Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. May 15, 2003; 9(5): 1045-1050
Published online May 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i5.1045
Published online May 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i5.1045
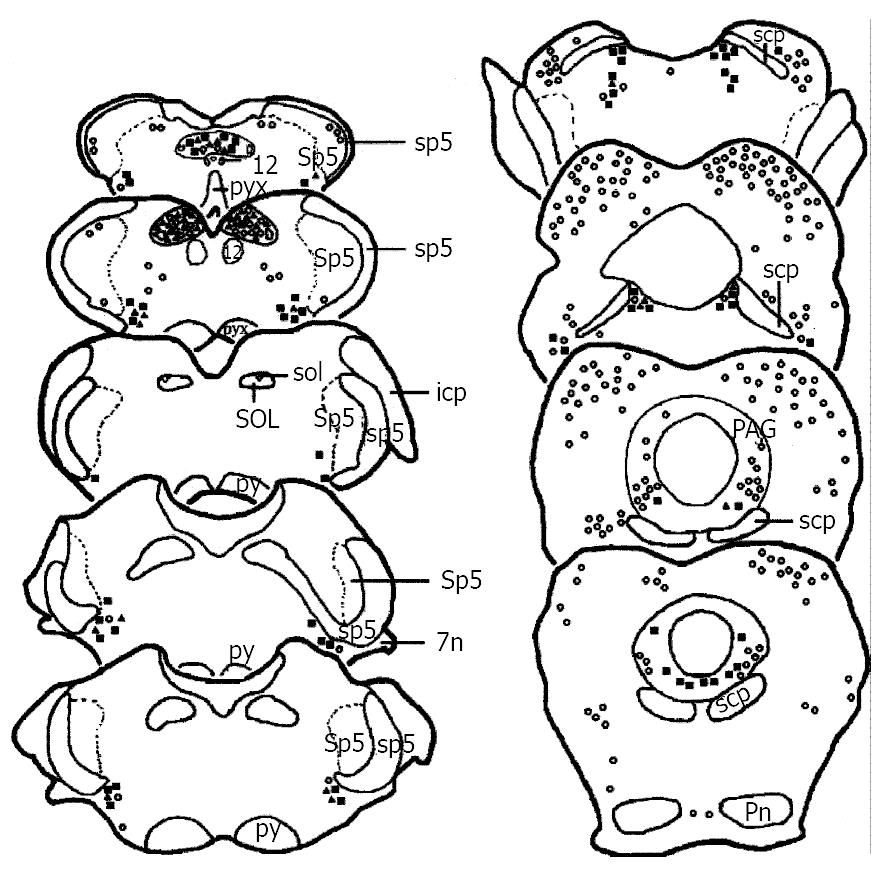
Figure 1 Drawing of the brainstem areas showing the distribution of TH, Fos and TH/Fos immunoreactive neurons after visceral noxious stimulation.
Each■represents three TH-ir neurons. Each○represents five Fos-ir neurons. Each▲represents one TH/Fos double-labeled neuron. Abbreviations: 12: hypoglossal nuclei; 7n: facial nerve or its root; icp: inferior cerebellar peduncle; PAG: the midbrain periaqueductal gray; Pn: pontine nuclei; py: pyramidal tract; pyx: pyramidal decussation; scp: superior cerebellar peduncle; sol: solitary trace; SOL: solitary trace nuclei; sp5: spinal trigeminal tract; Sp5: spinal trigeminal nuclei.
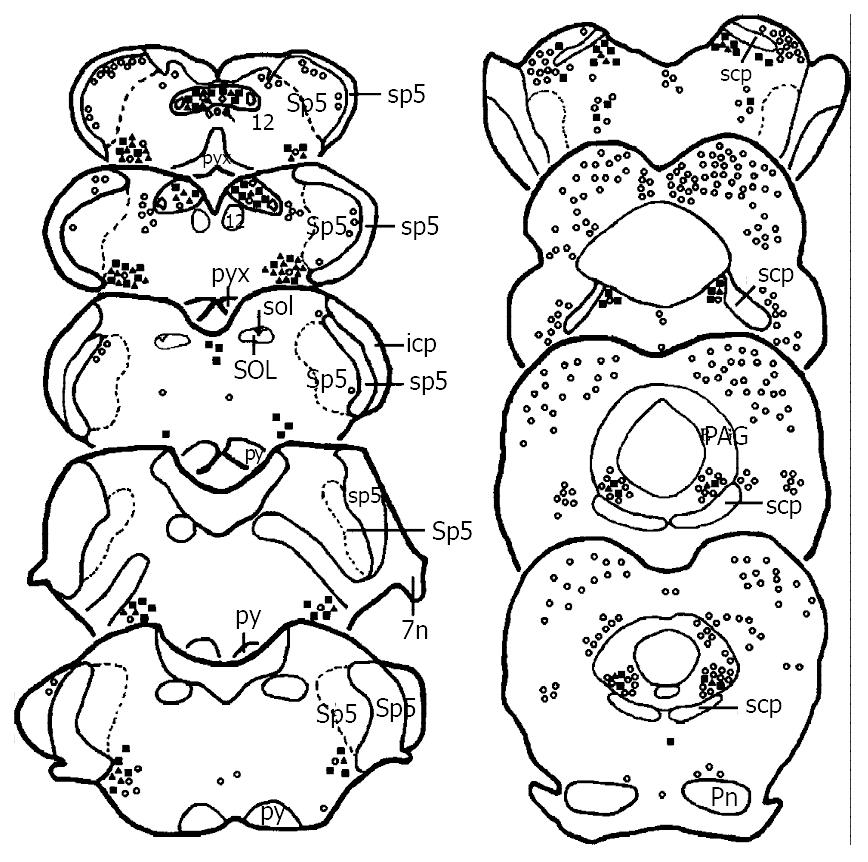
Figure 2 Drawing of the brainstem areas showing the distribution of TH (■), Fos (○) and TH/Fos (▲) immunoreactive neurons after subcutaneous noxious stimulation on the left forepaw.
The ratios for each marker to present the number of TH, Fos and TH/Fos immunoreactive neurons and the abbreviations are the same as Figure 1.
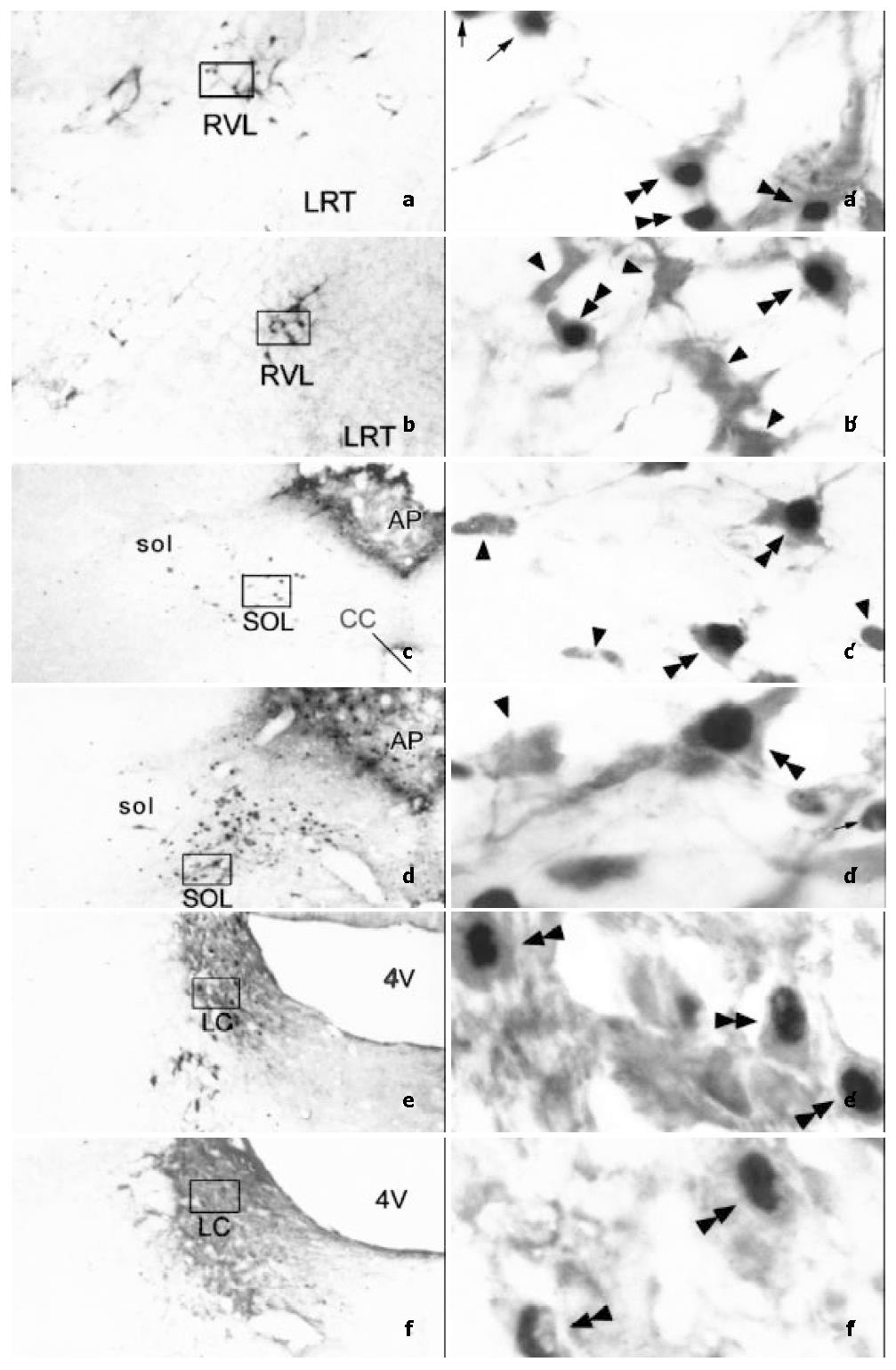
Figure 3 Photomicrographs showing the distribution and morphological characteristics of TH-ir neurons (arrowheads), Fos-ir neurons (arrows) and TH/Fos double-labeled neurons (double arrowheads) in SOL (a, a’ and b, b’), RVL (c, c’ and d, d’) and LC (e, e’ and f, f’).
a, a’, c, c’ and e, e’ were taken from visceral noxious stimulating rats, while b, b’, d, d’ and f, f’ were taken from subcutaneous noxious stimulating rats, respectively. a, b, c, d, e and f are lower magnification photomicrograph (original magnification × 100). a’, b’, c’, d’, e’ and f’ are higher magnification photomicrograph (original magnification × 1000) of the rectangle in a, b, c, d, e and f, respectively. Abbreviations: 4V: The fourth ventricle. cc: Central canal. LC: Locus coeruleus. LRT: Lateral reticular nucleus. RVL: Rostroventrolateral reticular nucleus. sol: Solitary tract. SOL: Solitary tract nucleus.
- Citation: Han F, Zhang YF, Li YQ. Fos expression in tyrosine hydroxylase-containing neurons in rat brainstem after visceral noxious stimulation: an immunohistochemical study. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(5): 1045-1050
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i5/1045.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i5.1045