Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 15, 2003; 9(9): 1935-1939
Published online Sep 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.1935
Published online Sep 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.1935
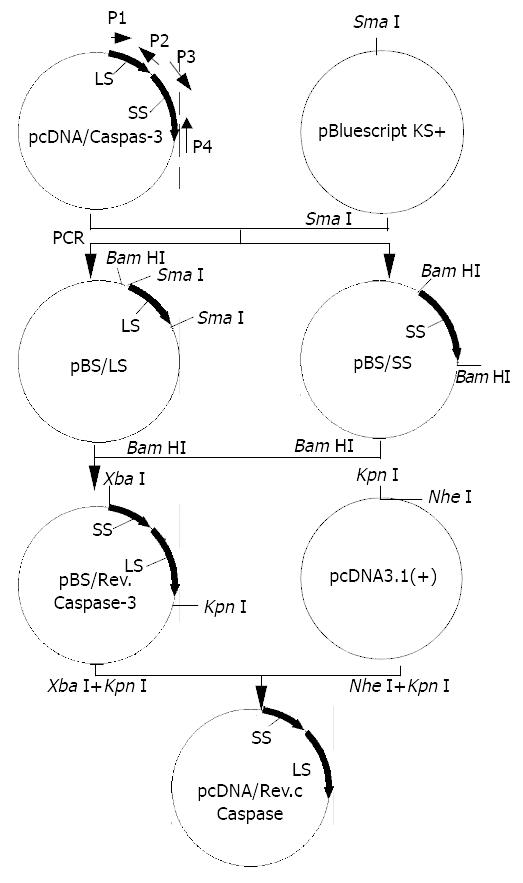
Figure 1 Schematic map of constructions of recombinant Caspases-3 and eukaryotic expression plasmid pcDNA/Rev-Caspases-3.
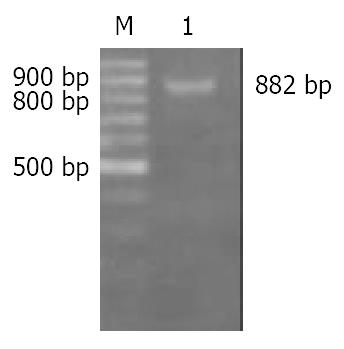
Figure 2 Identification of plasmid pBS/Rev-Caspase-3 by PCR with SS-forward and LS-reverse as primers.
M: 100 bp ladder DNA marker, 1: PCR product, 882 bp.
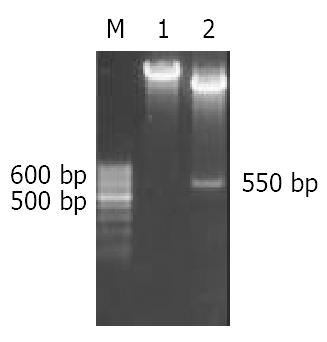
Figure 3 Enzyme digestion analysis of plasmid pcDNA/Rev-Caspase-3.
M: 100 bp ladder DNA marker, 1: pcDNA/Rev-Caspase-3 cut with Stu I, 2: pcDNA/Rev-Caspase-3 cut with
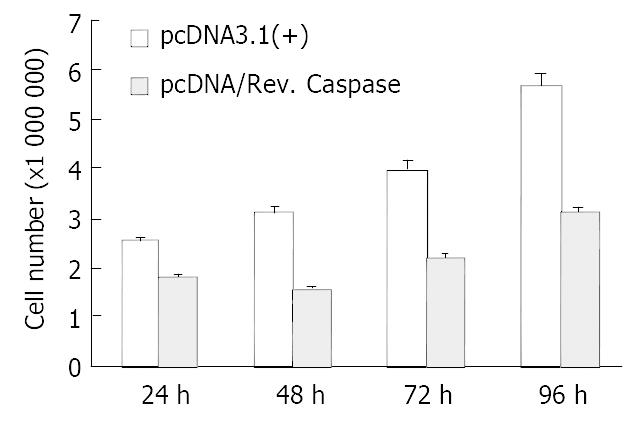
Figure 4 Comparison of cell count between SGC7901 cells trans-fected with pcDNA3.
1 (+) and pcDNA/Rev. Caspase.
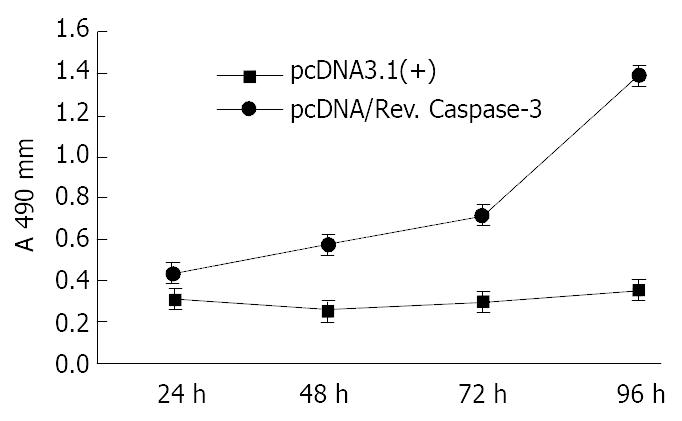
Figure 5 Comparison of MTT assays between SGC7901 cells transfected with pcDNA3.
1 (+) and pcDNA/Rev.Caspase-3.
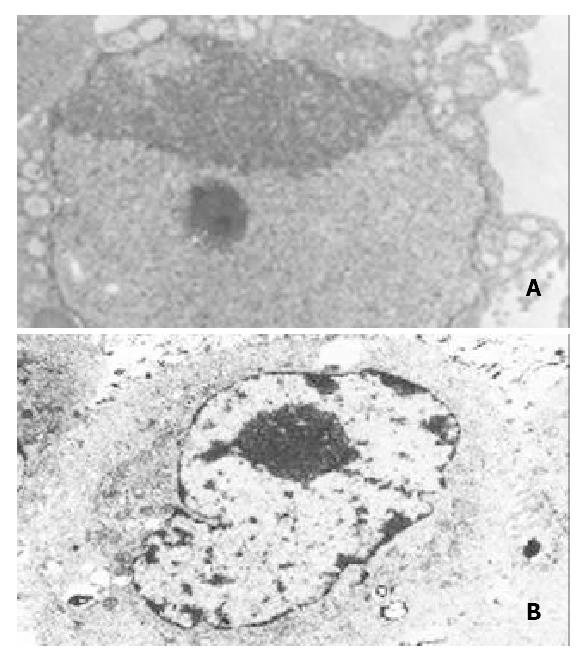
Figure 6 Electron microscopy of SGC7901 cells transfected with pcDNA3.
1 (+) or pcDNA/Rev.Caspases-3. A: SGC7901 trans-fected with pcDNA/Rev. Caspases-3. Notice the chromatin condensation, crescent formation, original margination (× 5000); B: SGC7901 transfected with pcDNA3.1 (+), Notice no characteristics of apoptosis (× 5000).
- Citation: Fu YG, Qu YJ, Wu KC, Zhai HH, Liu ZG, Fan DM. Apoptosis-inducing effect of recombinant Caspase-3 expressed by constructed eukaryotic vector on gastric cancer cell line SGC7901. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(9): 1935-1939
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i9/1935.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.1935