Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2023; 29(48): 6179-6197
Published online Dec 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i48.6179
Published online Dec 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i48.6179
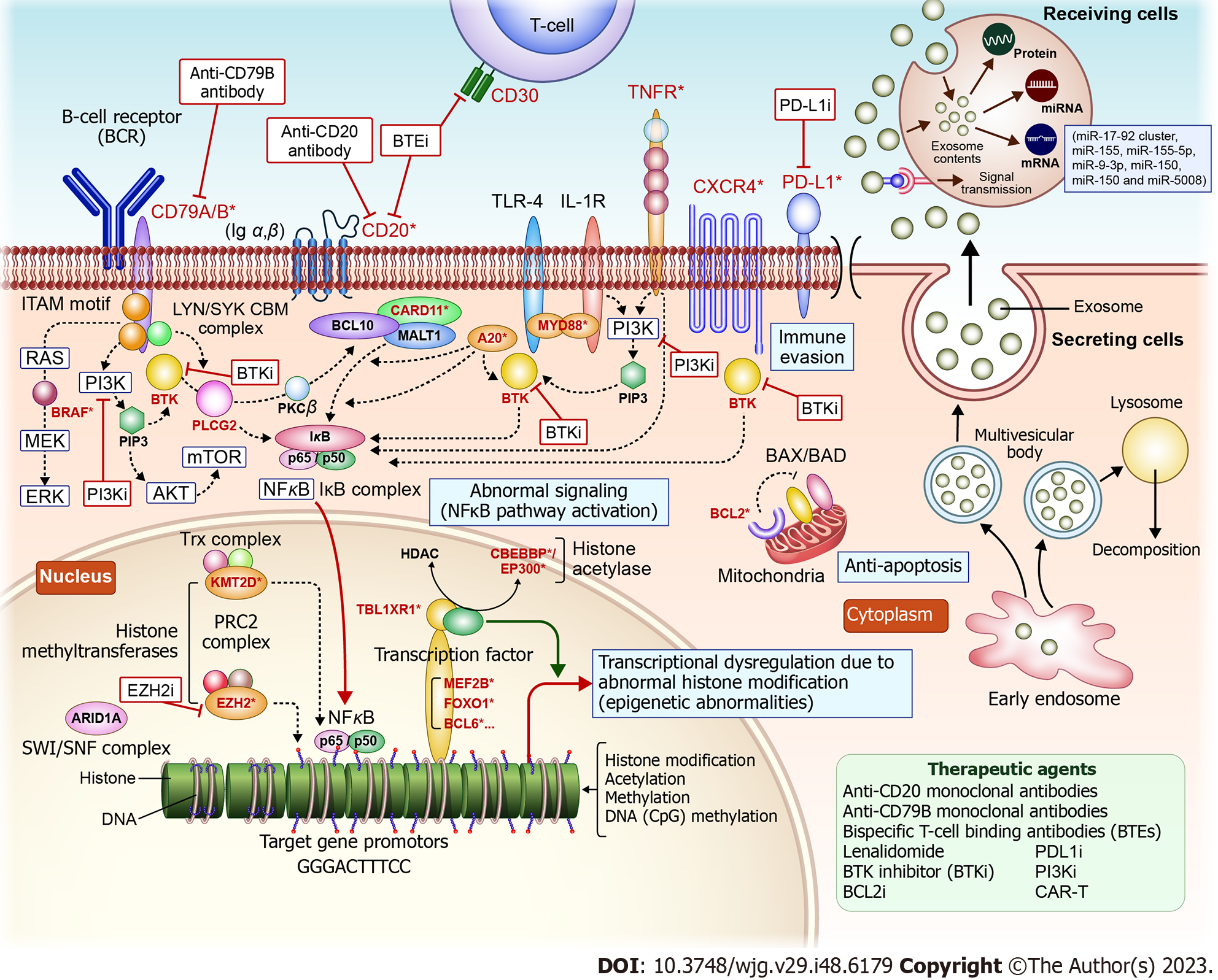
Figure 1 Follicular lymphoma-related genes involved in follicular lymphoma pathogenesis and proliferation, and the action of novel therapeutic agents targeting them.
MicroRNAs are secreted from the follicular lymphoma cytoplasm as exosomes, taken up by recipient cells, and regulate gene expression (right side of the figure).
Figure 2 Genetic mutations that cause follicular lymphoma development and microRNAs that regulate onset and tumor cell growth.
Novel therapeutic agents have been developed to target FL-associated gene mutations involved in follicular lymphoma (FL) pathogenesis and proliferation. MicroRNAs are secreted from the FL cytoplasm as exosomes and internalized into recipient cells where they are transduced and regulate gene expression via upregulation or downregulation. FL: Follicular lymphoma; BCR: B-cell receptor; BTE(i): Bispecific T-cell binding antibodies (inhibitor); PD-L1(i): Programmed death ligand 1 antibody (inhibitor); miRNA: MicroRNA; mRNA: Messenger RNA; PI3K(i): Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (inhibitor); BTK(i): Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (inhibitor); AKT: Protein kinase B; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin; EZH2(i): Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (inhibitor).
- Citation: Watanabe T. Gene targeted and immune therapies for nodal and gastrointestinal follicular lymphomas. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(48): 6179-6197
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i48/6179.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i48.6179