延长, 可能效果更好.
早在1986年Mosmann et al 就发现小鼠的CD4+细胞株接受抗原刺激可分化成Th1和Th2两个亚群. 前者分泌IL-2, IFN-γ, TFN-β等可促进细胞免疫. 后者分泌IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, IL-13等可促进体液免疫. 以后研究又进一步证实在人类也存在这两种亚型. 日前, 越来越多的证据表明, Th1/Th2平衡的变化会影响感染的结局[44-48]. 我们曾报道35例CHC患者Th2类细胞因子占优势, 还报道30例CHB患者Th2类细胞因子较Th1类细胞因子水平高, 分别与正常对照组比, 均有统计学差异. 本研究中, 以IFN-γ代表Th1, IL-4代表Th2, 从而计算Th1/Th2比值. 在Tα1组, 治疗前后Th1/Th2比值变化有统计学差异, 可能是由于IFN-γ浓度变化幅度大于IL-4所致. Th1/Th2比值增高可促进机体细胞免疫应答, 有利于病毒清除和疾病的恢复.
总之, 如何有效提高机体的细胞免疫功能, 如何终止病毒复制, 从而维持患者的肝功能稳定, 是目前急需解决的问题. 免疫调节剂(Tα1)有利于肝炎病毒的清除和疾病的恢复. 加大药物剂量或延长疗程可能效果更好. 联合抗病毒药物(贺普丁)治疗可能更具优势, 既可利用Tα1提高细胞免疫功能的特点, 又可利用贺普丁持续抑制病毒复制的特点, 从而达到提高疗效的目的.
感谢第四军医大学唐都医院中心实验室张盈华主任的大力支持.
| 1. | Zhao LS, Qin S, Zhou TY, Tang H, Liu L, Lei BJ. DNA based vaccination induces humoral and cellular immune responses against hepatitis B virus surface antigen in mice without activation of c-myc. World J Gastroenterol. 2000;6:239-243. [PubMed] |
| 2. | Wen SJ, Xiang KJ, Huang ZH, Zhou R, Qi XZ. Construction of HBV specific ribozyme and its recombinant with HDV and their cleavage activity in vitro. World J Gastroenterol. 2000;6:377-380. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 3. | Huang ZH, Zhuang H, Lu S, Guo RH, Xu GM, Cai J, Zhu WF. Humoral and cellular immunogenecity of DNA vaccine based on hepatitis B core gene in rhesus monkeys. World J Gastroenterol. 2001;7:102-106. [DOI] |
| 4. | Kakimi K, Guidotti LG, Koezuka Y, Chisari FV. Natural killer T cell ac tivation inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in vivo. J Exp Med. 2000;192:921-930. [DOI] |
| 5. | Fang JN, Jin CJ, Cui LH, Quan ZY, Choi BY, Ki MR, Park HB. A comparative study on serologic profiles of virus hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol. 2001;7:107-110. [DOI] |
| 6. | Cheng ML, Wu YY, Huang KF, Luo TY, Ding YS, Lu YY, Liu RC, Wu J. Clinical study on the treatment of liver fibrosis due to hepatitis B by IFNα-1 and traditional medicine preparation. World J Gastroenterol. 1999;5:267-269. [DOI] |
| 7. | Liu HB, Meng ZD, Ma JC, Han CQ, Zhang YL, Xing ZC, Zhang YW, Liu YZ, Cao HL. A 12 year cohort study on the efficacy of plasma-derived hepatitis B vaccine in rural newborns. World J Gastroenterol. 2000;6:381-383. [DOI] |
| 8. | Wieland SF, Guidotti LG, Chisari FV. Intrahepatic induction of alpha/beta interferon eliminates viral RNA-containing capsids in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. J Virol. 2000;74:4165-4173. [DOI] |
| 9. | Li H, Li RC, Liao SS, Yang JY, Zeng XJ, Wang SS. Persistence of hepatitis B vaccine immune protection and response to hepatitis B booster immunization. World J Gastroenterol. 1998;4:493-496. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 10. | Zhuang L, You J, Tang BZ, Ding SY, Yan KH, Peng D, Zhang YM, Zhang L. Preliminary results of Thymosin-a1versus interferon-α treatment in patients with HBeAg negative and serum HBV DNA positive chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol. 2001;7:407-410. [DOI] |
| 11. | He XS, Huang JF, Chen GH, Fu Q, Zhu XF, Lu MQ, Wang GD, Guan XD. Ortho topic liver transplantation for fulminant hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol. 2000;6:398-399. [DOI] |
| 12. | Zeng XJ, Yang GH, Liao SS, Chen AP, Tan J, Huang ZJ, Li H. Survey of coverage, strategy and cost of hepatitis B vaccination in rural and urban areas of China. World J Gastroenterol. 1999;5:320-323. [DOI] |
| 13. | McClary H, Koch R, Chisari FV, Guidotti LG. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication during schistosoma mansoni infection in transgenic mice. J Exp Med. 2000;192:289-294. [DOI] |
| 14. | Heise T, Guidotti LG, Cavanaugh VJ, Chisari FV. Hepatitis B virus RNA -binding proteins associated with cytokine-induced clearance of viral RNA from the liver of transgenic mice. J Virol. 1999;73:474-481. [PubMed] |
| 15. | Heise T, Guidotti LG, Chisari FV. Characterization of nuclear RNases that cleave hepatitis B virus RNA near the La protein binding site. J Virol. 2001;75:6874-6883. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 16. | Yan JC, Ma JY, Pan BR, Ma LS. Studies on virus hepatitis B in China. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:611-616. |
| 17. | Liu QM, Fu JR, Zhang HQ, Wang FX, Gong ZJ, Zhang RY, Zhang SL. Clinical studies of Chinese drug ganshuning on chronic hepatitis and hepatic fibrosis. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:1096-1098. |
| 18. | Wang FS, Xing LH, Liu MX, Zhu CL, Liu HG, Wang HF, Lei ZY. Dysfunction of peripheral blood dendritic cells from patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. World J Gastroenterol. 2001;7:537-541. [DOI] |
| 19. | Liao SS, Li RC, Li H, Yang JY, Zeng XJ, Gong J, Wang SS, Li YP, Zhang KL. Long term efficacy of plasma-derived hepatitis B vaccine among Chinese children: a 12-year follow up study. World J Gastroenterol. 1999;5:165-166. [DOI] |
| 20. | Hu YP, Hu WJ, Zheng WC, Li JX, Dai DS, Wang XM, Zhang SZ, Yu HY, Sun W, Hao GR. Establishment of transgenic mouse harboring hepatitis B virus (adr subtype) genomes. World J Gastroenterol. 2001;7:111-114. [DOI] |
| 21. | Guidotti LG, Rochford R, Chung J, Shapiro M, Purcell R, Chisari FV. Viral clearance without destruction of infected cells during acute HBV infection. Science. 1999;284:825-829. [DOI] |
| 22. | Tang RX, Gao FG, Zeng LY, Wang YW, Wang YL. Detection of HBV DNA and its existence status in liver tissues and peripheral blood lymphocytes from chronic hepatitis B patients. World J Gastroenterol. 1999;5:359-361. [DOI] |
| 23. | Wang JY, Wang XL, Liu P. Detection of serum TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6 and IL-8 in patients with hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol. 1999;5:38-40. [DOI] |
| 24. | Pasquetto V, Wieland S, Chisari FV. Intracellular hepatitis B virus nucleocapsids survive cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-induced apoptosis. J Virol. 2000;74:9792-9796. [DOI] |
| 25. | Guidotti LG, Borrow P, Brown A, McClary H, Koch R, Chisari FV. Noncyto pathic clearance of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus from the hepatocyte. J Exp Med. 1999;189:1555-1564. [DOI] |
| 26. | Fang DX, Li FQ, Tan WG, Chen HB, Jin HY, Li SQ, Lin HJ, Zhou ZX. Transient expression and antigenic characterization of HBsAg of HBV nt551 A to G mutant. World J Gastroenterol. 1999;5:73-74. [DOI] |
| 27. | Wang Y, Liu H, Zhou Q, Li X. Analysis of point mutation in site 1896 of HBV precore and its detection in the tissues and serum of HCC patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2000;6:395-397. [DOI] |
| 28. | Hu YP, Yao YC, Li JX, Wang XM, Li H, Wang ZH, Lei ZH. The cloning of 3'-truncated preS/S, gene from HBV genomic DNA and its expression in transgenic mice. World J Gastroenterol. 2000;6:734-737. [DOI] |
| 29. | Chen K, Han BG, Ma XK, Zhang HQ, Meng L, Wang GH, Xia F, Song XG, Ling SG. Establishment and preliminery use of hepatitis B virus preS1/2 antigen ass ay. World J Gastroenterol. 1999;5:550-552. [DOI] |
| 30. | Hong Y, Cheng J, Dong J, Li K, Wang L, Wang G, Liu Y. Experimental study on the immune responses in H-2b mice immunized by recombinant HBsAg vaccine and DNA vaccines of HBV envelope genes. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2002;10:137-140. |
| 31. | Han P, Liu Y, Cheng J, Wang G, Lu YY, Li K, Li L. The expression of oncogene c-myc upregulated by c-terminally truncated middle surface protein o f hepatitis B virus. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2002;10:141-144. |
| 32. | Lu YY, Li K, Cheng J, Wang L, Liu Y, Duan HJ, Zhang LX. Cloning and expression of hepatitis B virus X gene in yeast. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2002;10:15-18. |
| 33. | Wu W, Zhang S, Wu YL, Ye J, Xi RP. Relationship between insulin-like growth factorI and liver function and number connection test. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:1391-1394. |
| 34. | Li D, Zhang LJ, Chen ZX, Huang YH, Wang XZ. Effects of TNFα, IL-6 and IL-10 on the development of experimental rat liver fibrosis. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:1242-1245. |
| 35. | He Y, Zhou J, Dou KF. Construction of hepatocyte growth factor expression vector and detection of expression in human hepatocytes. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:1143-1146. |
| 36. | Qin JM, Zhang YD. Expression of eNOS and iNOS in rats of acute liver failure. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:1003-1007. |
| 37. | Han JQ, Hu C, Liu SX, Xiu HM, Xu Z, Hu DR. The mechanism of the Chinese herbal compound in protecting hepatocyte in vitro. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:902-906. |
| 38. | Jiang YG, Wang YM, Li QF. Expression and significance of HLA-DR antigen and heat shock protein 70 in chro nic hepatitis B. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:907-910. |
| 39. | Yan JC, Chen WB, Ma Y, Tian RX, Ding TL, Xu CJ. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta-1 and vascular diseases in hepatitis B. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:751-754. |
| 40. | Zhang XL, Yao XX, Li YJ, Wang LF. Effect of high-dose vitamin C on hepatic function and cell immunity in patients with liver cirrhosis. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:649-652. |
| 41. | Bai Y, Cao ZC, Zhuang JJ, Gou LY, Liu JD, Song YG. Protective effect of phlebotomy in experimental liver damage. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:149-152. |
| 42. | Shi H, Wang FS. Host factors in chronicity of hepatitis B virus infection and their significances in clinic. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zaizhi. 2001;9:66-69. |
| 43. | Lau GK. Hepatitis B infection in China. Clin Liver Dis. 2001;5:361-379. [DOI] |
| 44. | Li J, Tang B. Effect on replication of hepatitis B virus by Chinese traditional medicine. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2000;8:945-946. |
| 45. | Farrell G. Hepatitis be antigen seroconversion: effects of lamivudine alone or in combination with interferon alpha. J Med Virol. 2000;61:374-379. [DOI] |
| 46. | Liu J, McIntosh H, Lin H. Chinese medicinal herbs for chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review. Liver. 2001;21:280-286. [DOI] |
| 47. | Wang JP, Li XH, Zhu Y, Wang AL, Lian JQ, Jia ZS, Xie YM. Detection of serum sIL-2R, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α and lymphocytes subsets, mIL-2R in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2000;8:763-766. |
| 48. | Li CP, Wang KX, Wang J, Pan BR. mIL-2R, T cell subsets & hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:298-300. [DOI] |