Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 15, 2003; 9(6): 1246-1250
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1246
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1246
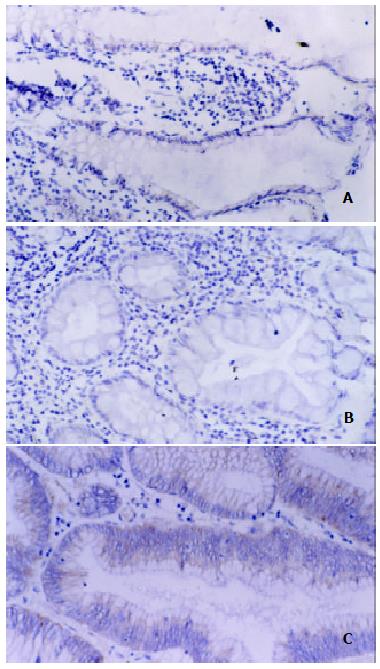
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical analysis for iNOS protein in ACF.
(A) weak staining was observed in the cytoplasm of nonhyperplastic ACF. (SP method, × 200). (B) weak staining was observed in the cytoplasm of hyperplastic ACF. (SP method, × 200). (C) strong staining was observed in the cytoplasm of dysplastic ACF. (SP method, × 200).
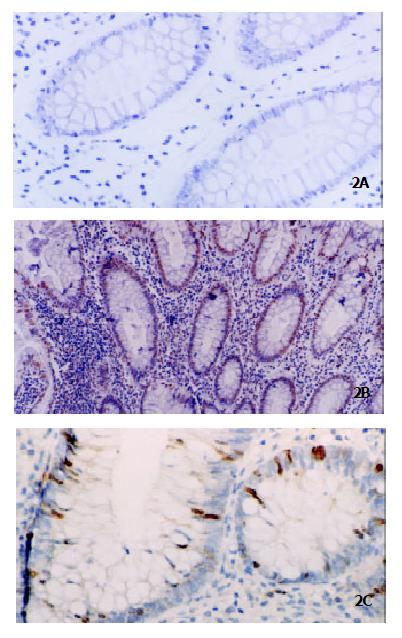
Figure 2 Histochemical detection of apoptosis by TUNEL in ACF.
Few apoptotic cells were detected in nonhyperplastic ACF (Panel A, original magnification × 200), and more apoptotic cells were detected in hyperplastic ACF (Panel B, original magnification × 100) whereas they decreased significantly after transition to dysplastic ACF (Panel C, original magnification × 200).
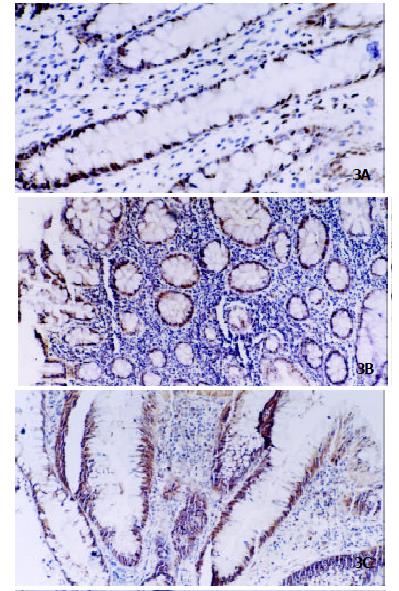
Figure 3 Immunohistochemistry of PCNA protein in ACF.
PCNA expression was gradually increased from nonhyperplastic ACF (Panel A, original magnification × 200), hyperplastic ACF (Panel B, original magnification × 100) to dysplastic ACF (Panel C, original magnification × 100).
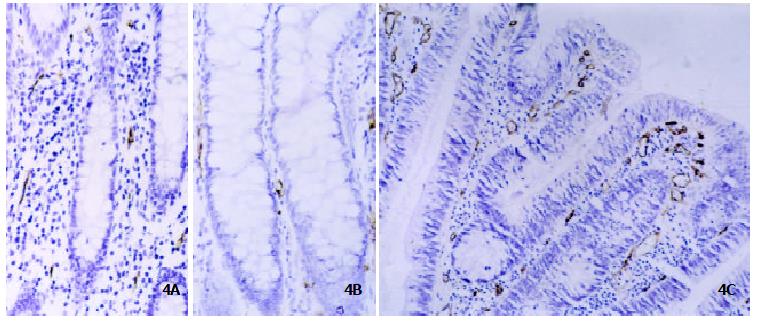
Figure 4 Immunohistochemistry of CD34 protein in ACF.
MVD determined by anti-CD34 antibody was low in nonhyperplastic ACF (Panel A, original magnification × 200) and hyperplastic ACF (Panel B, original magnification × 200) whereas significantly increased in dysplastic ACF (Panel C, original magnification × 200).
- Citation: Xu MH, Deng CS, Zhu YQ, Lin J. Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in aberrant crypt foci-adenoma-carcinoma sequence. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(6): 1246-1250
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i6/1246.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1246