Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2021; 27(9): 835-853
Published online Mar 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.835
Published online Mar 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.835
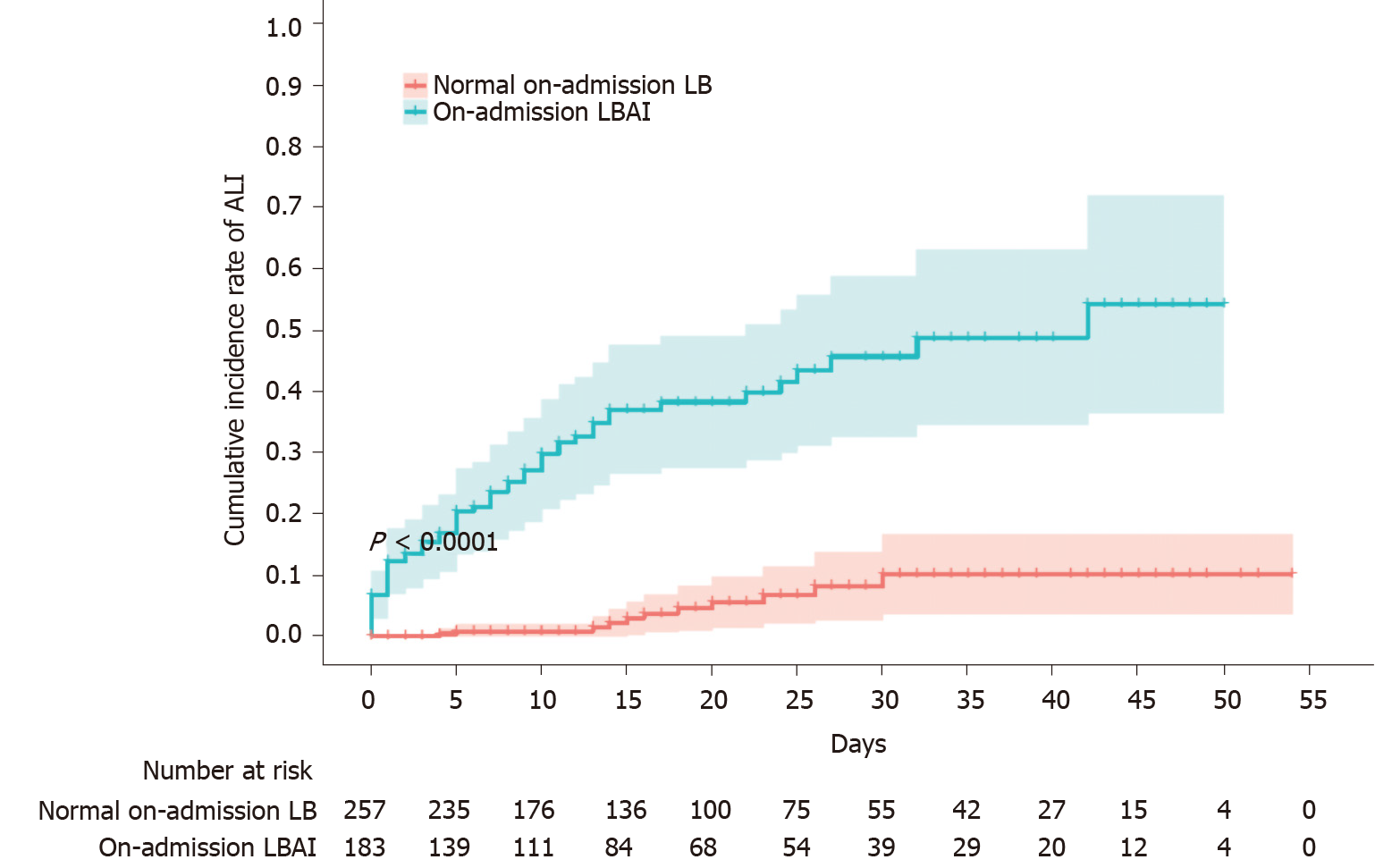
Figure 1 Cumulative incidence rate of acute liver injury stratified by on-admission liver biochemistry.
Shadows indicate the 95% confidence intervals of the corresponding estimates cumulative incidence rate. ALI: Acute liver injury; LB: Liver biochemistry; LBAI: Liver biochemical abnormality or injury.
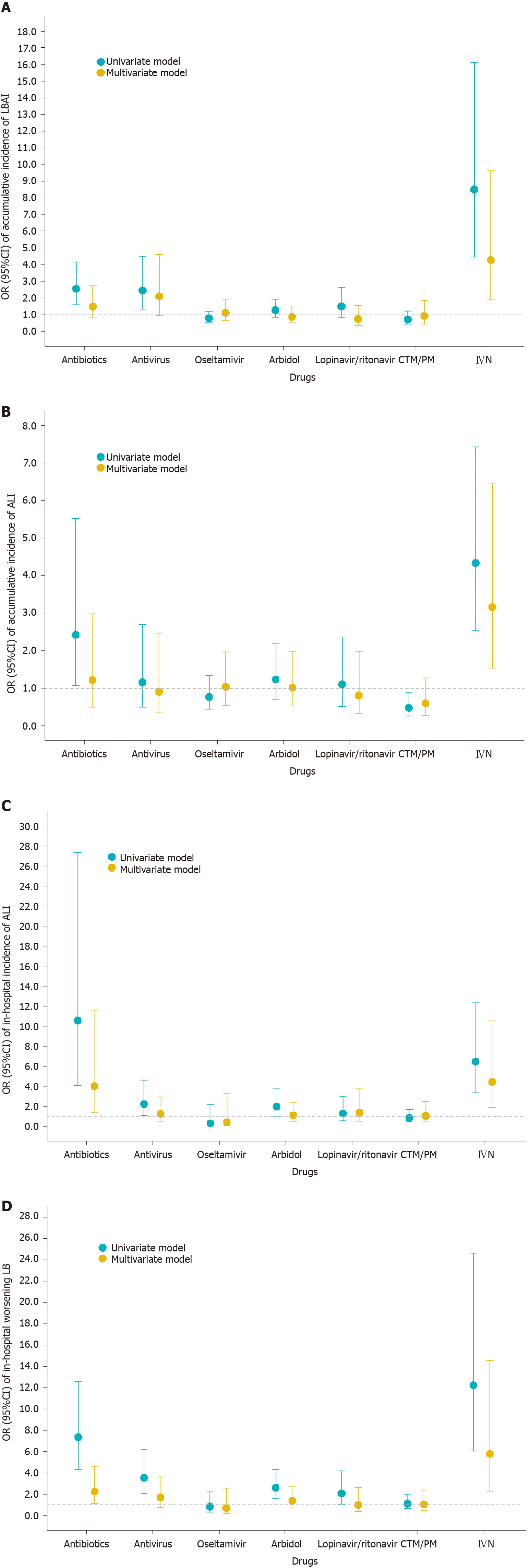
Figure 2 Association between drugs and liver injury.
A: Cumulative incidence of liver biochemical abnormality or injury and drugs used during the whole course; B: Cumulative incidence of acute liver injury and drugs used during the whole course; C: In-hospital incidence of acute liver injury and drugs used after admission; D: In-hospital worsening liver biochemistry and drugs used after admission. Univariate model refers to univariate binary logistic regression model. Multivariate model refers to multivariate binary logistic regression model adjusted by age, sex, comorbidities (defined as history of at least one disease out of hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, chronic renal disease, chronic respiratory disease, and chronic liver disease), in-hospital disease severity status, lymphocyte count, D-dimer, and serum ferritin. Antivirals included oseltamivir, arbidol, lopinavir/ritonavir, and some other uncommonly used antiviral drugs. OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval; ALI: Acute liver injury; LB: Liver biochemistry; LBAI: Liver biochemical abnormality or injury.
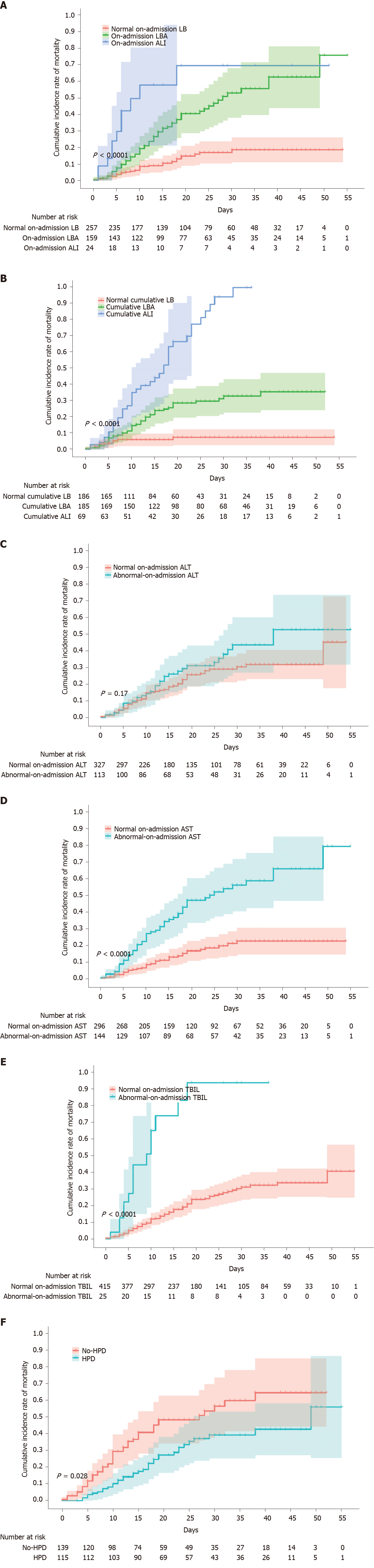
Figure 3 Cumulative incidence of in-hospital mortality of patients with coronavirus disease 2019, stratified by liver disease indicators or hepatoprotective drugs.
A-F: Shadows indicate the 95% confidence intervals of the corresponding estimates: Stages of on-admission liver injury (A), stages of cumulative liver injury (B), on-admission alanine aminotransferase (C), on-admission aspartate aminotransferase (D), on-admission total bilirubin (E), and hepatoprotective drug uses in patients with abnormal liver function (F). LB: Liver biochemistry; LBA: Liver biochemical abnormality; ALI: Acute liver injury; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TBIL: Total bilirubin; HPD: Hepatoprotective drugs.
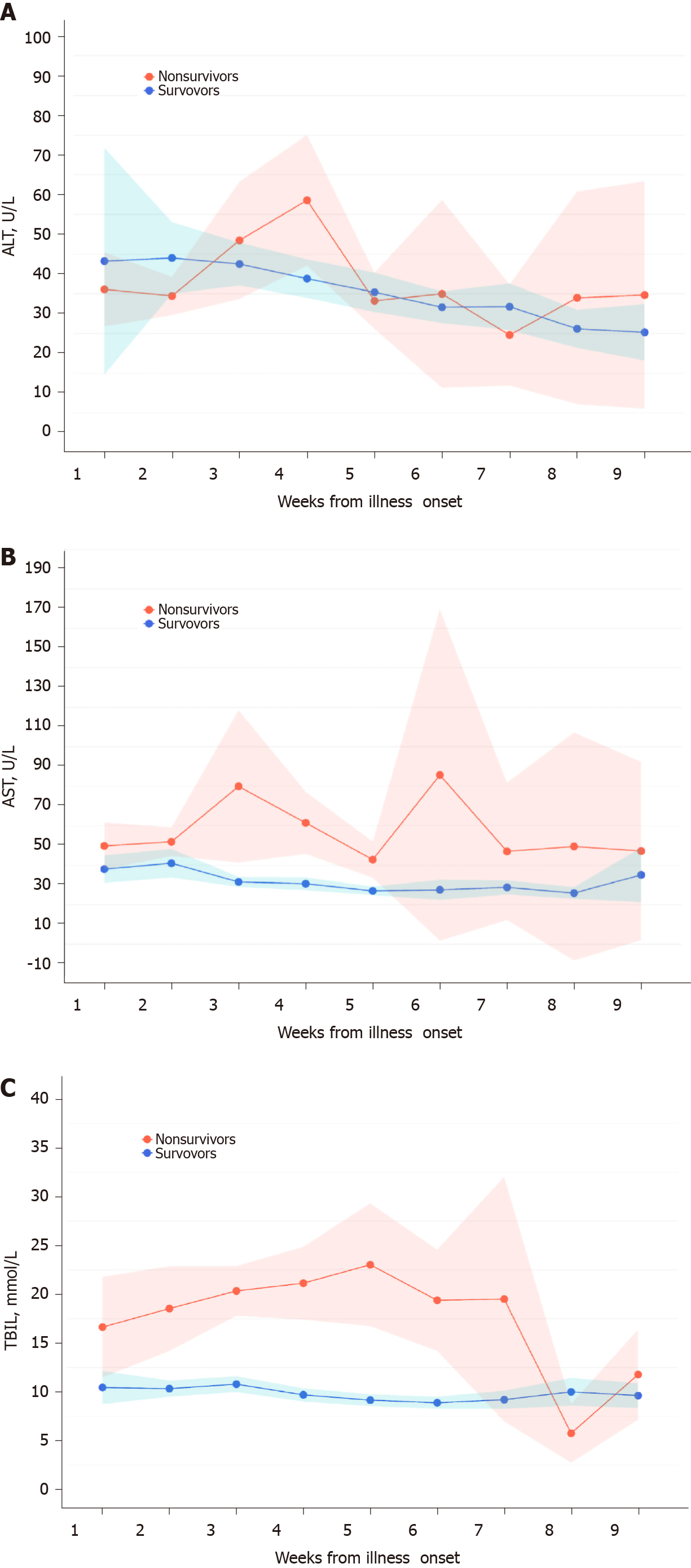
Figure 4 Dynamic variations of liver biochemistry from illness onset.
A-C: Shadows indicate the 95% confidence intervals of the corresponding estimates: Alanine aminotransferase (A), aspartate aminotransferase (B), and total bilirubin (C). TBIL: Total bilirubin.
- Citation: Zhang SS, Dong L, Wang GM, Tian Y, Ye XF, Zhao Y, Liu ZY, Zhai JY, Zhao ZL, Wang JH, Zhang HM, Li XL, Wu CX, Yang CT, Yang LJ, Du HX, Wang H, Ge QG, Xiu DR, Shen N. Progressive liver injury and increased mortality risk in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study in China. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(9): 835-853
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i9/835.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.835