Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2021; 27(28): 4687-4696
Published online Jul 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4687
Published online Jul 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4687
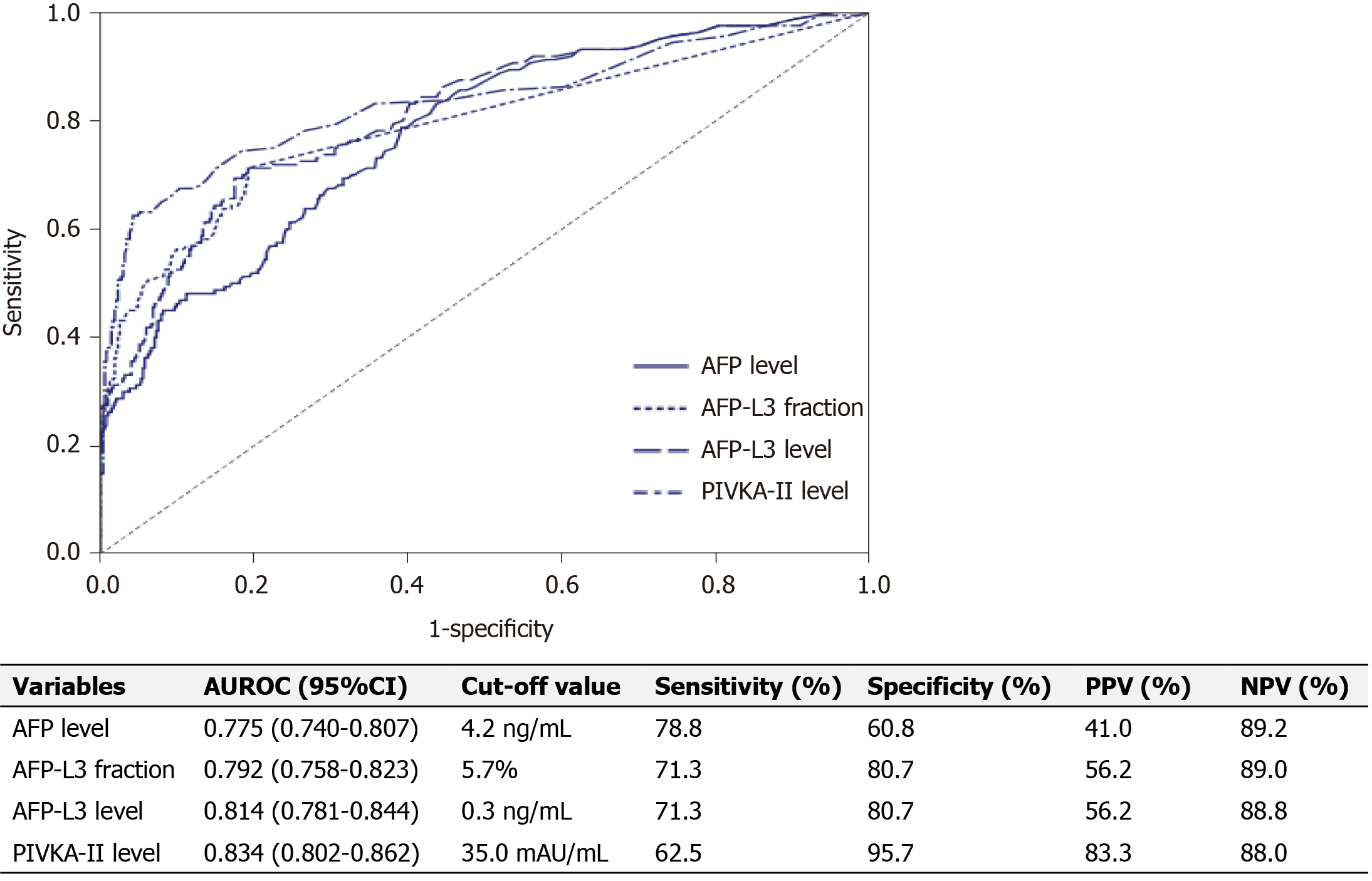
Figure 1 The area under the receiver operating characteristic curves of the tumor markers for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis in the total population.
AUROC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; AFP-L3: Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of AFP; PIVKA-II: Protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II; NPV: Negative predictive value; PPV: Positive predictive value.
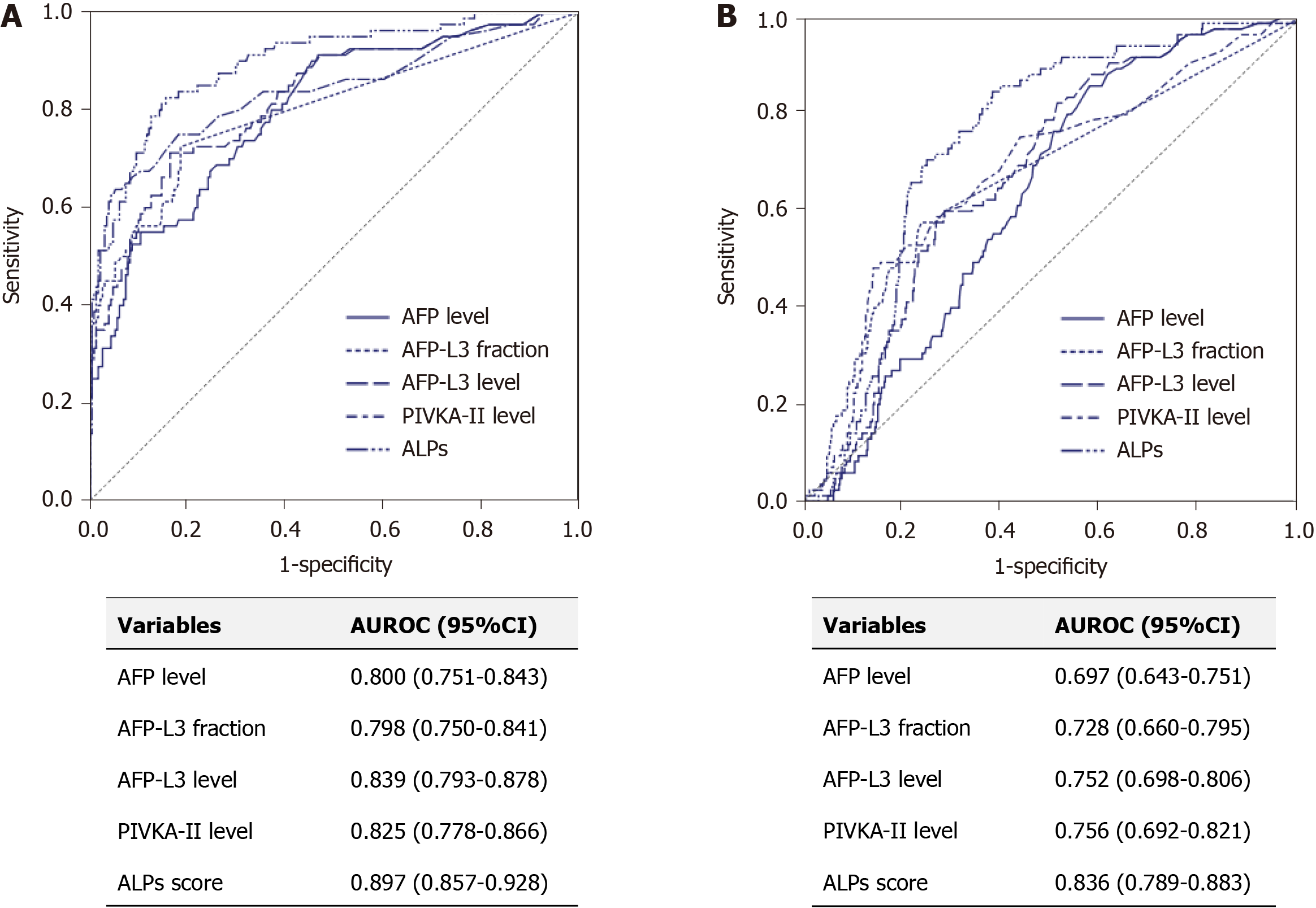
Figure 2 The area under the receiver operating characteristic curves of tumor markers for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis in the training set and the validation set.
A: Training set; B: Validation set. AUROC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; AFP-L3: Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of AFP; PIVKA-II: Protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II; ALPs: AFP, AFP-L3 fraction, and PIVKA-II.
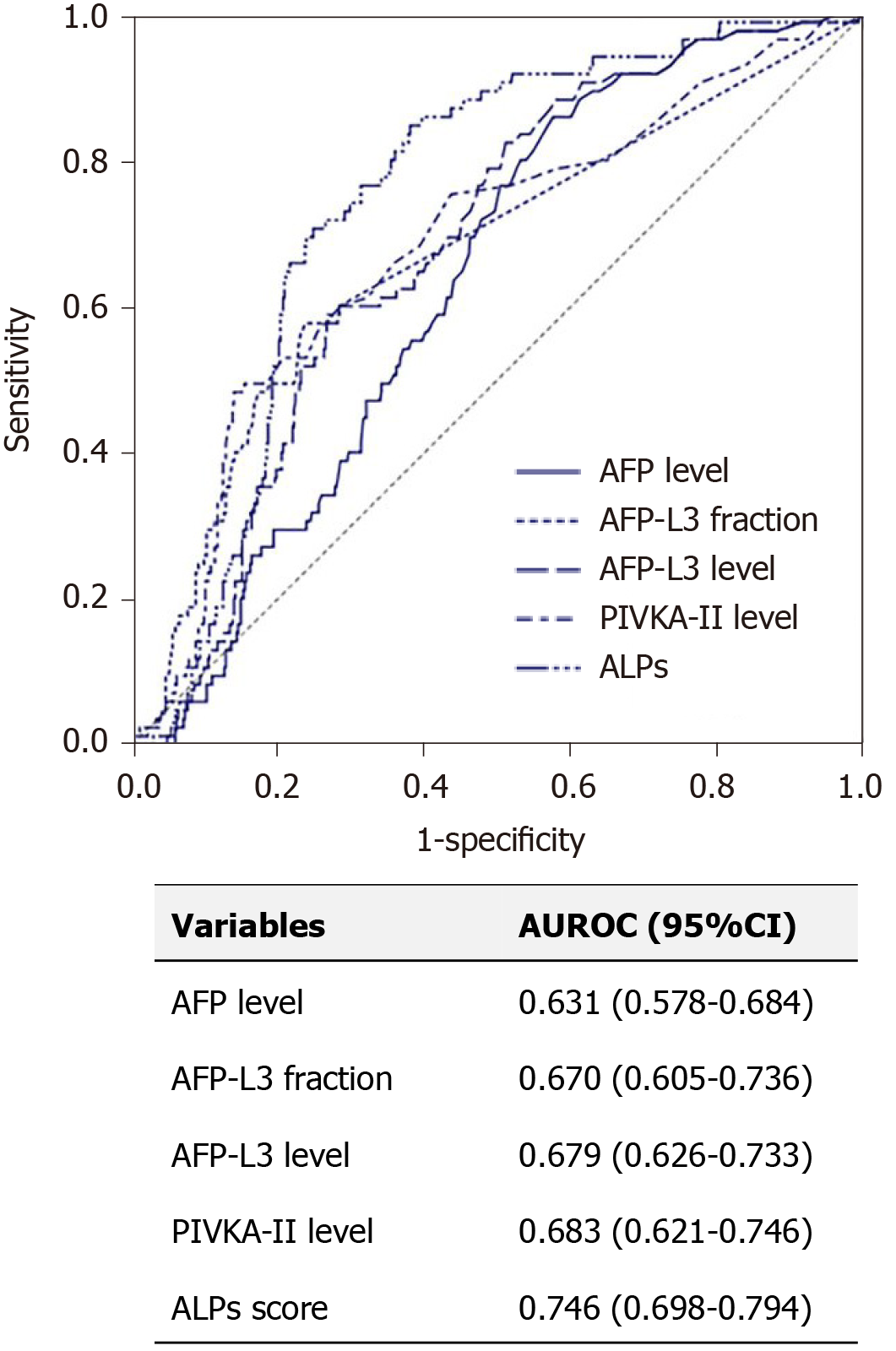
Figure 3 The area under the receiver operating characteristic curves of tumor markers for the diagnosis of very early and early-stage hepatocellular carcinom in the total population.
AUROC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; AFP-L3: Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of AFP; PIVKA-II: Protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II; ALPs: AFP, AFP-L3 fraction, and PIVKA-II.
- Citation: Lee HA, Lee YR, Lee YS, Jung YK, Kim JH, An H, Yim HJ, Jeen YT, Yeon JE, Byun KS, Seo YS. Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein improves diagnostic accuracy for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(28): 4687-4696
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i28/4687.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4687