Copyright
©The Author(s) 2000.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 15, 2000; 6(2): 281-283
Published online Apr 15, 2000. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i2.281
Published online Apr 15, 2000. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i2.281
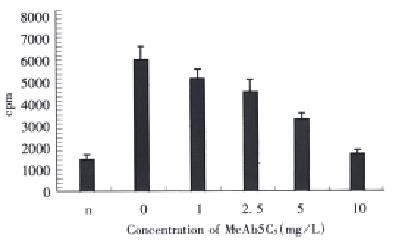
Figure 1 Neutralization of 5C5 to the VEGF-induced HUVEC growth.
n: no VEGF or antibody added, 0.10: VEGF 2 mg/L and antibody 5C5 in various concentration were added.
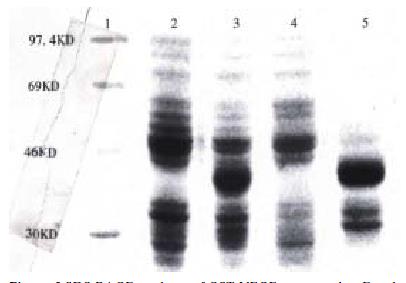
Figure 2 RT-PCR of VEGF121 cDNA and identific ation of recombinant PGEX2T-VEGF.
1: 585/985 bp DNA marker, 2: PCR product of VEGF from MGC803 cells, 3: PCR product of VEGF from HUVEC, 4: PGEX2T-VEGF digested with Bam-H I/Eco-R I.
Figure 3 SDS-PAGE analysis of GST-VEGF expressed in E.
coli XL-1 blue-1. Standards of protei nmolecular weight, 2. Total proteins from bacterial transformed with PGEX2T-VEGF121 without induced IPTG, 3. Proteins from bacterial induced by IPTG, 4. Protein pellet of bacterial lysis without induced IPTG, 5. Protein pellet of bacterial lysis induced by IPTG.
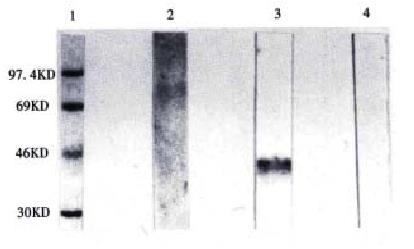
Figure 4 Western blot analysis of the bacterial expr essed GST-VEGF121 by 5C5.
1. Standards of protei nmolecular weight, 2. Uninduced bacterial protein treated with 5C5, 3. Induced bacterial protein treated with 5C5, 4. Induced bacterial protein treated with normal mouse IgG.
- Citation: Tian XJ, Wu J, Meng L, Dong ZW, Shou CC. Expression of VEGF121 in gastric carcinoma MGC803 cell line. World J Gastroenterol 2000; 6(2): 281-283
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v6/i2/281.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v6.i2.281