Published online Aug 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i32.4878
Peer-review started: May 20, 2020
First decision: June 4, 2020
Revised: June 13, 2020
Accepted: August 9, 2020
Article in press: August 9, 2020
Published online: August 28, 2020
Processing time: 100 Days and 1.7 Hours
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a leading cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. New treatments for HCV revolutionized management and prompted the world health organization to set the goal of viral elimination by 2030. These developments strengthen the need for HCV screening in order to identify asymptomatic carriers prior to development of chronic liver disease and its complications. Different screening strategies have been attempted, most targeting high-risk populations. Previous studies focusing on patients arriving at emergency departments showed a higher prevalence of HCV compared to the general population.
To identify previously undiagnosed HCV carriers among high risk emergency room attendees and link them to care for anti-viral treatment.
In this single center prospective study, persons visiting the emergency department in an urban hospital were screened by a risk factor-specific questionnaire. The risk factors screened for were exposure to blood products or organ transplantation before 1992; origins from countries with high prevalence of HCV; intravenous drug use; human immunodeficiency virus carriers; men who have sex with men; those born to HCV-infected mothers; prior prison time; and chronic kidney disease. Those with at least one risk factor were tested for HCV by serum for HCV antibodies, a novel oral test from saliva (OraQuick®) or both.
Five hundred and forty-one participants had at least one risk factor and were tested for HCV. Eighty four percent of all study participants had only one risk factor. Eighty five percent of participants underwent OraQuick® testing, 34% were tested for serum anti-HCV antibodies, and 25% had both tests. 3.1% of patients (17/541) had a positive result, compared to local population incidence of 1.96%. Of these, 82% were people who inject drugs (current or former), and 64% served time in prison. One patient had a negative HCV-RNA, and two patients died from non-HCV related reasons. On review of past medical records, 12 patients were found to have been previously diagnosed with HCV but were unaware of their carrier state. At 1-year follow-up none of the remaining 14 patients had completed HCV-RNA testing, visited a hepatology clinic or received anti-viral treatment.
Targeted high-risk screening in the emergency department identified undiagnosed and untreated HCV carriers, but did not improve treatment rates. Other strategies need to be developed to improve linkage to care in high risk populations.
Core tip: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a leading cause of chronic liver disease. We attempted to identify previously undiagnosed HCV infected patients by screening high-risk populations arriving in the emergency department and link them to care. Although we identified infected persons at a higher rate than the Israeli population prevalence, none have started treatment despite multiple efforts.
- Citation: Houri I, Horowitz N, Katchman H, Weksler Y, Miller O, Deutsch L, Shibolet O. Emergency department targeted screening for hepatitis C does not improve linkage to care. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(32): 4878-4888
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i32/4878.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i32.4878
Hepatitis C viral (HCV) infection is a leading cause of liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma and liver transplantation worldwide[1]. The heavy burden of disease and the recent marked advances in HCV treatment have led the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare a goal of elimination of viral hepatitis as a major public health threat by 2030[2], and to propose that each country develop a strategy to promote prevention and treatment of viral hepatitis. The goals set were a 30% reduction of new cases of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) and HCV and a 10% reduction of viral hepatitis-associated deaths by 2020, and by 2030 - a 90% reduction of new cases and a 65% reduction of deaths. Many countries have begun implementing programs to that end[3-6].
In order to achieve these goals, two main obstacles need to be overcome. The first is to identify HCV infected persons, and the second is to link them to care. Globally, less than 5% of viral hepatitis (HBV and HCV) carriers are aware of their diagnosis[7]. A study in the United States showed that 50% of patients diagnosed with HCV were unaware of their status[8]. Therefore, in order to achieve the WHO goals, we need to integrate viral hepatitis testing into routine health policies and define priority populations for screening.
The benefits of early detection of HCV are significant, as timely treatment decreases the risk for all liver-related complications, as well as the potential for virus transmission.
Different strategies for identifying these patients have been used[9]. Universal screening was implemented in France and was found to be effective[10]. Other screening programs target high-risk populations, as previous studies have shown that 85%-90% of HCV-infected patients had an identifiable risk factor[11,12]. These included people who inject drugs (PWID), recipients of blood transfusion before 1992 and abnormally elevated liver enzymes. In addition to these risk factors there are population groups with high prevalence of HCV, including dialysis patients, people who have been incarcerated, HIV-infected individuals, men who have sex with men (MSM) and those born in the United Stated between 1945-1965 (“baby-boomers”).
Additionally, screening is recommended for patients with high risk of virus transmission, such as pregnant women.
Worldwide, some programs have focused efforts for HCV screening on patients arriving at the emergency department (ED). The reasoning behind this strategy is mainly the over-representation of at-risk groups in this population, including PWID, immigrants, etc[13,14]. Studies have shown a higher prevalence of HCV among ED patients compared to the general population[15-17]. Furthermore, HCV-infected patients utilize more medical services than non-HCV carriers[13], and have more ED visits[18,19]. The ED often serves as a “safety net” for these vulnerable populations, providing unique access to them[20].
In a single-center United States based study from 1992, 18% of all patients presenting to an inner-city hospital ED were positive for HCV[21]. A study by Hsieh et al[22] from an american urban ED screened all patients arriving at the ED during an 8-wk period. 13.8% of patients had positive anti-HCV antibodies, with 31.3% of them previously undiagnosed. The study estimated that 25% of newly diagnosed patients would not have been screened using risk-/birth-cohort based testing, and suggested a practice of 1-time universal testing for all ED attendees.
A Swiss study from 2007 screened 5000 patients arriving to the ED for various complaints, with an anti-HCV prevalence twice as high as the general population[16]. Finally, a study conducted in tertiary care EDs from Germany screened 28809 patients unselectively for anti-HCV antibodies, with an overall prevalence of positive screening of 2.6%, compared to an estimated 0.4%-0.6% in the German population, and overall positive HCV- polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in 1.6%[17]. Nineteen percent of HCV-RNA positive patients were previously undiagnosed.
All these studies were conducted in the pre-direct acting anti-viral agents (DAA) era and did not assess linkage to care. One study conducted in an urban ED in the United States at 2013 screened “baby boomers” arriving in the ED. Of 102 patients diagnosed with HCV, only 20% attended an initial appointment with a liver specialist[23].
Recently, a study conducted in an ED in Melbourne, Australia was published[24]. In this study, comers to the ED were screened for risk factors and were offered the OraQuick® oral HCV antibody test. Those with positive results had confirmatory testing with HCV-RNA. 34% of participants screened reported at least one risk factor. Of those, 14% had a reactive result on OraQuick®. Among the patients with positive HCV-RNA, 37% commenced treatment and 70% of these obtained a cure.
Data regarding the epidemiology of HCV in Israel is limited. A systematic review by Cornberg et al[25] estimated HCV prevalence in Israel at 1.96% of the population, while prevalence among immigrants from the former Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) was 4%. It was estimated that approximately 27000, or 33% of infected patients were already diagnosed. Risk factors for HCV carrier state in Israel include: immigration from the former USSR; PWID, current or past; reception of blood transfusions before 1992; close contact with infected individuals; and surgery.
In this study, we implemented a screening program in high risk populations attending our ED in order to assess the prevalence of undiagnosed HCV in this population and to analyze linkage to care.
This was a single-center prospective trial. Patients arriving at the ED in Tel-Aviv Medical Center for any cause and their accompanying parties in selected days during March-August 2018 were screened via questionnaire for risk factors for HCV infection. Inclusion criteria were: Ages 18-75, ability to give consent, clinical stability and at least one positive answer for risk factors on the verbal questionnaire. Exclusion criteria were a known HCV diagnosis (as reported on initial screening) and special populations (pregnant women, children). Patients declaring a known HCV diagnosis were immediately offered a referral to the hepatology clinic for further treatment.
The questionnaires were administered by clinicians from our research team who worked in shifts in the ED, additional to ED personnel. Shifts varied in hours during the day, not including night shifts. Non-critical patients and their accompanying parties were approached, and those consenting to participate were screened. Initially, verbal screening was conducted to identify those with risk factors. The verbal questions included country of birth, a known HCV diagnosis, and the different risk factors as in the written questionnaire. Those with at least one positive answer were given a written questionnaire.
The written questionnaire included 9 questions for established national and international risk factors for HCV infection. The risk factors screened for were: Exposure to blood transfusion, blood products or organ transplantation before 1992; those born in countries from the former USSR; current/past IV drug use; HIV carriers; MSM; those born to HCV-infected mothers; prior prison time; and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Additionally, participants were asked of prior knowledge of a diagnosis of HCV.
Those with any positive answer for a risk factor on the questionnaire were tested for HCV.
The study was conducted in compliance with the declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional review board (IRB) (0634-16). All participants screened gave informed consent.
Two screening methods were used. All participants were planned for OraQuick® testing (based on availability of the kit), that detects HCV antibodies in saliva[26]. The OraQuick® is a highly accurate, rapid, point-of-care test for HCV antibodies, with sensitivity of 98.1% in oral fluid and specificity of 100%[27].
Participants who had blood taken in the ED for other reasons also had serology testing for anti-HCV antibodies.
Patients who tested positive for HCV on either screening test were referred to complete HCV-RNA-PCR and HCV genotype testing via healthcare providers.
Multiple attempts at contacting patients testing positive for HCV were made via phone calls to numbers given by the patients at the time of signing informed consent and those in electronic medical records. Contact was also attempted though opioid substitution therapy clinics for 3 patients, and through HIV clinics for 2 patients.
Descriptive analyses were performed for all variables. Continuous data are reported as mean ± SD, and categorical data are presented as percentages. Univariate analyses were used for the comparison of variable's distribution between the study groups. To test differences in continuous variables between two groups the independent samples t-test was used. To test the differences in categorical variables the Pearson Chi-Square test was performed, P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant for all analyses. We used stepwise Logistic Regression analysis for prediction modeling of positive HCV testing according to the risk factors. All statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 25.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, United States). The statistical methods of this study were reviewed by Dr. Liat Deutsch from Tel-Aviv medical center.
Five hundred and forty-one participants had at least one positive answer and formed the study group. Fifty three percent of participants were male. The average age was 47.2 ± 15.3 years (range 19-88). Seventy one percent of participants were patients arriving for care in the ED, while 29% were their accompanying party.
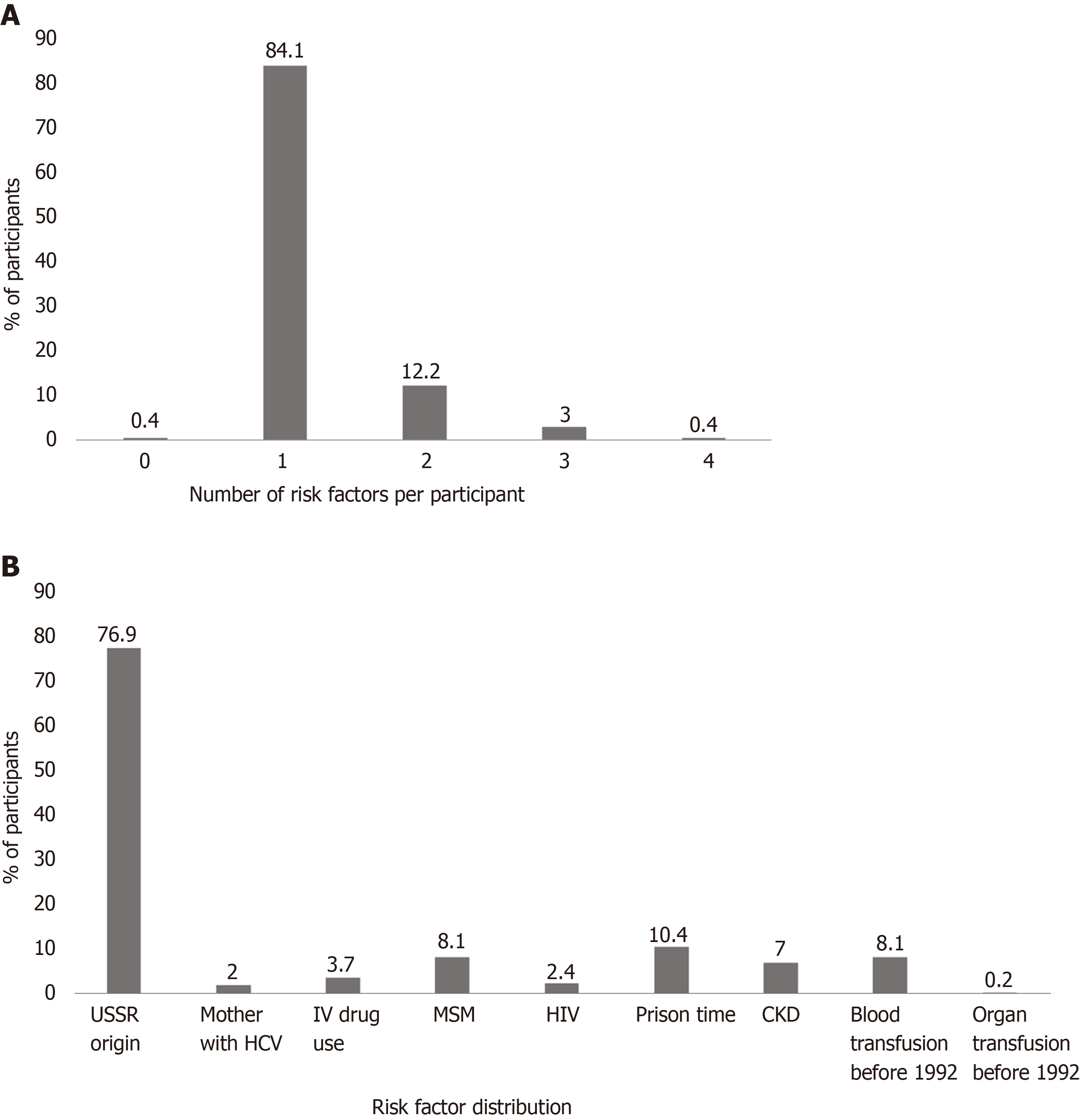
As shown in Figure 1A, most participants had only one risk factor for HCV infection. Figure 1B details the risk factors among the participants. The most common risk factor was immigration from the former USSR (76% of participants).
All participants had at least one HCV diagnostic test performed. All were planned for OraQuick® testing, though only 88% (476/541) underwent the test due to kit availability. Thirty six percent (199/541) of all participants who had blood drawn in the ED for other reasons had serology testing. Twenty five percent (134/541 participants) underwent both tests.
Seventeen participants (3.1% of all screened, CI: 1.8%-5%) were positive for HCV (Table 1). Two participants who had a negative OraQuick® but positive serum anti-HCV had lower antibody levels than other positive participants. One of the two later completed testing for HCV-RNA-PCR which was negative, coinciding with previous reports indicating the sensitivity of the test from oral fluids is lower in non-viremic patients[27,28].
| Patient ID | OraQuick® | anti-HCV | Anti-HCV levels |
| 84 | Positive | ||
| 195 | Positive | ||
| 263 | Positive | Positive | 11 < |
| 267 | Positive | Positive | 11 < |
| 333 | Positive | ||
| 348 | Positive | Positive | 11 < |
| 373 | Positive | Positive | 11 < |
| 374 | Positive | Positive | 11 < |
| 410 | Positive | Positive | 11 < |
| 413 | Negative | Positive | 1.35 |
| 422 | Negative | Positive | 9.67 |
| 424 | Positive | Positive | 11 < |
| 426 | Positive | ||
| 428 | Positive | Positive | 11 < |
| 435 | Positive | ||
| 490 | Positive | 11 < | |
| 515 | Positive | 11 < |
Twelve of the HCV-positive patients had a previous diagnosis of HCV infection. Five of them answered negatively in the initial screening to the question of a known HCV diagnosis, but later reported a known HCV diagnosis in the written questionnaire. In examining prior medical records, we found 7 additional patients who had a previous diagnosis of HCV but were unaware of it. They all had not received anti-viral treatment and were not followed up by a hepatologist.
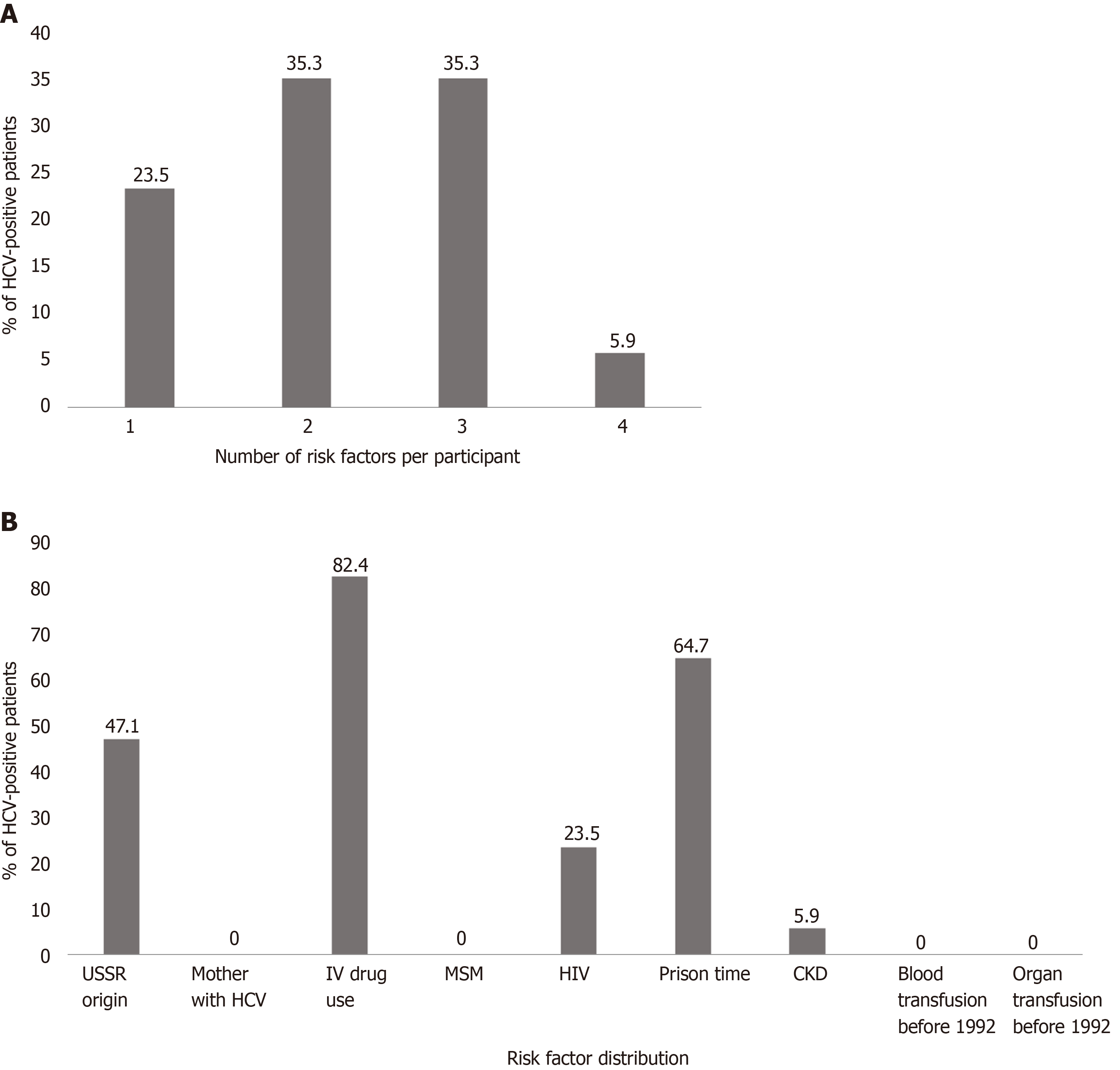
Table 2 compares the characteristics of the anti-HCV positive to negative groups. Most of the patients testing positive for HCV had multiple risk factors (Figure 2A), the most common being IV drug use (82%) and serving time in prison (65%) (Figure 2B). Univariate analysis showed that gender, PWID, HIV carriers, and time served in prison were all associated with positive HCV screening. Patients positive for HCV were less likely to have been born in the former USSR, though this is most probably a selection bias, as the participants were screened based on known risk factors. The only risk factor that remained independently associated with positive HCV screening in the multivariate analysis was PWID (P < 0.001, Table 3).
| HCV negative (% of patients, n = 524) | HCV positive (% of patients, n = 17) | P value | |
| Males | 52 | 93.8 | 0.001 |
| Born in the former USSR | 77.9 | 47.1 | 0.003 |
| PWID | 1.1 | 82.4 | < 0.001 |
| Served time in prison | 8.6 | 64.7 | < 0.001 |
| HIV | 1.7 | 23.5 | < 0.001 |
| MSM | 8.4 | 0.0 | 0.212 |
| Received blood products prior to 1992 | 8.4 | 0.0 | 0.213 |
| Mother with HCV infection | 2.1 | 0.0 | 0.546 |
| Received organ transplant prior to 1992 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.857 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 7.1 | 5.9 | 0.85 |
| Univariate logistic regression | Multivariate logistic regression | |||||
| Variable | Exp (b) | 95%CI | P value | Exp (b) | 95%CI | P value |
| Gender (female vs male) | 0.072 | 0.009-0.55 | 0.011 | 0.578 | 0.043-7.71 | 0.679 |
| PWID (yes vs no) | 402.889 | 91.3-1777.1 | < 0.001 | 188.95 | 33.88-1053.82 | < 0.001 |
| Served time in prison (yes vs no) | 19.515 | 6.89-55.25 | < 0.001 | 4.076 | 0.623-26.67 | 0.143 |
| HIV (yes vs no) | 17.6 | 4.8-64.6 | < 0.001 | 5.32 | 0.242-116.78 | 0.289 |
| Born in the former USSR (yes vs no) | 0.25 | 0.09-0.67 | 0.006 | 0.562 | 0.092-3.42 | 0.532 |
Our cohort did not show increased risk for HCV in CKD patients or those who had received blood products/organ transplant prior to 1992, though this may be due to the small sample size. Interestingly, although the study included 8.5% MSMs, none were found to be HCV positive, suggesting that this risk factor might be less significant than previously assumed.
Among all self-reported PWID’s in the cohort, anti-HCV prevalence was 70% (14/20), while among participants who served time in prison the prevalence was 19.6% (11/56). These data concur with previous publications where among PWID, HCV prevalence ranged from 35%[29] to 75%[25].
Multiple attempts were made to contact patients with positive HCV results. Of the 17 patients found positive in this study, none received anti-viral treatment at the end of follow-up. Two of the patients died from non-liver related diseases. One patient completed a blood test for HCV-RNA-PCR that was negative. Three patients were interested in treatment in initial phone conversations; however, they did not arrive for clinic appointments. Eleven of the patients, mostly PWID or homeless, had no updated contact information and were unreachable.
High-risk targeted HCV screening in the ED identified higher rates of HCV, compared to previously published HCV prevalence rates in the Israeli general population (3.1% compared to 1.96%[25]). More than half of the HCV-positive patients identified in our study had a previous diagnosis, but most were unaware of the diagnosis and none were treated or followed-up in a hepatology clinic.
Linkage to care in this population proved difficult, and despite repeated efforts, none have started anti-viral treatment during 1 year of follow up. Many of the HCV-positive patients were homeless and without correct contact information. Since the results of the screening tests were available usually 24 h after the ED visit, patients had already been discharged by that time. Similar issues were described in studies in other countries[30,31]. One study in an American urban hospital targeted PWID’s for screening at ED visits. Although HCV prevalence was 26% in the individuals tested, only 1/22 was treated at 1 year follow-up[32].
Additionally, all Israeli citizens have medical insurance and access to medical care, thus the ED serves as a “safety net” for extreme cases only.
These findings suggest that though ED screening in Israel may identify HCV infection in high-risk patients, some of whom are otherwise without regular medical care, this does not improve treatment rates.
Screening with OraQuick® had similar results to anti-HCV serum antibodies. Our study design did not allow to accurately assess the performance of the test, though previous publications and the high correlation with serum antibody levels suggests that this is a good alternative for HCV blood testing and may allow quicker response times and better access to difficult-to-screen populations.
The extremely high prevalence of HCV infection among PWID and people who were incarcerated suggests that these populations are an essential and critical target for intervention in order to achieve viral elimination, as shown also in the Australian study[24].
Future avenues for investigation include targeted screening in high-risk populations, conducted in facilities with long-term follow-up to ensure linkage to care, such as opioid substitution therapy clinics, HIV clinics, prisons etc. Additionally, further studies will be needed to address whole-population non-targeted screening in order to assess linkage to care in these populations. Furthermore, efforts are being made to identify previously diagnosed but yet untreated patients and link them to care.
Our study had several limitations. This was a single-center study in an urban city hospital that has a relatively large population of high-risk patients. Thus, the relatively high prevalence of HCV may not be indicative of other EDs in Israel. Additionally, risk factors were patient-reported and thus are prone to biases related to this method. Only patients who were clinically stable and able to give informed consent were included, thus excluding high-risk groups, such as intoxicated patients, those with mental health issues, etc. Finally, the number of HCV-positive patients was low.
In conclusion, although we identified more HCV carriers than the expected population rate, ED targeted-screening of high-risk patients did not improve anti-viral treatment rates.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a leading cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. In the last few years, new treatments for HCV have revolutionized management of this infection.
A major obstacle to viral elimination is identifying asymptomatic infected patients. Most screening strategies focus on high-risk patients, while others target the general population. Prior studies showed that HCV prevalence in emergency department attendees is higher than the general population.
A single center prospective study, aimed at identifying undiagnosed HCV carriers among high risk emergency room attendees and linking them to anti-viral treatment.
Persons visiting the emergency department were screened by a 9-question risk factor-specific questionnaire. Those with at least one risk factor were tested for HCV with blood and saliva antibody tests.
Five hundred and forty-one participants were tested for HCV. Eighty five percent of participants underwent saliva testing, 34% were tested for serum antibodies, and 25% had both tests. 17 patients (3.1%) had a positive result, compared to local population incidence of 1.96%. Eighty two percent of patients with positive HCV were people who inject drugs, and 64% served time in prison. Twelve patients were found to have been previously diagnosed with HCV but were unaware of the diagnosis. At 1-year follow-up, only one patient completed HCV-RNA testing and was found negative. None of the remaining patients completed the recommended testing, visited a hepatology clinic or received anti-viral treatment.
Targeted high-risk screening in the emergency department identified undiagnosed and untreated HCV carriers, but did not improve treatment rates.
This study suggests that in order to achieve viral elimination, other avenues need to be explored to find a framework that will enable treatment completion for this population.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited Manuscript
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Israel
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Asghar K S-Editor: Zhang H L-Editor: A P-Editor: Ma YJ
| 1. | Lavanchy D. Evolving epidemiology of hepatitis C virus. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17:107-115. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 919] [Cited by in RCA: 945] [Article Influence: 67.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 2. | WHO. Combating hepatitis B and C to reach elimination by 2030. [cited 18 May 2019]. In: World Health Organization [Internet]. Available from: http://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/hep-elimination-by-2030-brief/en/. |
| 3. | Dore GJ, Ward J, Thursz M. Hepatitis C disease burden and strategies to manage the burden (Guest Editors Mark Thursz, Gregory Dore and John Ward). J Viral Hepat. 2014;21 Suppl 1:1-4. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in RCA: 80] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Wedemeyer H, Duberg AS, Buti M, Rosenberg WM, Frankova S, Esmat G, Örmeci N, Van Vlierberghe H, Gschwantler M, Akarca U, Aleman S, Balık I, Berg T, Bihl F, Bilodeau M, Blasco AJ, Brandão Mello CE, Bruggmann P, Calinas F, Calleja JL, Cheinquer H, Christensen PB, Clausen M, Coelho HS, Cornberg M, Cramp ME, Dore GJ, Doss W, El-Sayed MH, Ergör G, Estes C, Falconer K, Félix J, Ferraz ML, Ferreira PR, García-Samaniego J, Gerstoft J, Giria JA, Gonçales FL, Guimarães Pessôa M, Hézode C, Hindman SJ, Hofer H, Husa P, Idilman R, Kåberg M, Kaita KD, Kautz A, Kaymakoglu S, Krajden M, Krarup H, Laleman W, Lavanchy D, Lázaro P, Marinho RT, Marotta P, Mauss S, Mendes Correa MC, Moreno C, Müllhaupt B, Myers RP, Nemecek V, Øvrehus AL, Parkes J, Peltekian KM, Ramji A, Razavi H, Reis N, Roberts SK, Roudot-Thoraval F, Ryder SD, Sarmento-Castro R, Sarrazin C, Semela D, Sherman M, Shiha GE, Sperl J, Stärkel P, Stauber RE, Thompson AJ, Urbanek P, Van Damme P, van Thiel I, Vandijck D, Vogel W, Waked I, Weis N, Wiegand J, Yosry A, Zekry A, Negro F, Sievert W, Gower E. Strategies to manage hepatitis C virus (HCV) disease burden. J Viral Hepat. 2014;21 Suppl 1:60-89. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 146] [Cited by in RCA: 146] [Article Influence: 13.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Younossi Z, Papatheodoridis G, Cacoub P, Negro F, Wedemeyer H, Henry L, Hatzakis A. The comprehensive outcomes of hepatitis C virus infection: A multi-faceted chronic disease. J Viral Hepat. 2018;25 Suppl 3:6-14. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Papatheodoridis GV, Hatzakis A, Cholongitas E, Baptista-Leite R, Baskozos I, Chhatwal J, Colombo M, Cortez-Pinto H, Craxi A, Goldberg D, Gore C, Kautz A, Lazarus JV, Mendão L, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Razavi H, Schatz E, Tözün N, van Damme P, Wedemeyer H, Yazdanpanah Y, Zuure F, Manns MP. Hepatitis C: The beginning of the end-key elements for successful European and national strategies to eliminate HCV in Europe. J Viral Hepat. 2018;25 Suppl 1:6-17. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | WHO. Global health sector strategy on viral hepatitis 2016-2021. [cited 18 May 2019]. In: World Health Organization [Internet]. Available from: http://www.who.int/hepatitis/strategy2016-2021/ghss-hep/en/. |
| 8. | Spradling PR, Rupp L, Moorman AC, Lu M, Teshale EH, Gordon SC, Nakasato C, Boscarino JA, Henkle EM, Nerenz DR, Denniston MM, Holmberg SD; Chronic Hepatitis Cohort Study Investigators. Hepatitis B and C virus infection among 1.2 million persons with access to care: factors associated with testing and infection prevalence. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;55:1047-1055. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 132] [Cited by in RCA: 138] [Article Influence: 10.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on the Prevention and Control of Viral Hepatitis Infection. Hepatitis and Liver Cancer: A National Strategy for Prevention and Control of Hepatitis B and C. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US). Cited 15 July 2019. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK220039/. |
| 10. | Deuffic-Burban S, Huneau A, Verleene A, Brouard C, Pillonel J, Le Strat Y, Cossais S, Roudot-Thoraval F, Canva V, Mathurin P, Dhumeaux D, Yazdanpanah Y. Assessing the cost-effectiveness of hepatitis C screening strategies in France. J Hepatol. 2018;69:785-792. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 48] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Armstrong GL, Wasley A, Simard EP, McQuillan GM, Kuhnert WL, Alter MJ. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1999 through 2002. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:705-714. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1484] [Cited by in RCA: 1465] [Article Influence: 77.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Chou R, Cottrell EB, Wasson N, Rahman B, Guise JM. Screening for hepatitis C virus infection in adults: a systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med. 2013;158:101-108. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 67] [Cited by in RCA: 65] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Minassian A, Vilke GM, Wilson MP. Frequent emergency department visits are more prevalent in psychiatric, alcohol abuse, and dual diagnosis conditions than in chronic viral illnesses such as hepatitis and human immunodeficiency virus. J Emerg Med. 2013;45:520-525. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 50] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Woolard R, Degutis LC, Mello M, Rothman R, Cherpitel CJ, Post LA, Hirshon JM, Haukoos JS, Hungerford DW. Public health in the emergency department: surveillance, screening, and intervention--funding and sustainability. Acad Emerg Med. 2009;16:1138-1142. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Orkin C, Leach E, Flanagan S, Wallis E, Ruf M, Foster GR, Tong CY. High prevalence of hepatitis C (HCV) in the emergency department (ED) of a London hospital: should we be screening for HCV in ED attendees? Epidemiol Infect. 2015;143:2837-2840. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Russmann S, Dowlatshahi EA, Printzen G, Habicht S, Reichen J, Zimmermann H. Prevalence and associated factors of viral hepatitis and transferrin elevations in 5036 patients admitted to the emergency room of a Swiss university hospital: cross-sectional study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2007;7:5. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Vermehren J, Schlosser B, Domke D, Elanjimattom S, Müller C, Hintereder G, Hensel-Wiegel K, Tauber R, Berger A, Haas N, Walcher F, Möckel M, Lehmann R, Zeuzem S, Sarrazin C, Berg T. High prevalence of anti-HCV antibodies in two metropolitan emergency departments in Germany: a prospective screening analysis of 28,809 patients. PLoS One. 2012;7:e41206. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Thakarar K, Morgan JR, Gaeta JM, Hohl C, Drainoni M-L. Predictors of Frequent Emergency Room Visits among a Homeless Population. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124552. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Dibonaventura MD, Yuan Y, Lescrauwaet B, L'italien G, Liu GG, Kamae I, Mauskopf JA. Multicountry burden of chronic hepatitis C viral infection among those aware of their diagnosis: a patient survey. PLoS One. 2014;9:e86070. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Rhodes KV, Gordon JA, Lowe RA. Preventive care in the emergency department, Part I: Clinical preventive services--are they relevant to emergency medicine? Society for Academic Emergency Medicine Public Health and Education Task Force Preventive Services Work Group. Acad Emerg Med. 2000;7:1036-1041. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 131] [Cited by in RCA: 130] [Article Influence: 5.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Kelen GD, Green GB, Purcell RH, Chan DW, Qaqish BF, Sivertson KT, Quinn TC. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C in emergency department patients. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:1399-1404. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 195] [Cited by in RCA: 206] [Article Influence: 6.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Hsieh YH, Rothman RE, Laeyendecker OB, Kelen GD, Avornu A, Patel EU, Kim J, Irvin R, Thomas DL, Quinn TC. Evaluation of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Recommendations for Hepatitis C Virus Testing in an Urban Emergency Department. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62:1059-1065. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 59] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Galbraith JW, Franco RA, Donnelly JP, Rodgers JB, Morgan JM, Viles AF, Overton ET, Saag MS, Wang HE. Unrecognized chronic hepatitis C virus infection among baby boomers in the emergency department. Hepatology. 2015;61:776-782. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 97] [Cited by in RCA: 104] [Article Influence: 10.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Hutton J, Doyle J, Zordan R, Weiland T, Cocco A, Howell J, Iser S, Snell J, Fry S, New K, Sloane R, Jarman M, Phan D, Tran S, Pedrana A, Williams B, Johnson J, Glasgow S, Thompson A. Point-of-care Hepatitis C virus testing and linkage to treatment in an Australian inner-city emergency department. Int J Drug Policy. 2019;72:84-90. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Cornberg M, Razavi HA, Alberti A, Bernasconi E, Buti M, Cooper C, Dalgard O, Dillion JF, Flisiak R, Forns X, Frankova S, Goldis A, Goulis I, Halota W, Hunyady B, Lagging M, Largen A, Makara M, Manolakopoulos S, Marcellin P, Marinho RT, Pol S, Poynard T, Puoti M, Sagalova O, Sibbel S, Simon K, Wallace C, Young K, Yurdaydin C, Zuckerman E, Negro F, Zeuzem S. A systematic review of hepatitis C virus epidemiology in Europe, Canada and Israel. Liver Int. 2011;31 Suppl 2:30-60. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 301] [Cited by in RCA: 287] [Article Influence: 20.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Cha YJ, Park Q, Kang ES, Yoo BC, Park KU, Kim JW, Hwang YS, Kim MH. Performance evaluation of the OraQuick hepatitis C virus rapid antibody test. Ann Lab Med. 2013;33:184-189. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 61] [Article Influence: 5.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Lee SR, Kardos KW, Schiff E, Berne CA, Mounzer K, Banks AT, Tatum HA, Friel TJ, Demicco MP, Lee WM, Eder SE, Monto A, Yearwood GD, Guillon GB, Kurtz LA, Fischl M, Unangst JL, Kriebel L, Feiss G, Roehler M. Evaluation of a new, rapid test for detecting HCV infection, suitable for use with blood or oral fluid. J Virol Methods. 2011;172:27-31. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 77] [Cited by in RCA: 81] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Pallarés C, Carvalho-Gomes Â, Hontangas V, Conde I, Di Maira T, Aguilera V, Benlloch S, Berenguer M, López-Labrador FX. Performance of the OraQuick Hepatitis C virus antibody test in oral fluid and fingerstick blood before and after treatment-induced viral clearance. J Clin Virol. 2018;102:77-83. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Loebstein R, Mahagna R, Maor Y, Kurnik D, Elbaz E, Halkin H, Olchovsky D, Ezra D, Almog S. Hepatitis C, B, and human immunodeficiency virus infections in illicit drug users in Israel: prevalence and risk factors. Isr Med Assoc J. 2008;10:775-778. [PubMed] |
| 30. | White DA, Anderson ES, Pfeil SK, Trivedi TK, Alter HJ. Results of a Rapid Hepatitis C Virus Screening and Diagnostic Testing Program in an Urban Emergency Department. Ann Emerg Med. 2016;67:119-128. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 52] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Franco RA, Overton ET, Tamhane AR, Forsythe JM, Rodgers JB, Schexnayder JK, Guthrie D, Thogaripally S, Zinski A, Saag MS, Mugavero MJ, Wang HE, Galbraith JW. Characterizing Failure to Establish Hepatitis C Care of Baby Boomers Diagnosed in the Emergency Department. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016;3:ofw211. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Anderson ES, Pfeil SK, Deering LJ, Todorovic T, Lippert S, White DA. High-impact hepatitis C virus testing for injection drug users in an urban ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34:1108-1111. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |