Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2023; 29(15): 2283-2293
Published online Apr 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2283
Published online Apr 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2283
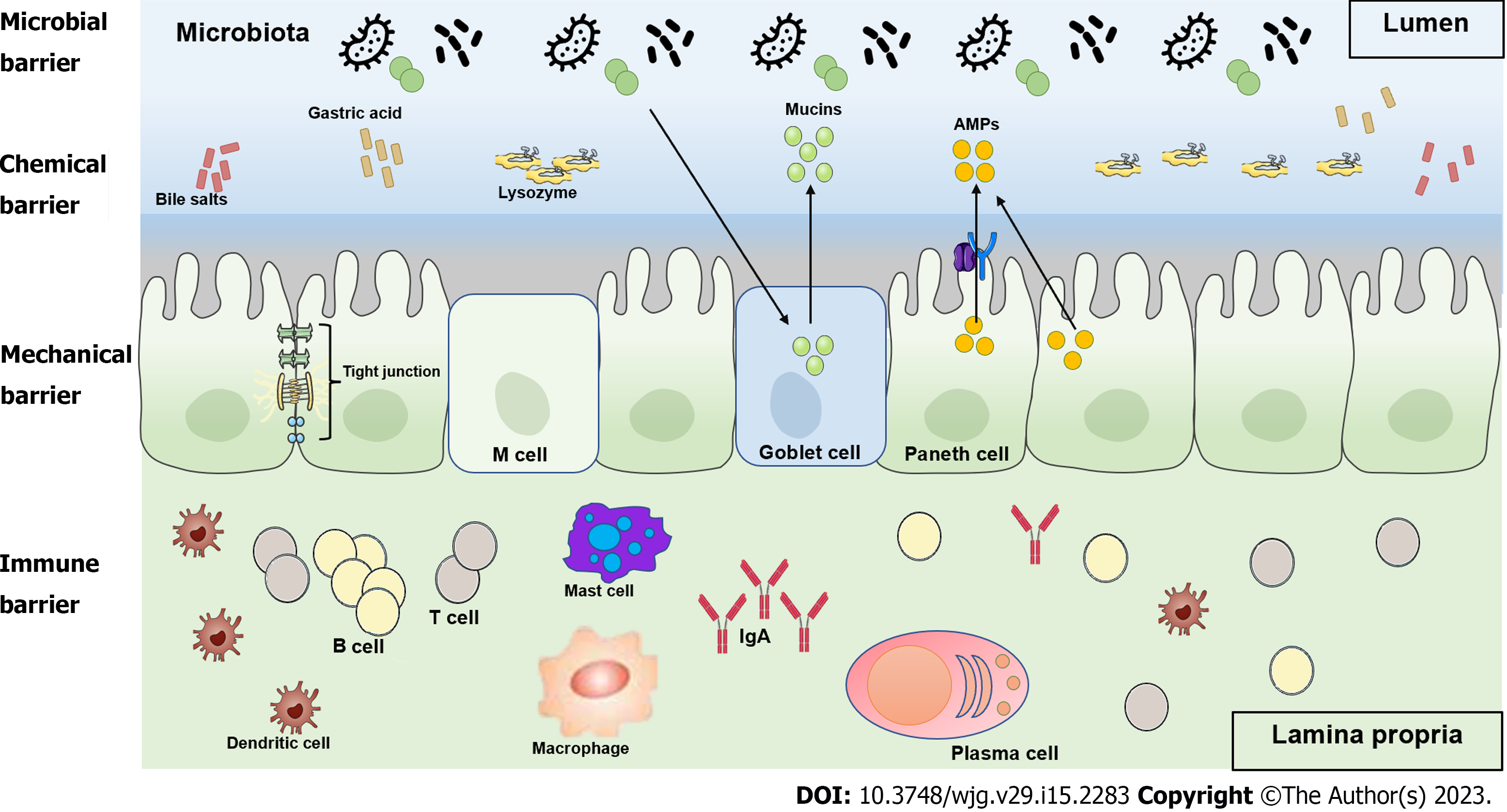
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the intestinal barrier.
The intestinal barrier is composed of biological, chemical, mechanical, and immune barriers. The intestinal lumen contains antimicrobial peptides, mucins, gastric acid, bile salts, lysozyme, and commensal bacteria, which together provide a protective barrier effect and inhibit pathogen colonization. The epithelial layer consists of a single layer of epithelial cells with tight junctions that prevent paracellular passage. In addition, this layer also harbors M cells, Goblet cells, and Paneth cells. The lamina propria contains a large number of immune cells, including B cells, T cells, plasma cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, and mast cells.
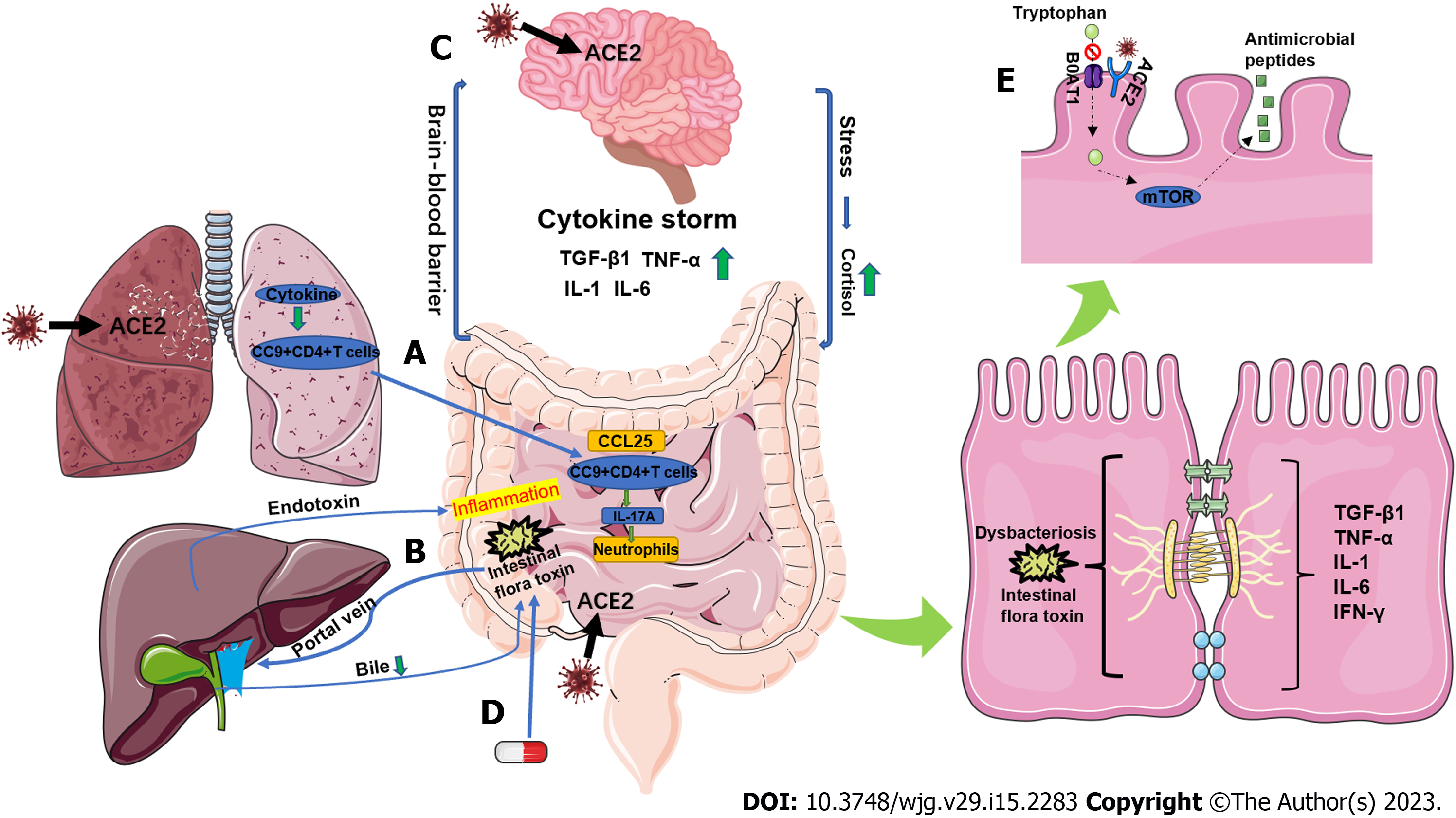
Figure 2 Mechanisms of gastrointestinal barrier dysfunction in coronavirus disease 2019 patients.
A: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) binds with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) to enter the lung and, through the CCL25-CCR9 axis, mediate the recruitment of lung-derived effector CD4+ T cells to the small intestine. This promotes the in-situ polarization of small intestinal Th17 cells and production of IL-17A leading to neutrophil aggregation and injuring the intestine; B: The intestinal flora is transferred to the liver through the portal vein, affecting liver function and leading to a decrease in endotoxin inactivation. Endotoxins enter the systemic circulation and induce an inflammatory response. In addition, decreased liver function also leads to reduced bile secretion and decreased inhibition of intestinal flora; C: The SARS-CoV-2 attack on cerebral neurons produces a large amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines that activate the systemic immune system, leading to damage of the gastrointestinal barrier. In addition, neurological damage activates the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, which causes an increase in adrenal cortisol secretion, impairing the gastrointestinal barrier; D: The use of antibacterial or antiviral drugs may cause dysbiosis or immune suppression resulting in gastrointestinal barrier disorders; E: Competitive binding of ACE2 receptors by the SARS-CoV-2 virus inhibits tryptophan absorption through the B0AT1/ACE2 transport pathway in enterocytes, thus impairing regulation of antimicrobial peptide expression and causing dysbiosis of the flora, which disrupts the gastrointestinal barrier. ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.
- Citation: Xue W, Honda M, Hibi T. Mechanisms of gastrointestinal barrier dysfunction in COVID-19 patients. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(15): 2283-2293
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i15/2283.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2283