Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2023; 29(42): 5768-5780
Published online Nov 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i42.5768
Published online Nov 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i42.5768
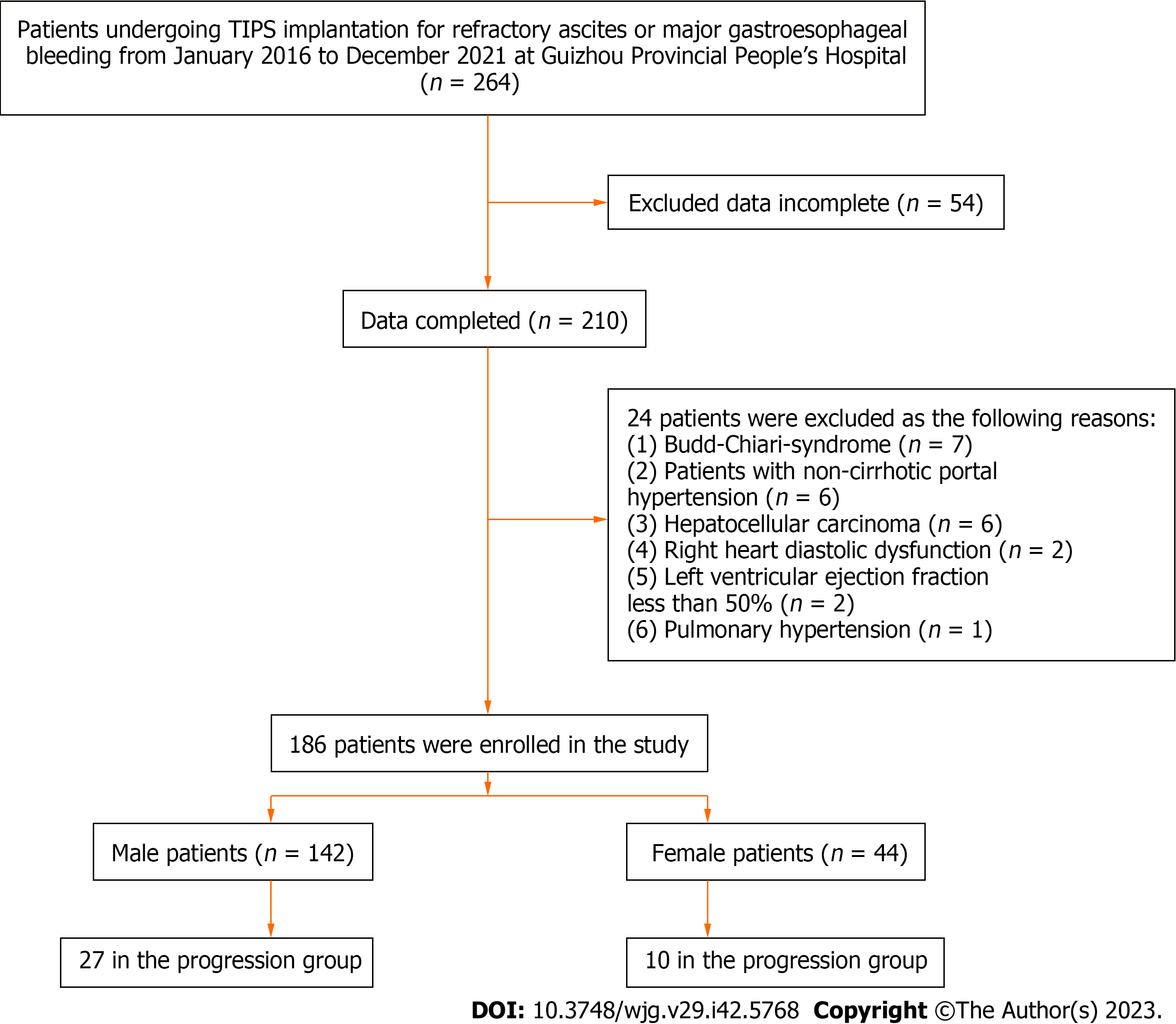
Figure 1 Flow diagram.
TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
Figure 2 Actuarial survival rates of cirrhotic patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt implantation according to sex-stratified analysis.
A: Actuarial survival in male patients with cirrhosis after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt implantation; B: Actuarial survival in female patients with cirrhosis after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt implantation. CI: Confidence interval; SMI: Skeletal muscle index; HR: Hazard ratio; TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
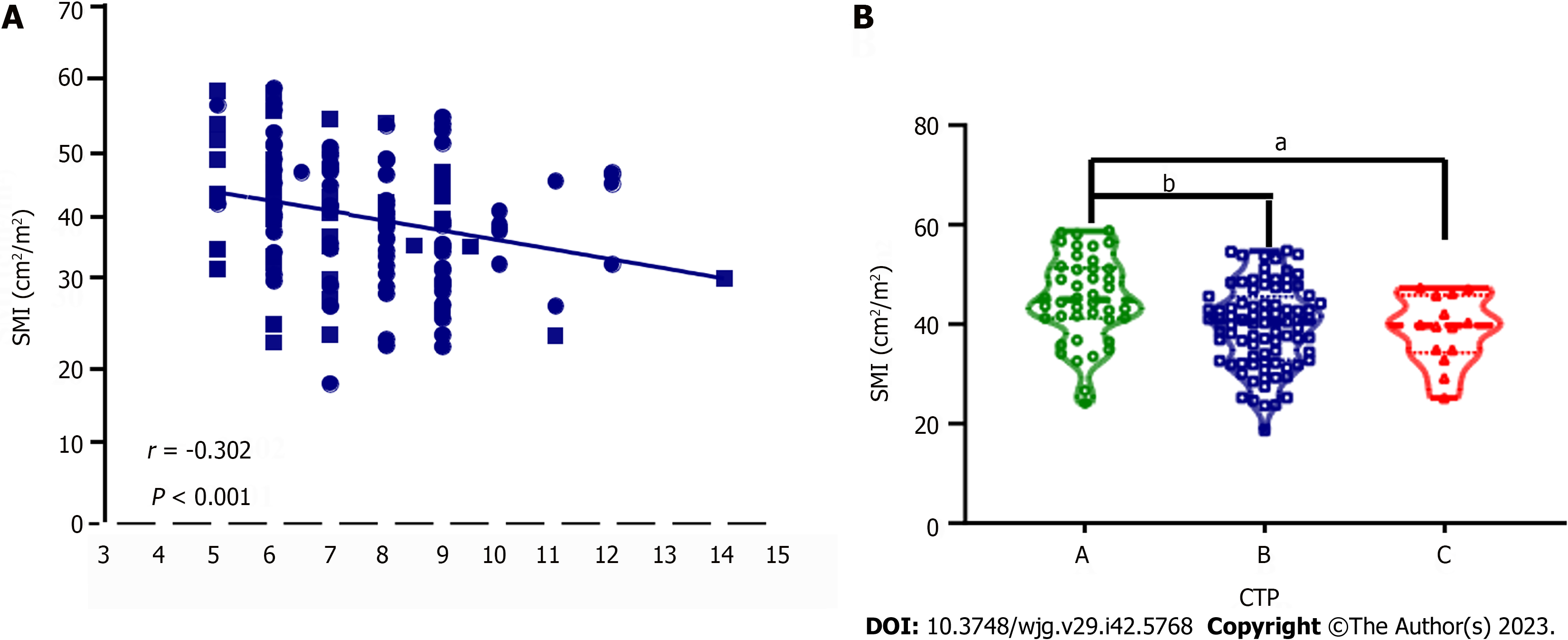
Figure 3 Relationship between changes in skeletal muscle index levels and Child-Turcotte-Pugh scores in cirrhotic patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt implantation.
A: Correlation between Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) scores and skeletal muscle index (SMI) in male patients with cirrhosis who underwent transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt implantation. Spearman’s correlation coefficients (r) are indicated; B: Comparisons of SMI levels among patients with different CTP grades. CTP: Child-Turcotte-Pugh; SMI: Skeletal muscle index; TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01.
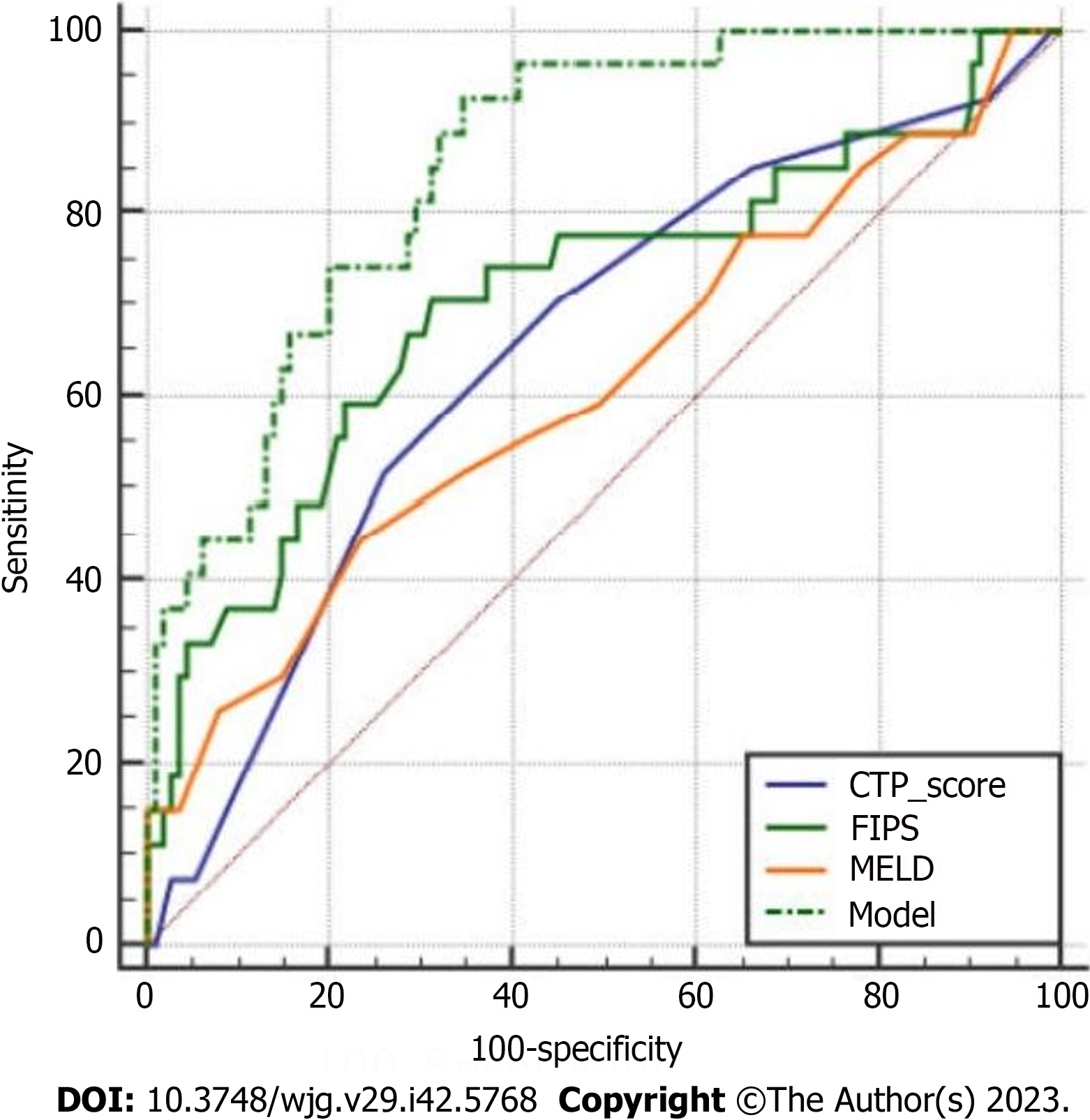
Figure 4 Comparisons of the newly constructed model against previous models including Child-Turcotte-Pugh, Freiburg index of post-transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt survival, and Model for End-Stage Liver Disease in terms of the value in predicting 30-mo mortality.
In the DeLong test, P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The constructed model involved creatinine, plasma ammonia, skeletal muscle index at baseline, and acute-on-chronic liver failure and hepatic encephalopathy occurring within half a year after surgery. CTP: Child-Turcotte-Pugh; FIPS: Freiburg index of post-transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt survival; MELD: Model for End-Stage Liver Disease.
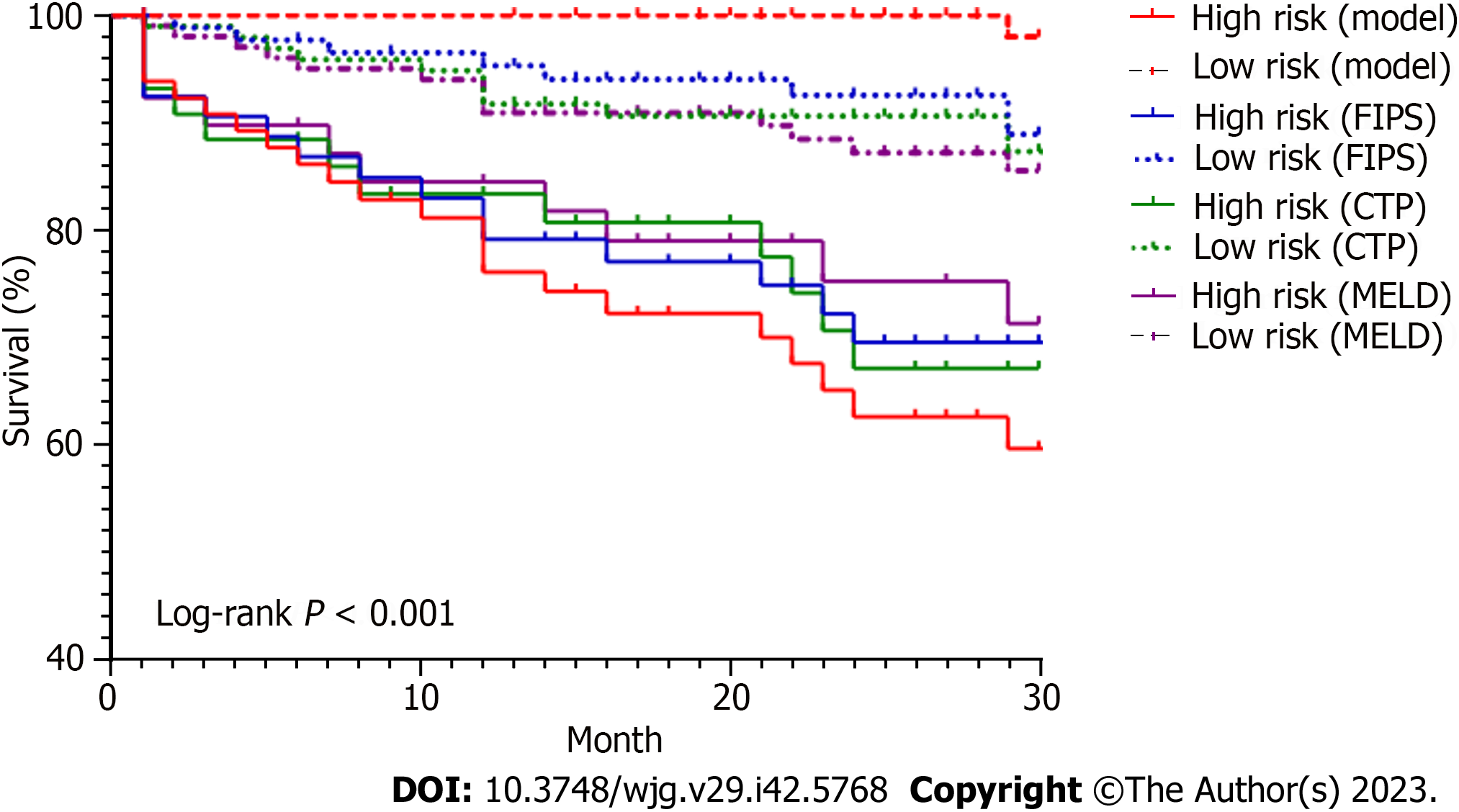
Figure 5 Kaplan-Meier plots showing the cumulative probability of liver transplant-free survival in different risk groups according to different models.
The constructed model involved creatinine, plasma ammonia, skeletal muscle index at baseline, and acute-on-chronic liver failure and hepatic encephalopathy occurring within half a year after surgery. CTP: Child-Turcotte-Pugh; FIPS: Freiburg index of post-TIPS survival; MELD: Model for End-Stage Liver Disease.
- Citation: Zhang Q, Long L, Zhu HL, Peng H, Luo XH, Zhu KS, Wang RP. Predicting disease progression in cirrhotic patients after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt implantation: A sex-stratified analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(42): 5768-5780
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i42/5768.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i42.5768