Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2021; 27(16): 1738-1750
Published online Apr 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i16.1738
Published online Apr 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i16.1738
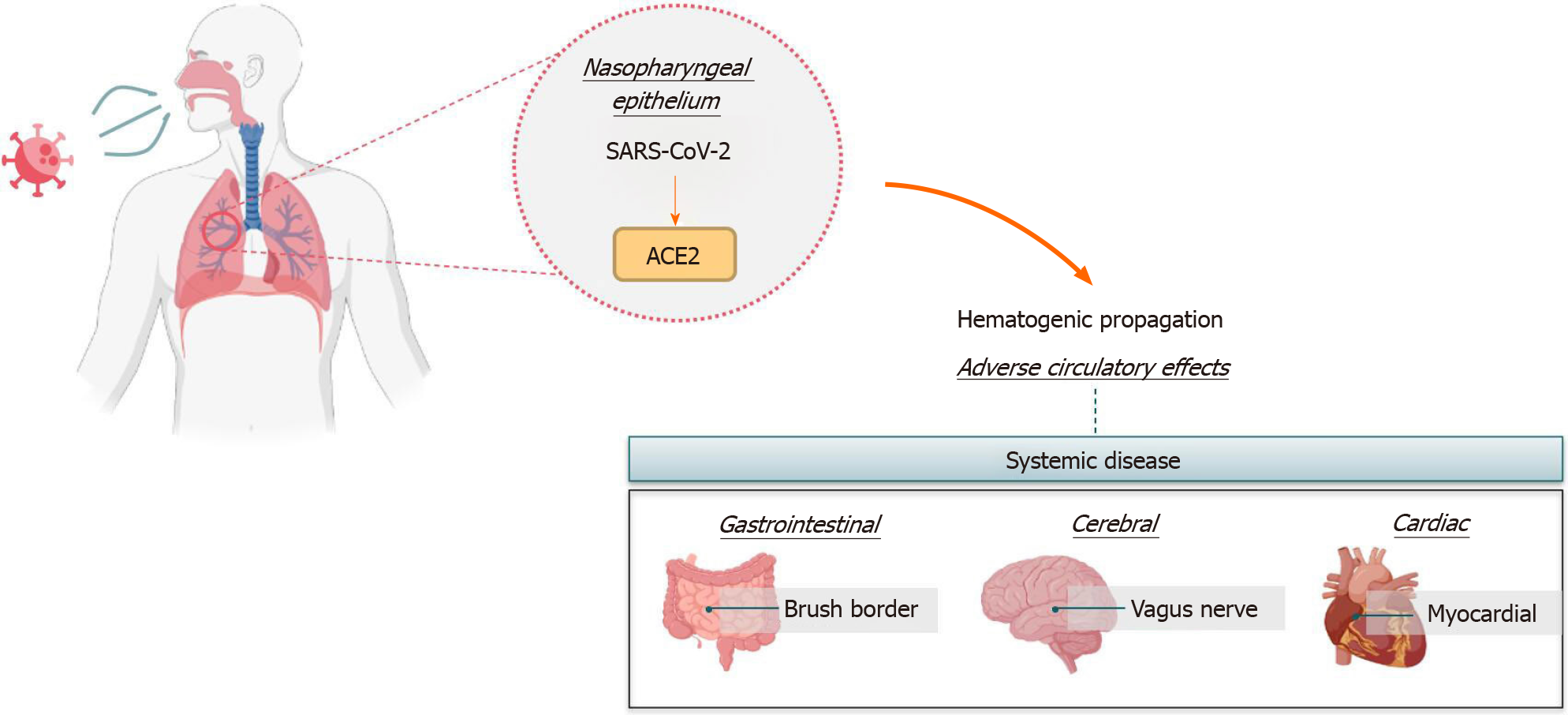
Figure 1 Most common infection and propagation pathways of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in the human body.
SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.
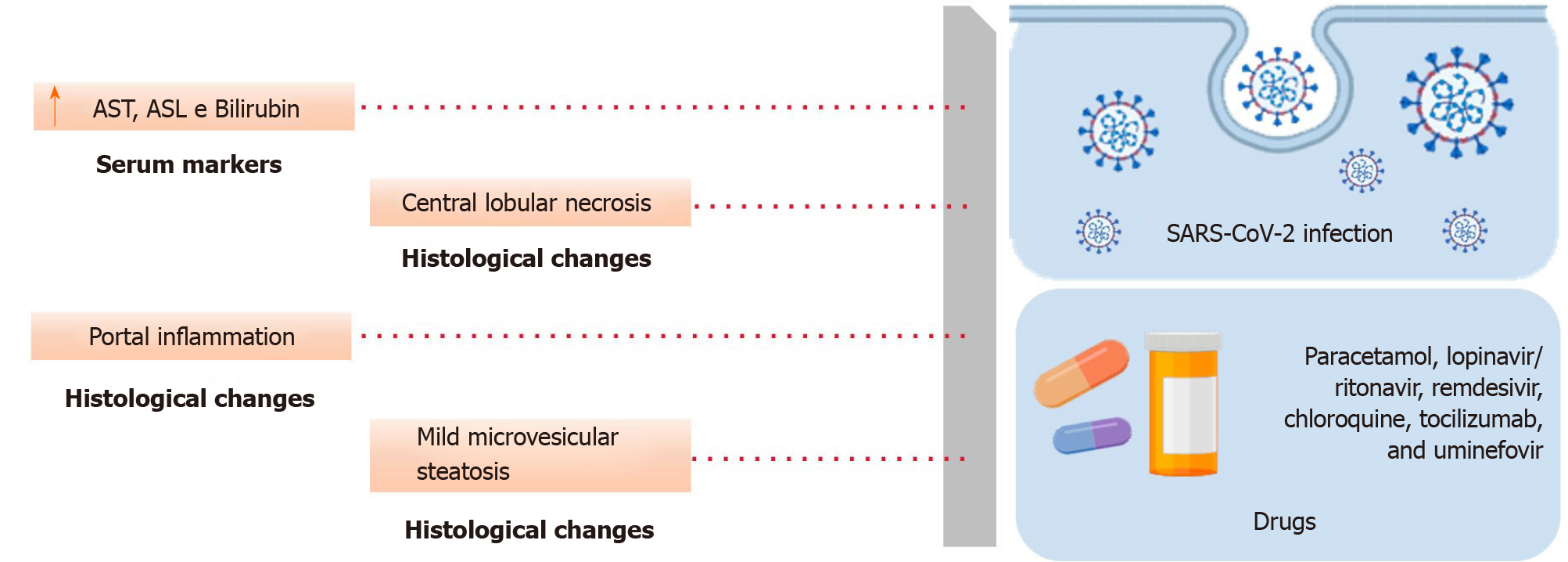
Figure 2 Clinical features and hepatological changes due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection (upper panel) and hepatotoxic effects of some drugs used as an attempt to treat coronavirus disease 2019 (lower panel).
SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase.
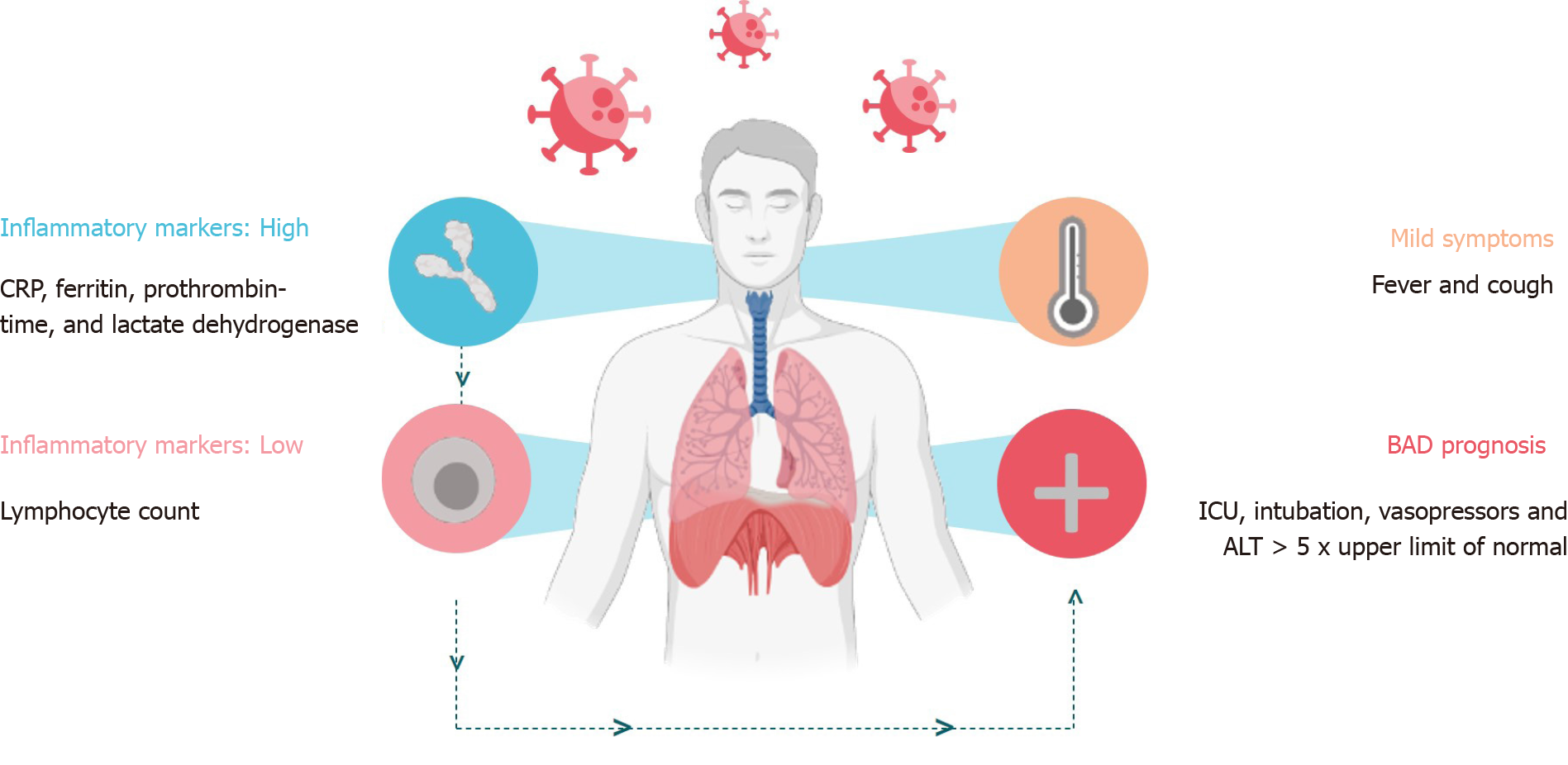
Figure 3 Mild symptoms, inflammatory markers, and serious developments of coronavirus disease 2019.
ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; CRP: C reactive protein; ICU: Intensive care unit.
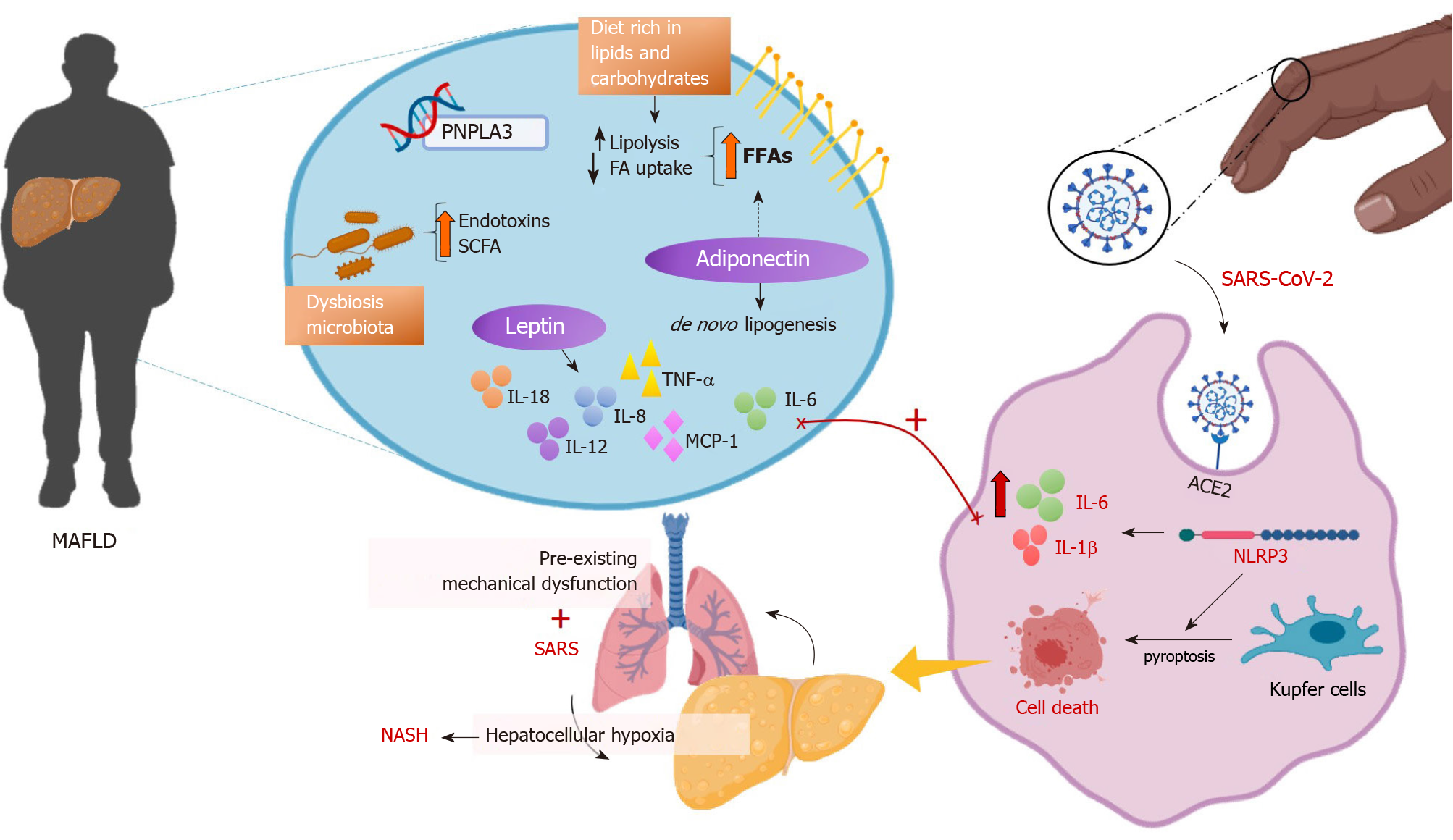
Figure 4 Graphical abstract.
Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) patients usually show a constellation of metabolic impairments that include altered adipokine profile, glucolipotoxicity with ectopic lipid accumulation, and gut dysbiosis, besides a genetic background that favors these hepatic alterations and pre-existing mechanical lung dysfunction when obese. These clinical conditions before coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection can aggravate the cytokine storm syndrome, with activation of macrophages that reside in the liver (Kupffer cells), resulting in inflammasome activation and cell death by pyroptosis. MAFLD patients are at high risk of complications and severe COVID-19 clinical course, with frequent mechanical ventilation, prolonged hospitalizations, and extended viral shedding. Upon survival, COVID-19 may act as a surrogate for MAFLD-non-alcoholic steatohepatitis progression, and hepatocellular hypoxia seems to underlie this process. ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; FFA: Free Fatty Acid; IL: Interleukin; MAFLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease; MCP1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; NASH: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; NEFAs: Non-esterified fatty acids; NLRP: NLR family pyrin domain-containing; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; SCFA: Short-chain fatty acid; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor.
- Citation: Vasques-Monteiro IML, Souza-Mello V. Coronavirus disease 2019 severity in obesity: Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in the spotlight. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(16): 1738-1750
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i16/1738.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i16.1738