Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 15, 2003; 9(6): 1273-1277
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1273
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1273
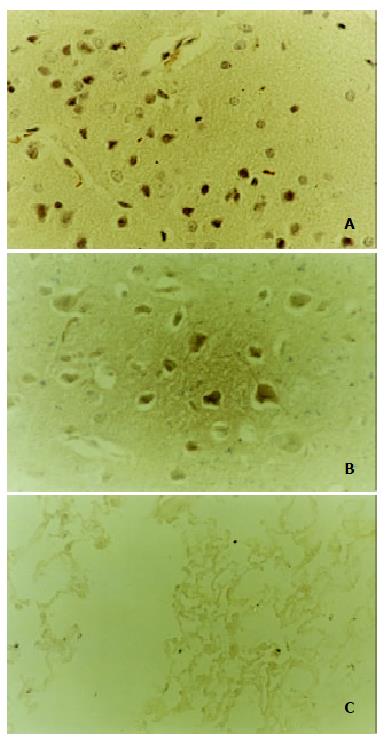
Figure 1 Appearance of positive and negative control tissue section for detecting in situ expression of CCK-AR and CCK-BR gene by in situ RT-PCR.
(A) In situ expression of CCK-BR gene in the brain of SD rats (× 400); (B) In situ expression of CCK-AR gene in the brain of SD rats (× 400); (C) Negative control section from the lung tissue of SD rats (× 200).
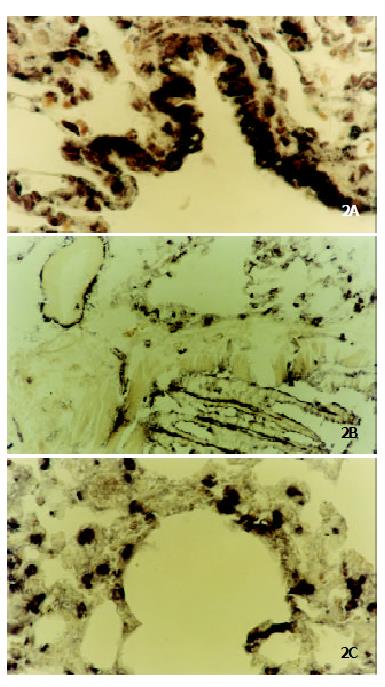
Figure 2 Localization of CCK-BR gene in the lung tissues of SD rats by in situ RT-PCR (× 400).
(A) Expression of CCK-BR gene in bronchial mucosal cells; (B) Expression of CCK-BR gene in vascular endothelial cells; (C) Expression of CCK-BR gene in macrophages and alveolar epithelial cells.
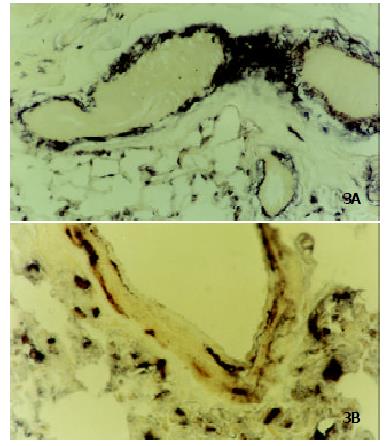
Figure 3 Localization of CCK-BR mRNA in rat lung tissues by in situ hybridization.
(A) Expression of CCK-BR gene in vascular endothelial cells (× 100); (B) Expression of CCK-BR gene in vascular endothelial cells and macrophages (× 400).
Figure 4 In situ expression of CCK-AR gene in the lung tissues of SD rats, detected by in situ RT-PCR (× 400).
(A) Expression of CCK-AR gene in vascular endothelial cells; (B) Expression of CCK-AR gene in bronchial mucosal cells and macrophages; (C)Expression of CCK-AR gene in alveolar epithelial cells.
Figure 5 No positive signal of CCK-AR gene was detected in lung tissues by in situ hybridization (× 200).
- Citation: Cong B, Li SJ, Ling YL, Yao YX, Gu ZY, Wang JX, You HY. Expression and cell-specific localization of cholecystokinin receptors in rat lung. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(6): 1273-1277
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i6/1273.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1273