Copyright
©The Author(s) 2001.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 15, 2001; 7(5): 642-646
Published online Oct 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i5.642
Published online Oct 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i5.642
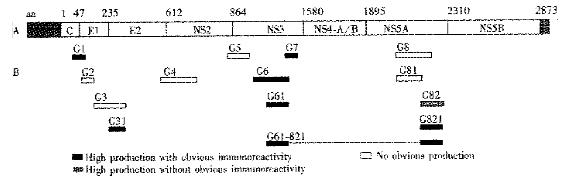
Figure 1 Schematic representation of HGV genome and expressed proteins.
A: Putative genomic organization of HGV CH strain; B: Fragments expressed from the HGV CH strain polyprotein.
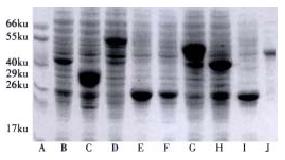
Figure 2 Expression of the recombinant HGV proteins in E.
coli analyzed by SDS-PAGE. A. Molecular mass standard; B.G1; C.G31; D.G6; E.G61; F.G61 in soluble form; G.G7; H.G82; I.G821; J.G61-821
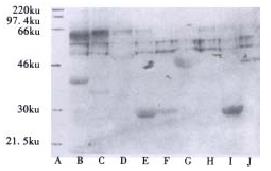
Figure 3 Western blot analysis of expressed recombinant HGV proteins.
A. Molecular mass standard; B.G1; C.G31; D.G6; E.G61 F.G61 in soluble form; G.G7; H.G82; I.G821; J.G61-821
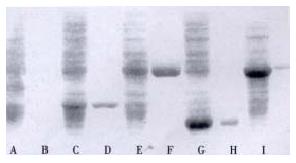
Figure 4 SDS-PAGE Analysis of purified recombinant HGV proteins.
Lane designations refer to purified HGV proteins or corresponding E. coli lysates: A.G1; B.purified G1; C.G31; D.purified G31; E.G61; F.purified G61; G.G821; H.purified G821; I.G61:821; J.purified G61-821
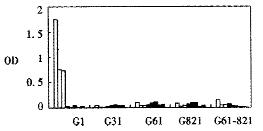
Figure 5 ELISA results of purified recombinant antigens.
□ Positive sera ■ Negative sera
- Citation: Xia NS, Yang HJ, Zhang J, Lin CQ, Wang YB, Wang J, Zhan MY, Ng M. Prokaryotical expression of structural and non-structural proteins of hepatitis G virus. World J Gastroenterol 2001; 7(5): 642-646
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v7/i5/642.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v7.i5.642