Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2012; 18(11): 1191-1201
Published online Mar 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i11.1191
Published online Mar 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i11.1191
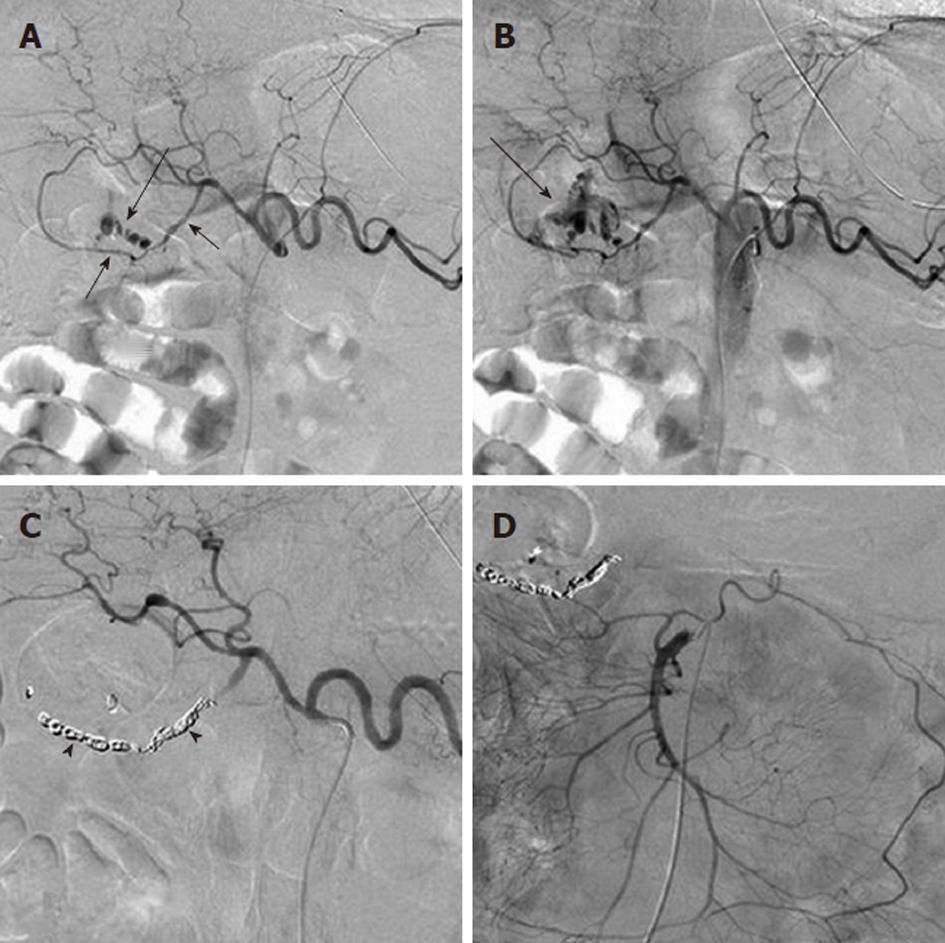
Figure 3 Angiographic diagnosis and transcatheter treatment of duodenal hemorrhage.
A: Celiac digital subtraction angiography (DSA) arteriogram obtained in a patient with copious bleeding seen endoscopically in the duodenum shows focal contrast extravasation (black arrow) arising from the gastroduodenal artery (GDA); B: An image slightly later in the arterial phase of the DSA shows increasing extravasation (black arrow); C: The GDA was successfully coil embolized using microcoils (black arrowheads) through a microcatheter; D: An superior mesenteric artery DSA arteriogram was performed after the coil embolization in order to exclude any additional contribution to the duodenal hemorrhage from the pancreaticoduodenal arcade, as the duodenum has a rich collateral blood supply.
- Citation: Walker TG, Salazar GM, Waltman AC. Angiographic evaluation and management of acute gastrointestinal hemorrhage. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(11): 1191-1201
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i11/1191.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i11.1191