Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2021; 27(23): 3342-3356
Published online Jun 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3342
Published online Jun 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3342
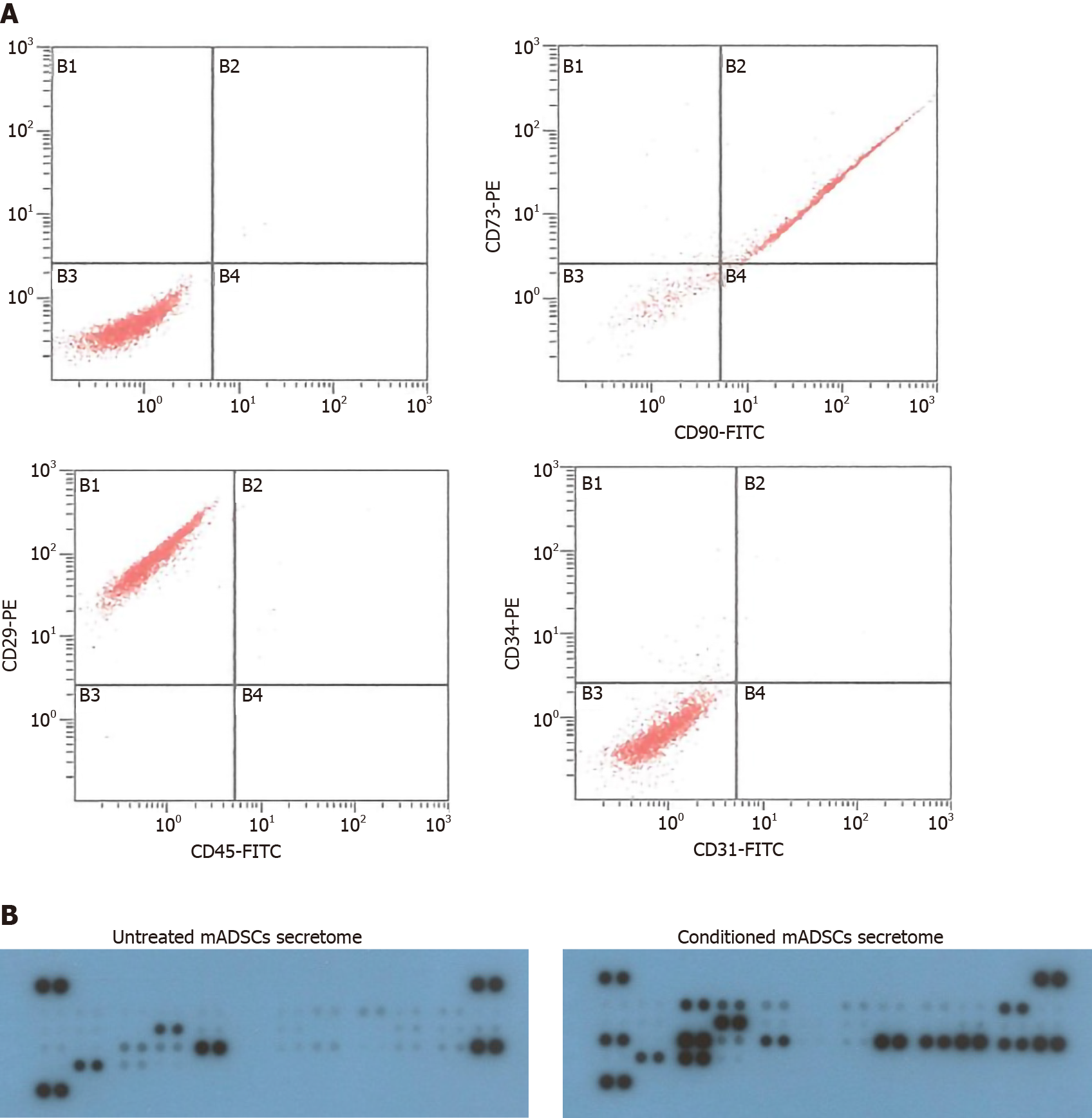
Figure 1 Characterization of mouse adipose-derived stem cells and secretome of mouse adipose-derived stem cells.
A: Flow cytometric analysis of surface antigens of mouse adipose-derived stem cells (mADSCs) isolated from C57BL/6 mice. They were positive for Crohn’s disease (CD)90, CD73 and CD29, and negative for CD45 and CD34, and CD31; B: Cytokine antibody arrays for secretome of mADSCs. Untreated mADSCs secretome was isolated from mADSCs without lipopolysaccharides (LPS) treatment, and conditioned mADSCs secretome was isolated from mADSCs cultured with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 24 h. Cell culture supernatants were subjected to cytokine antibody array. mADSCs: Mouse adipose-derived stem cells; CD: Crohn’s disease.
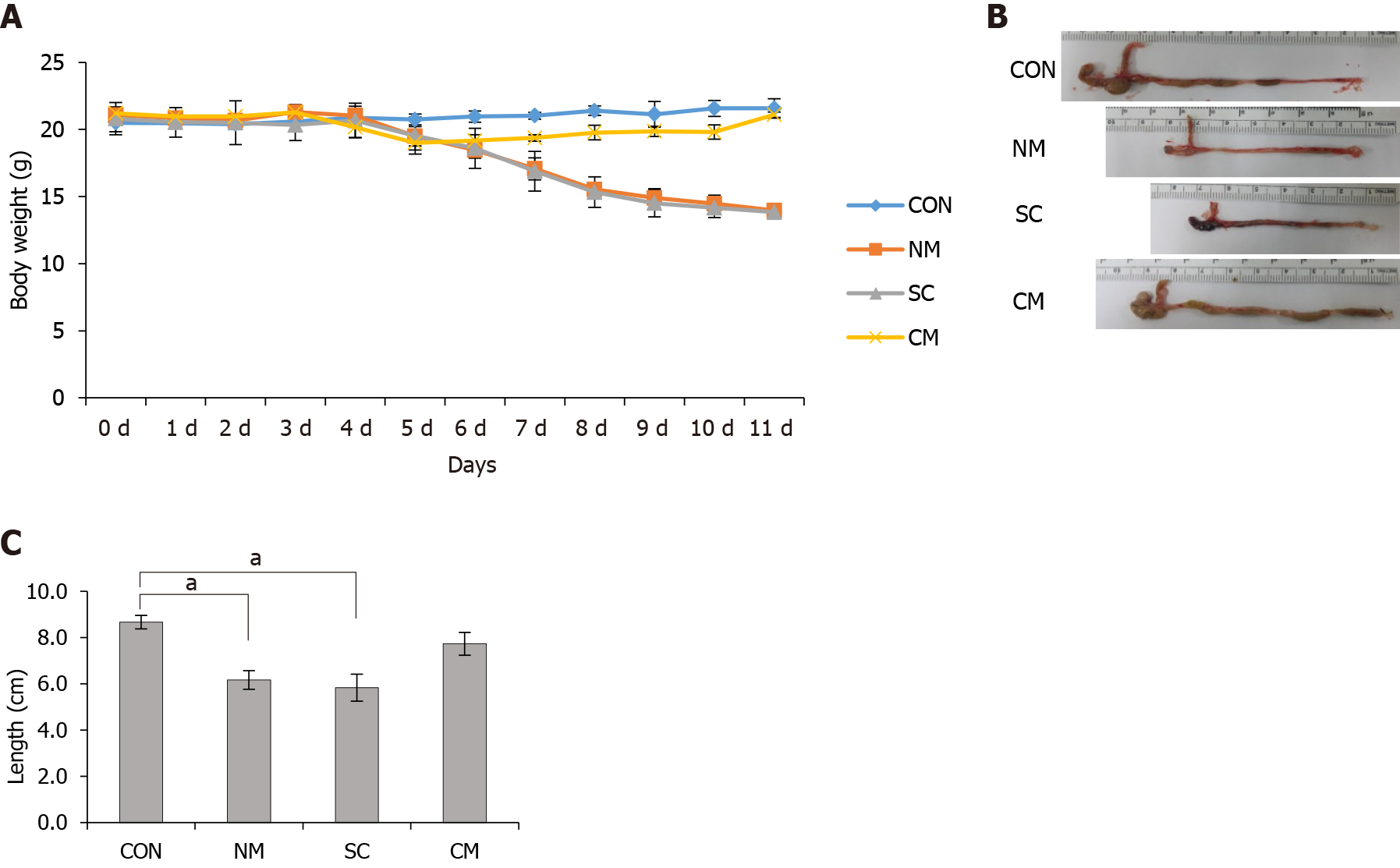
Figure 2 Effects of conditioned mouse adipose-derived stem cells secretome on body weight and colon length in dextran sulfate sodium-induced mice.
A: The treatment of Conditioned mouse adipose-derived stem cells (mADSCs) secretom (CM) ameliorated the loss of body weight of dextran sulfate sodium-induced mice. Normal culture medium or CM was injected intraperitoneally into mice on days 4, 6 and 8. mADSCs was injected via tail vein on day 4. Mice were sacrificed on day 11; B and C: The treatment of CM ameliorated the shortening of colon length. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 4-6 mice per group). aP < 0.05. CON: Control; NM: Normal culture medium; SC: Mouse adipose-derived stem cells (mADSCs); CM: Conditioned mADSCs secretome.
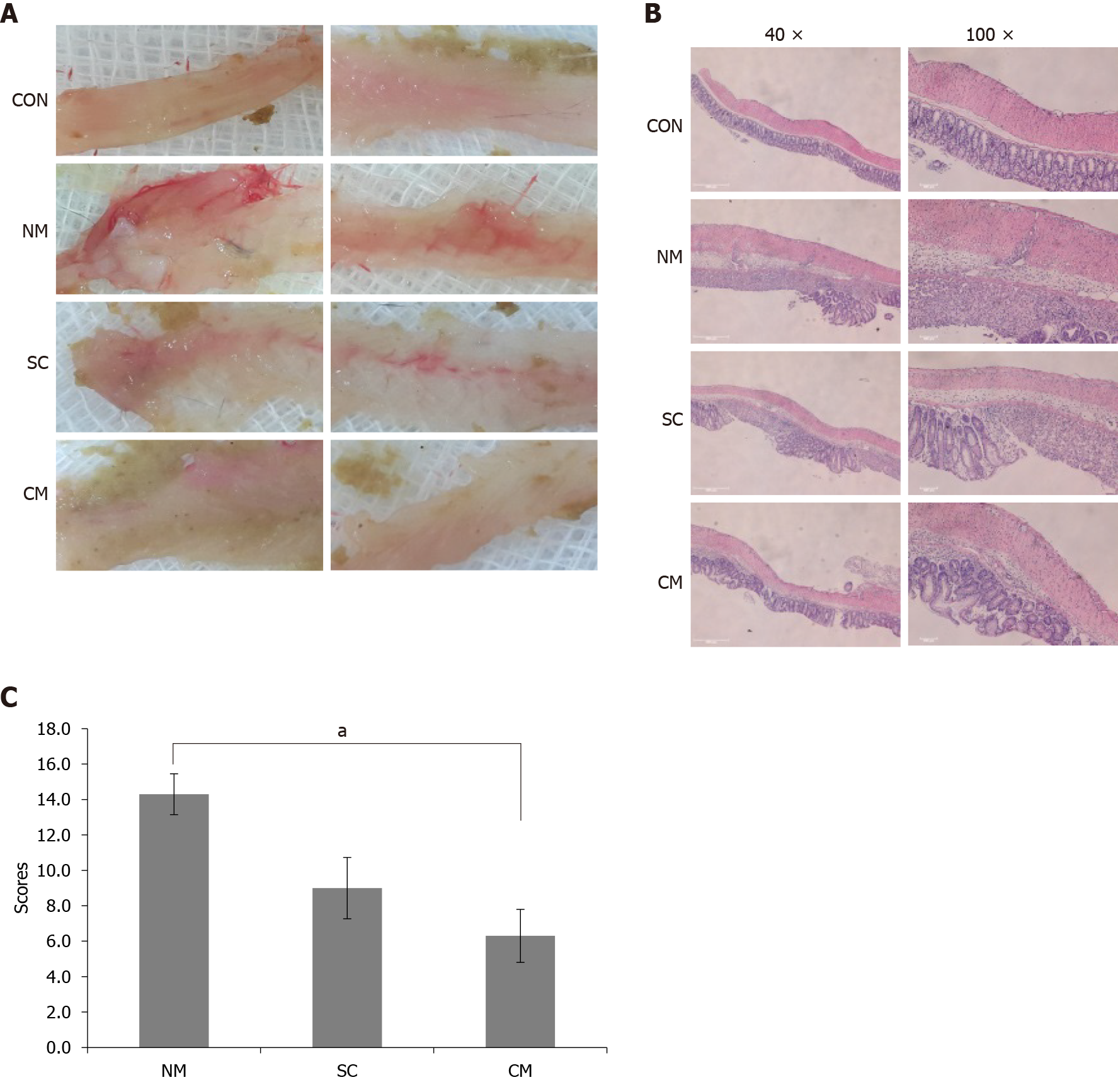
Figure 3 Effects of conditioned mouse adipose-derived stem cells secretome on damage of colon tissues in dextran sulfate sodium-induced mice.
A: Macroscopic appearance of colon tissues; B: Representative hematoxylin and eosin stained sections of damaged colon tissues are shown on magnification, 40 × or 100 ×; C: The damage of colon tissues was assessed by histological score. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 4-6 mice per group). aP < 0.05. CON: Control; NM: Normal culture medium; SC: Mouse adipose-derived stem cells (mADSCs); CM: Conditioned mADSCs secretome.
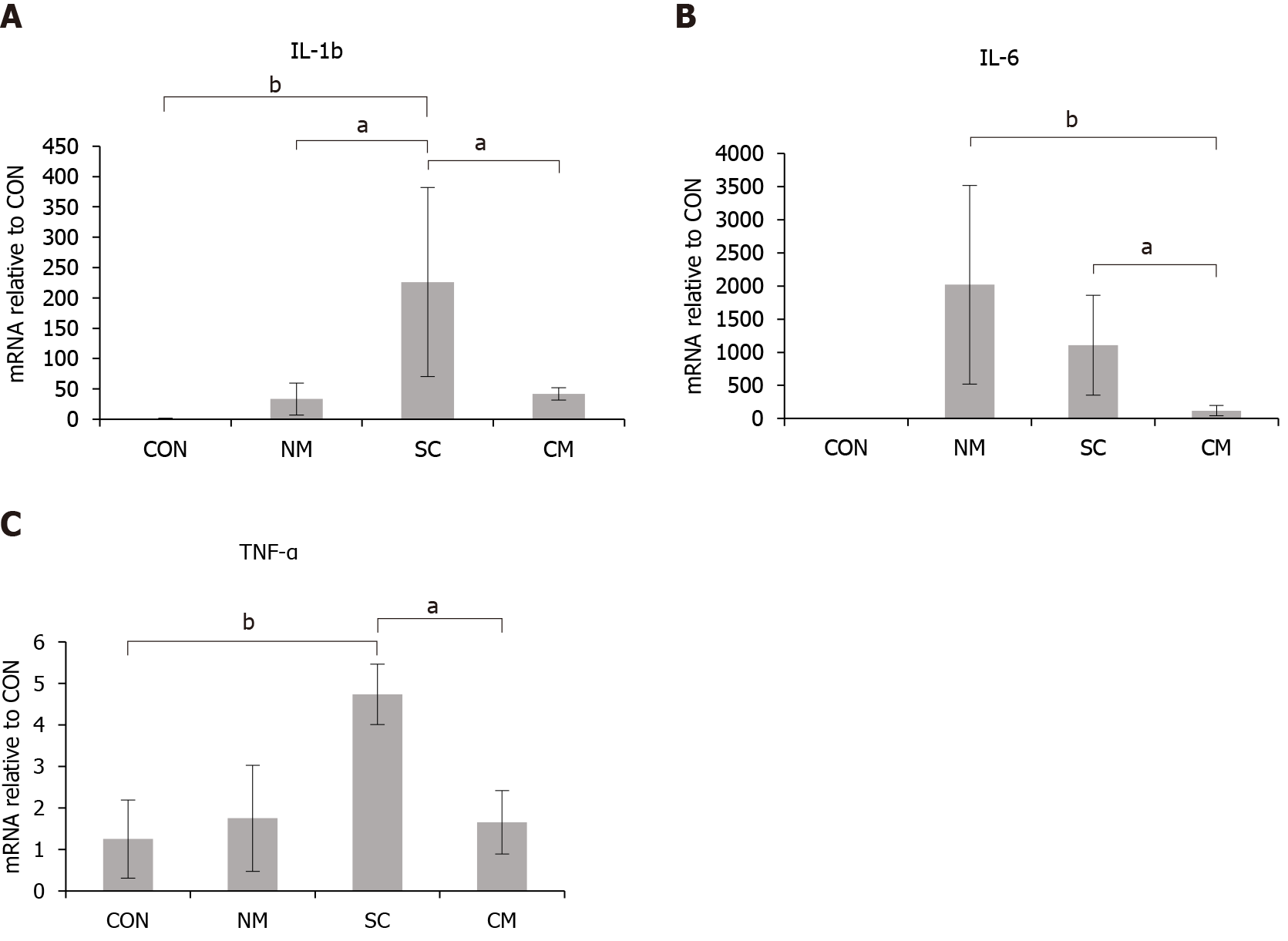
Figure 4 Effects of the conditioned mouse adipose-derived stem cells secretome on the expression of inflammatory cytokines in colon tissues of dextran sulfate sodium-induced mice on day 11.
The mRNA expression levels of inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-1b, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were evaluated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. The mRNA expression levels in normal culture medium, mouse adipose-derived stem cells (mADSCs) or conditioned mADSCs secretome were represented as the relative values to the expression levels in control. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 4-6 mice per group). A: IL-1b; B: IL-6; C: TNF-α. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.005. CON: Control; NM: Normal culture medium; SC: Mouse adipose-derived stem cells (mADSCs); CM: Conditioned mADSCs secretome; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
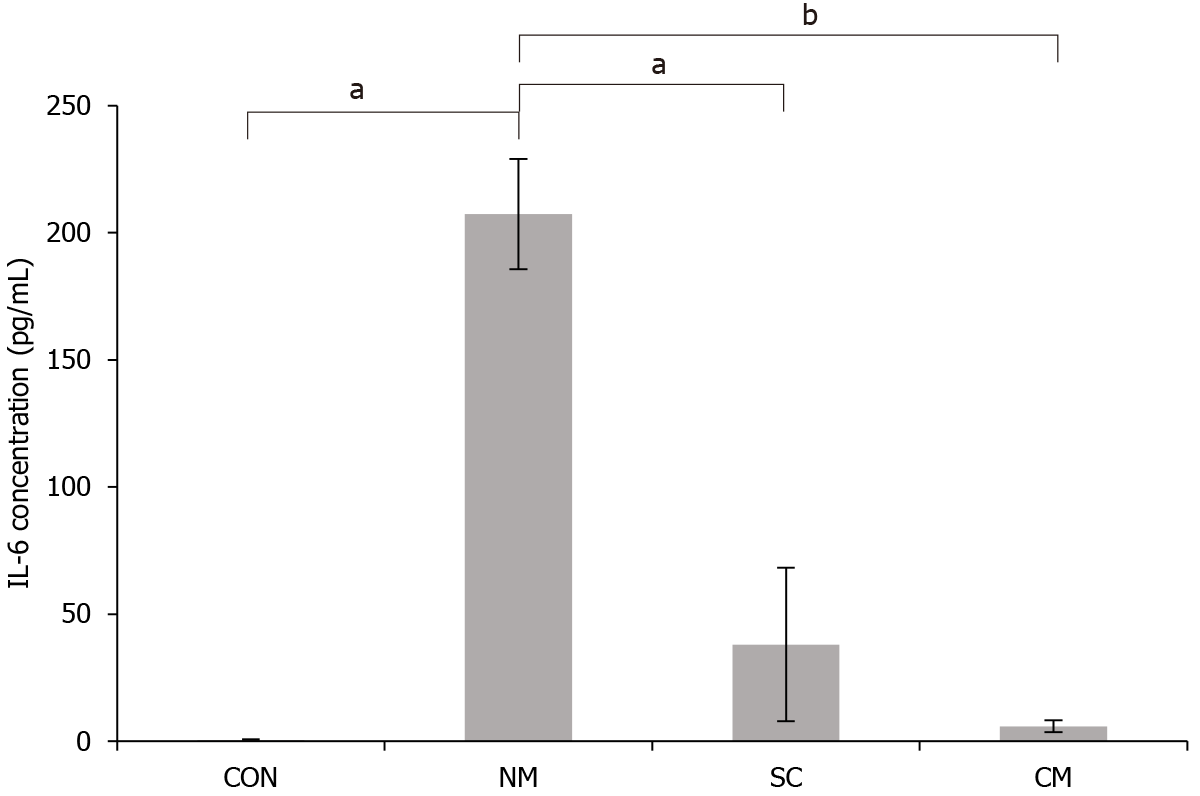
Figure 5 Effects of conditioned mouse adipose-derived stem cells secretome on the concentration of interleukin-6 in serum of dextran sulfate sodium-induced mice on day 11.
The concentration of interleukin-6 in serum was evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 4-6 mice per group). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.005. CON: Control; NM: Normal culture medium; SC: Mouse adipose-derived stem cells (mADSCs); CM: Conditioned mADSCs secretome; IL-6: Interleukin-6.
- Citation: Lee S, Heo J, Ahn EK, Kim JH, Kim YH, Chang HK, Lee SJ, Kim J, Park SJ. Conditioned secretome of adipose-derived stem cells improves dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(23): 3342-3356
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i23/3342.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3342