Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2025; 31(31): 105229
Published online Aug 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i31.105229
Published online Aug 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i31.105229
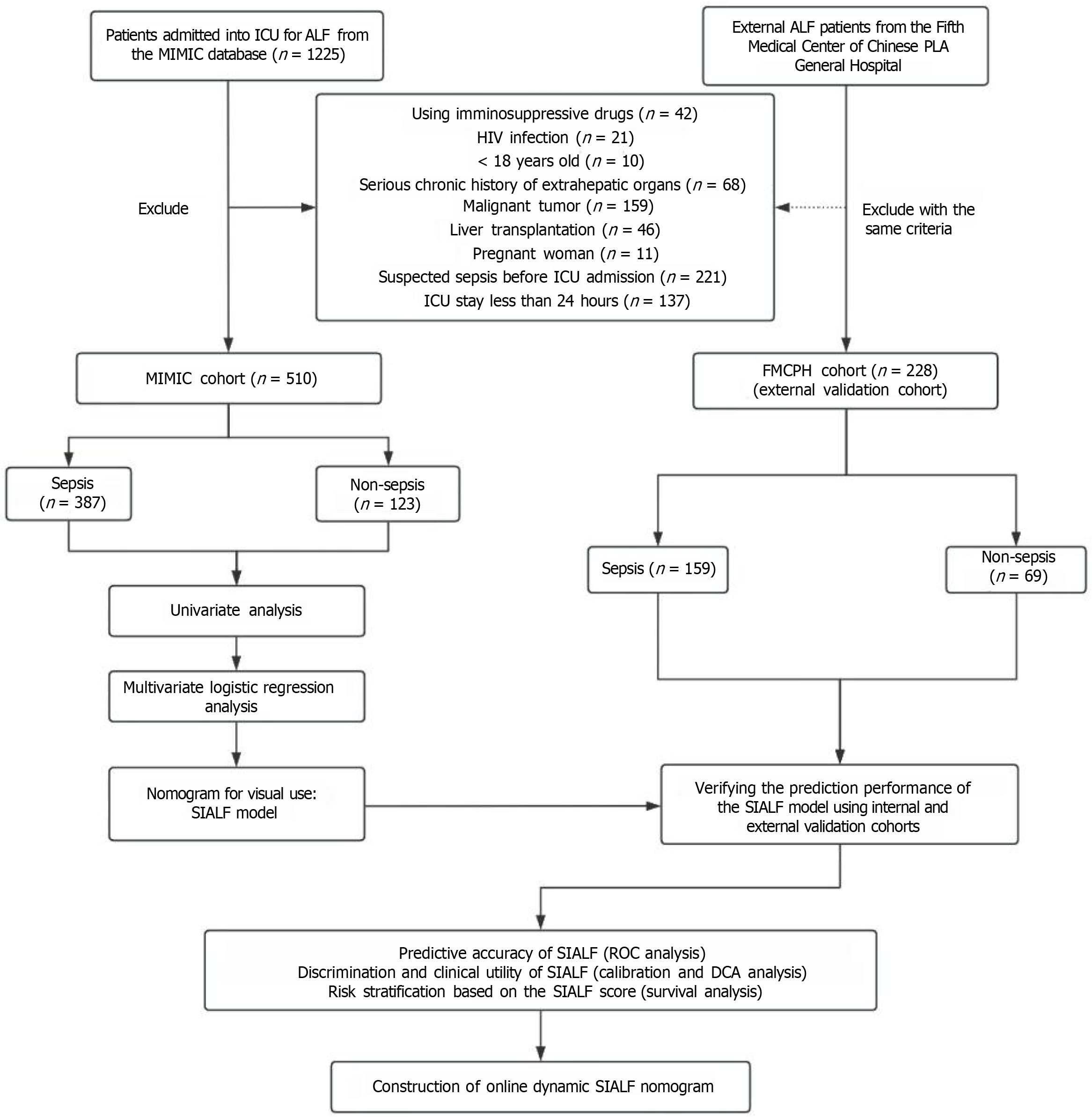
Figure 1 Flow chart of patient enrollment and study design.
MIMIC: Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care; FMCPH: The Fifth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital; ICU: Intensive care unit; ALF: Acute liver failure; SIALF: Sepsis in acute liver failure; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; DCA: Decision curve analysis.
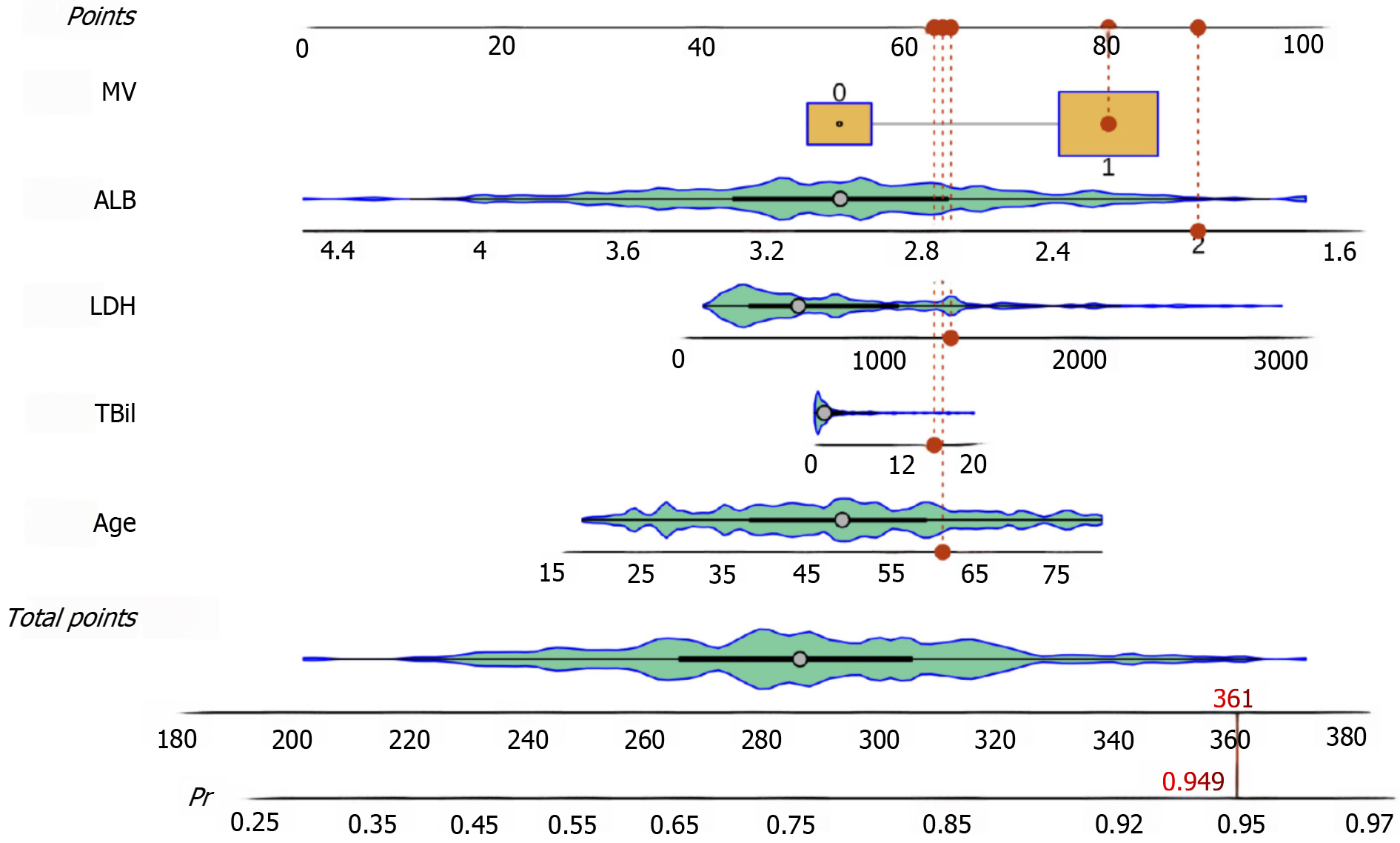
Figure 2 Sepsis in acute liver failure nomogram for predicting the risk of sepsis in acute liver failure.
The nomogram was constructed with five admission variables. Each patient admitted would receive an individualized score for each variable. Summing all scores generated a potential risk of sepsis in patients with acute liver failure (red dot). MV: Mechanical ventilation; ALB: Albumin; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; TBil: Total bilirubin.
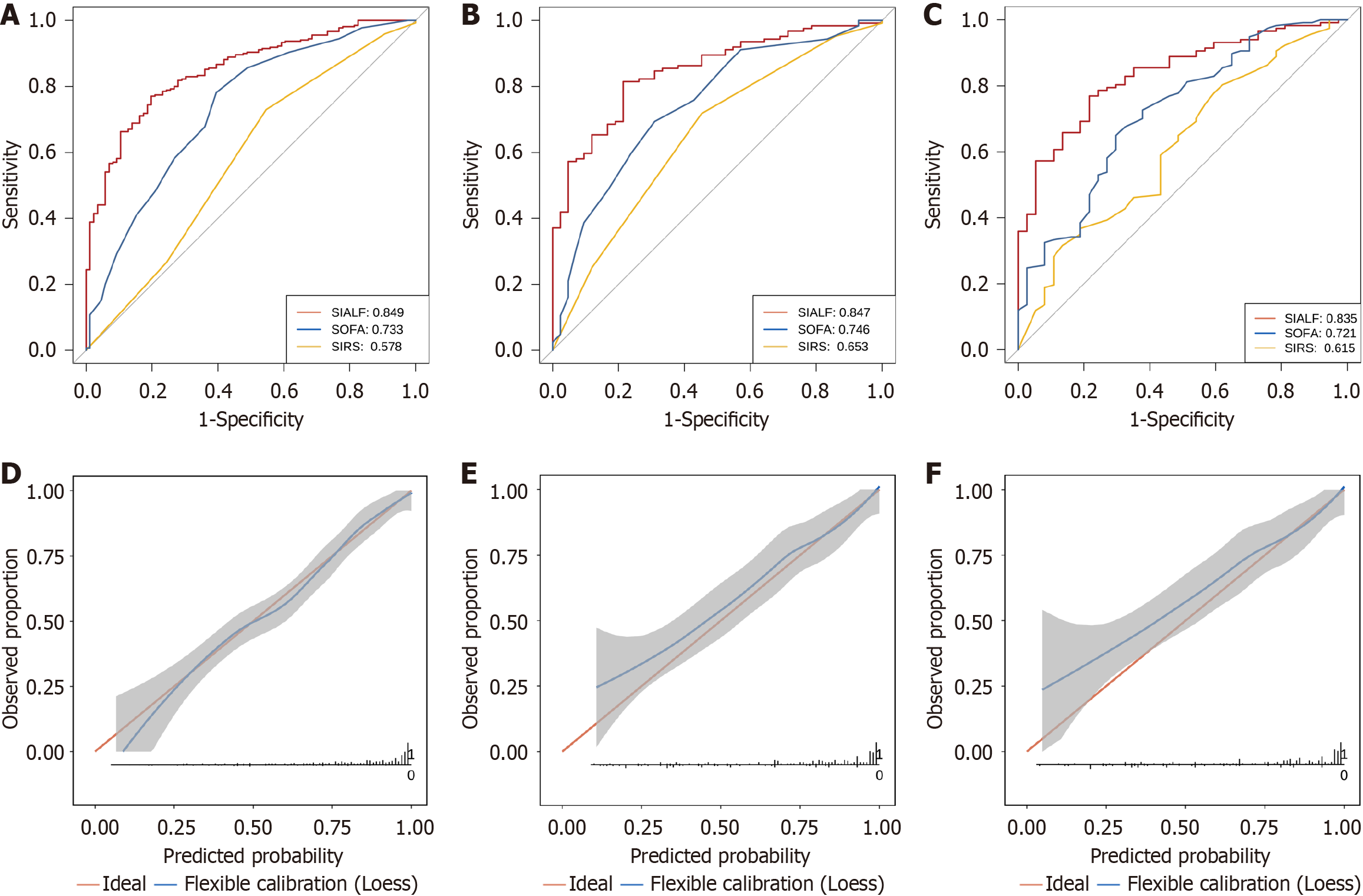
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic and calibration curves to assess the accuracy and calibration of sepsis in the acute liver failure model.
A: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) comparison for sepsis risk in the internal derivation cohort; B: ROC comparison in the internal validation cohort; C: ROC comparison in the external validation cohort; D: The calibration curve of the internal derivation cohort; E: The calibration curve of the internal validation cohort; F: The calibration curve of the external validation cohort. SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; SIRS: Systemic inflammatory response syndrome; SIALF: Sepsis in acute liver failure.
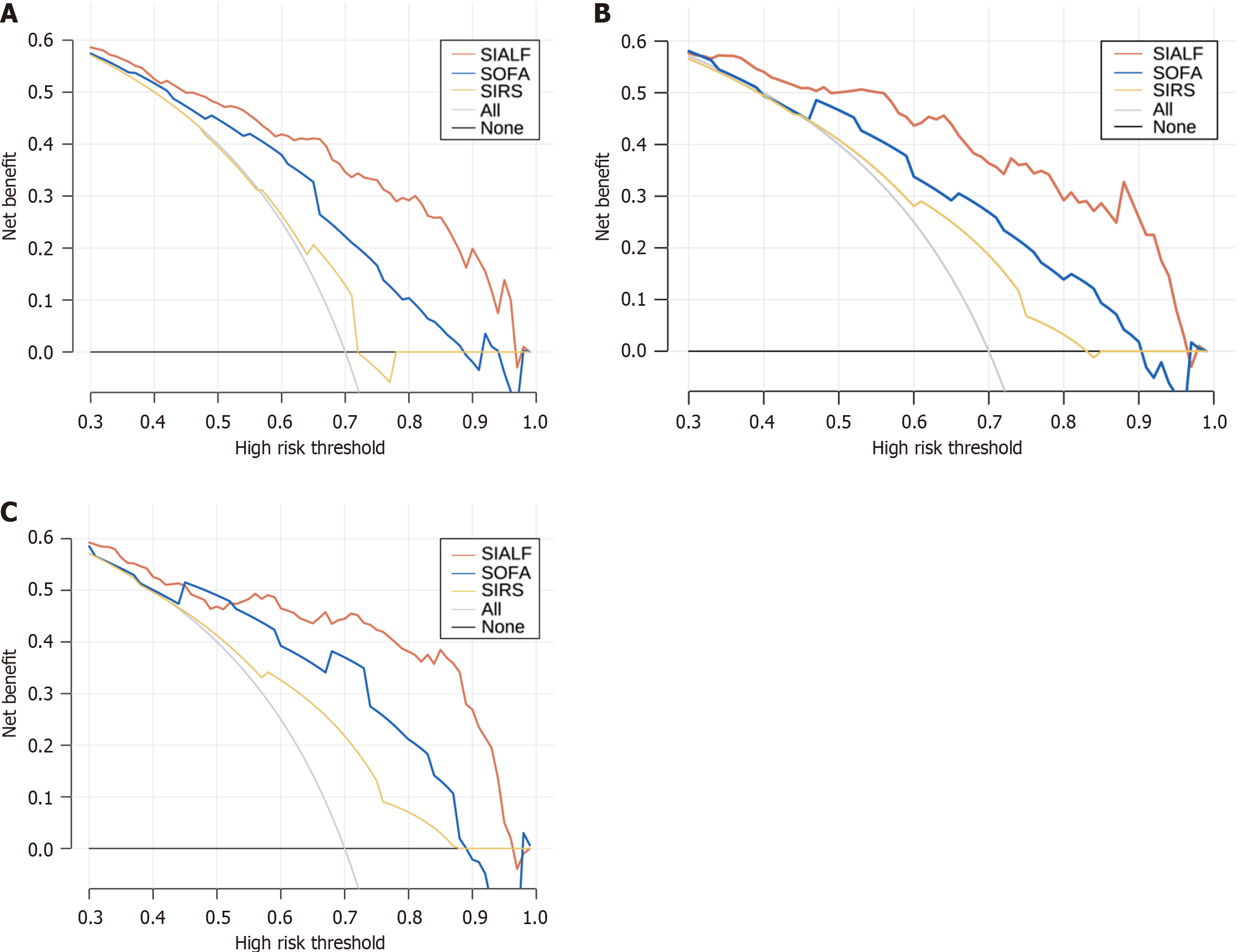
Figure 4 Comparison of the clinical utility of the sepsis in acute liver failure model for predicting sepsis risk in acute liver failure with other scoring systems using decision curve analysis.
A: The decision curve analysis (DCA) curve of the internal derivation cohort; B: The DCA curve of the internal validation cohort; C: The DCA curve of the external validation cohort. SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; SIRS: Systemic inflammatory response syndrome; SIALF: Sepsis in acute liver failure.
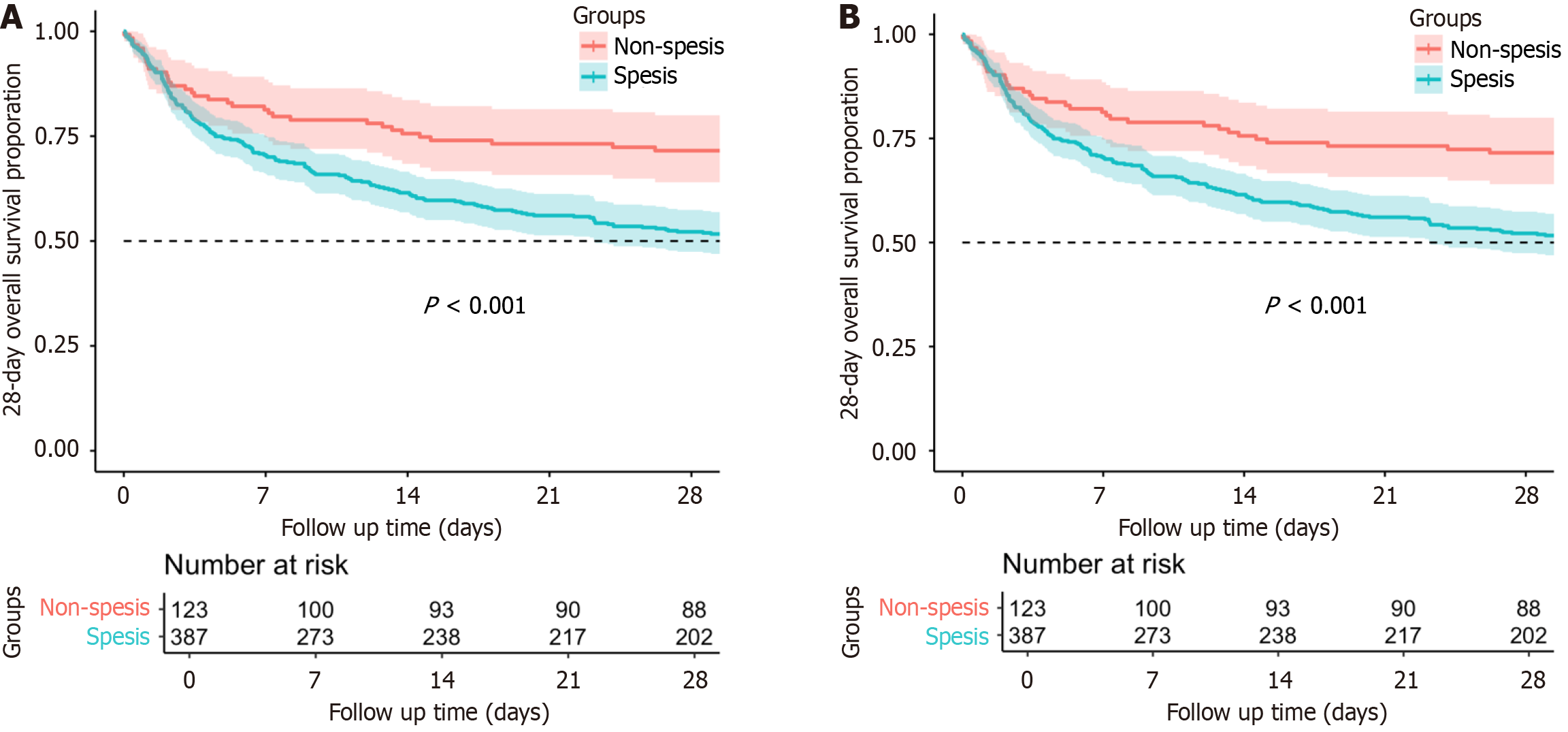
Figure 5 Survival analysis of the sepsis and non-sepsis groups in acute liver failure.
A: Survival analysis for 28-day mortality; B: Survival analysis for 90-day mortality.
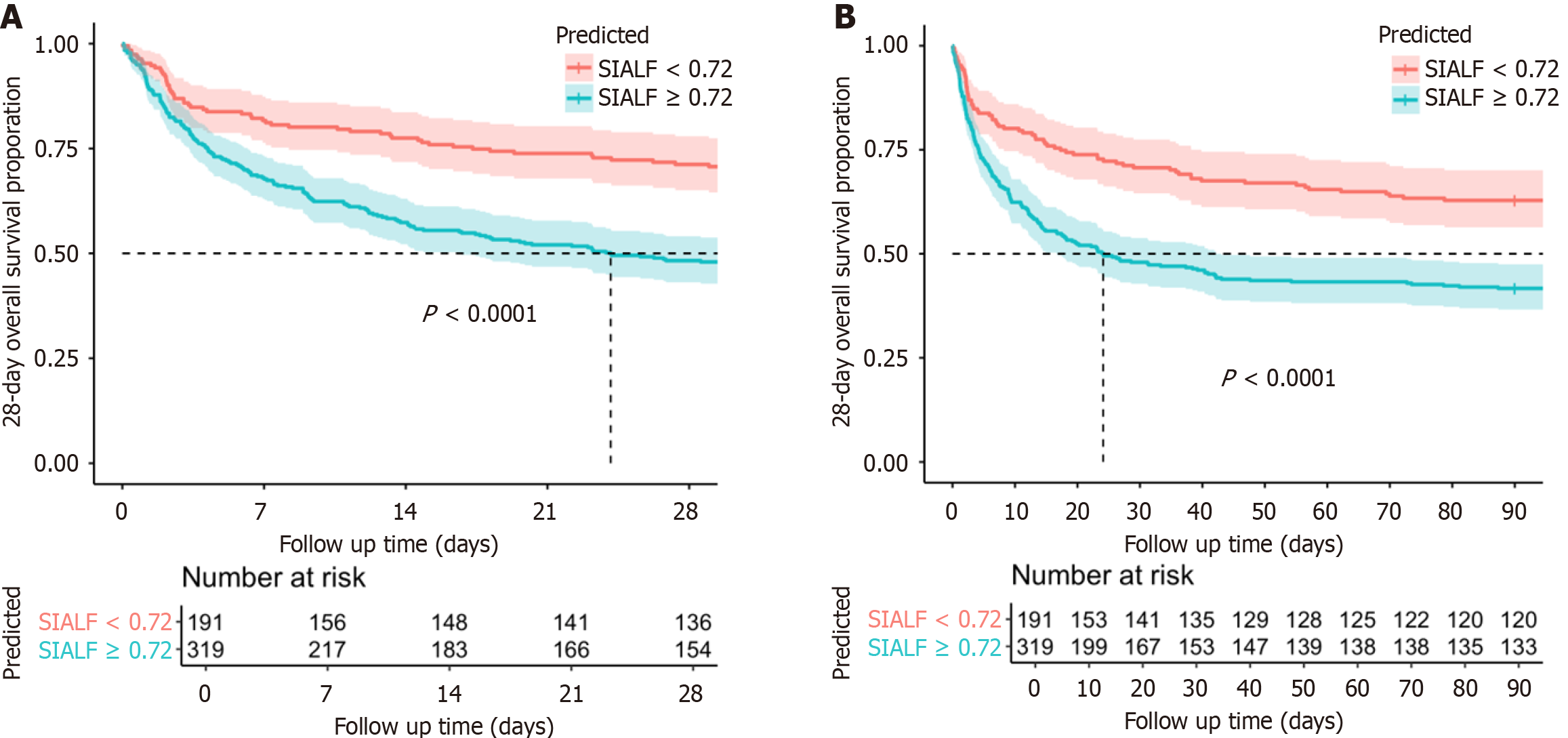
Figure 6 Survival analysis for risk stratification based on sepsis in acute liver failure score.
A: Survival analysis for 28-day mortality stratified by the sepsis in acute liver failure score; B: Survival analysis for 90-day mortality stratified by the sepsis in acute liver failure score. The cutoff point was 0.72. SIALF: Sepsis in acute liver failure.
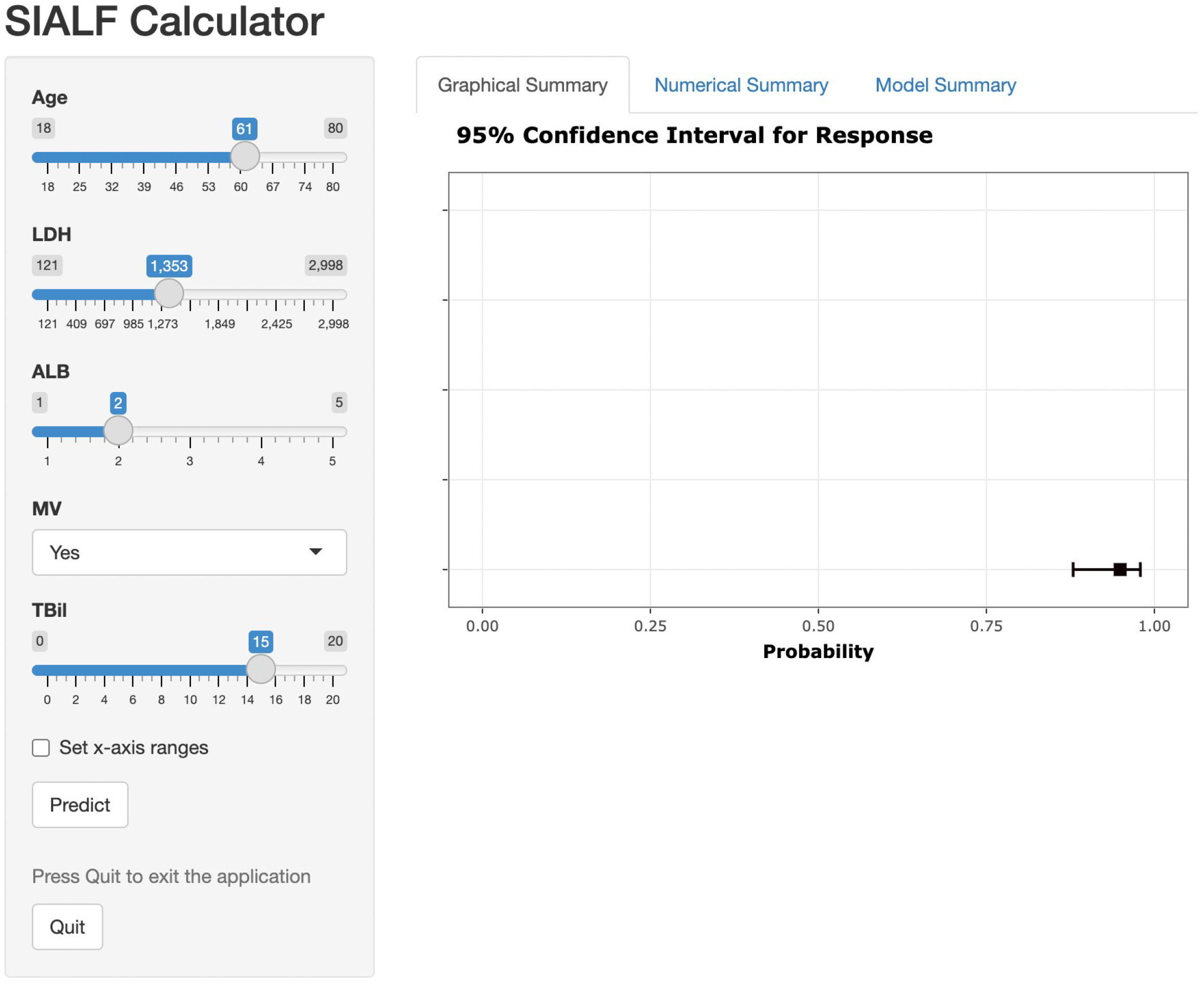
Figure 7 The dynamic online sepsis in acute liver failure nomogram for predicting sepsis risk in acute liver failure.
LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; ALB: Albumin; MV: Mechanical ventilation; TBil: Total bilirubin; SIALF: Sepsis in acute liver failure.
- Citation: Qi R, Wang X, Kuang ZD, Shang XY, Lin F, Chang D, Mu JS. Dynamic nomogram predicts sepsis risk in patients with acute liver failure: Analysis of intensive care database with external validation. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(31): 105229
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i31/105229.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i31.105229