Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2020; 26(30): 4489-4500
Published online Aug 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i30.4489
Published online Aug 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i30.4489
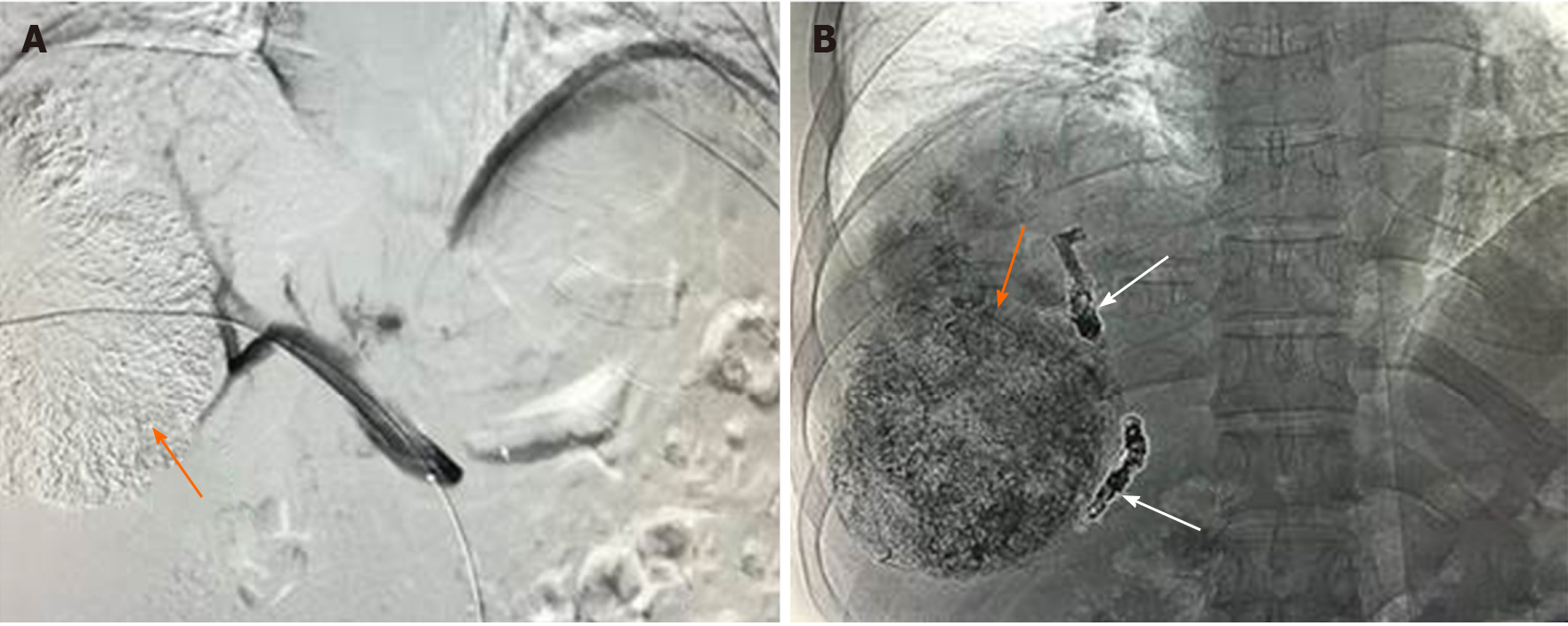
Figure 1 Transarterial chemoembolization and portal vein embolization.
A: Transarterial chemoembolization in a patient with large hepatocellular carcinoma in the right liver lobe (orange arrow); B: Coils (white arrow) and polyvinyl alcohol particles were used for portal vein embolization in the same patient.
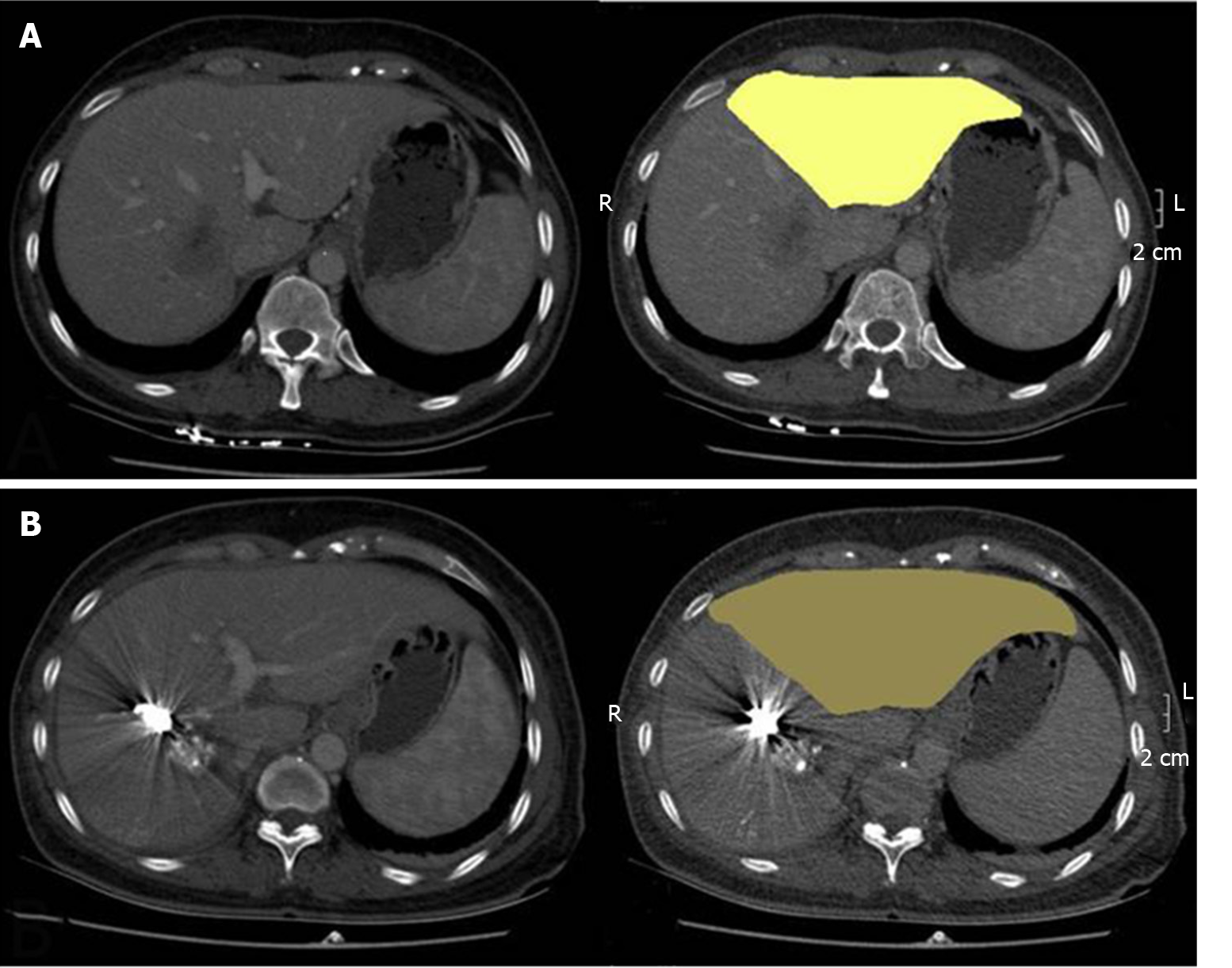
Figure 2 Future liver remnant volume of a patient was only 391 mL before simultaneous transarterial chemoembolization and portal vein embolization (A) and increased to 574 mL later by nearly 46% (B).
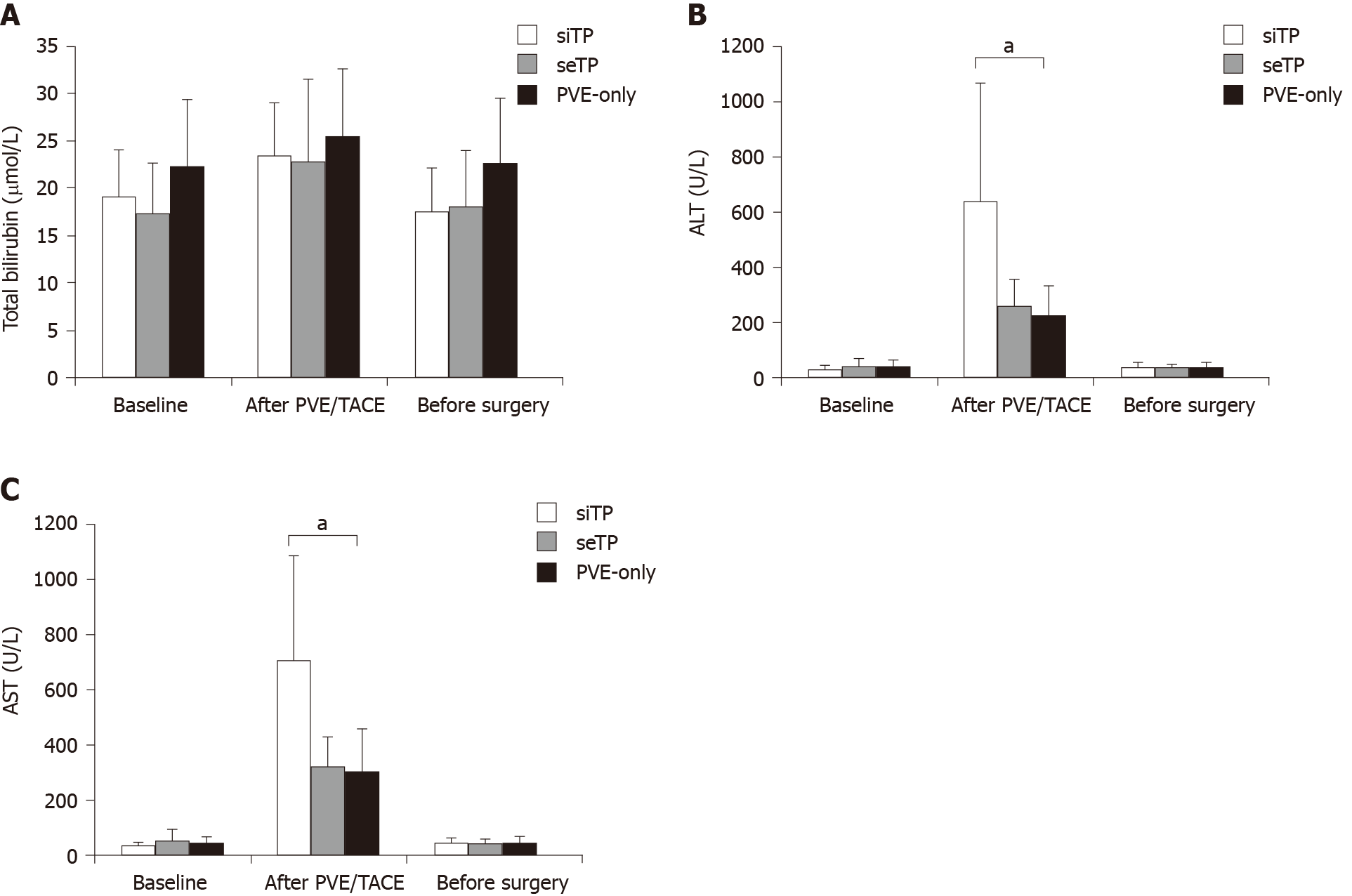
Figure 3 Liver function levels of the three groups from baseline to surgery (A-C).
aP < 0.05 among the groups. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; PVE: Portal vein embolization; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization.
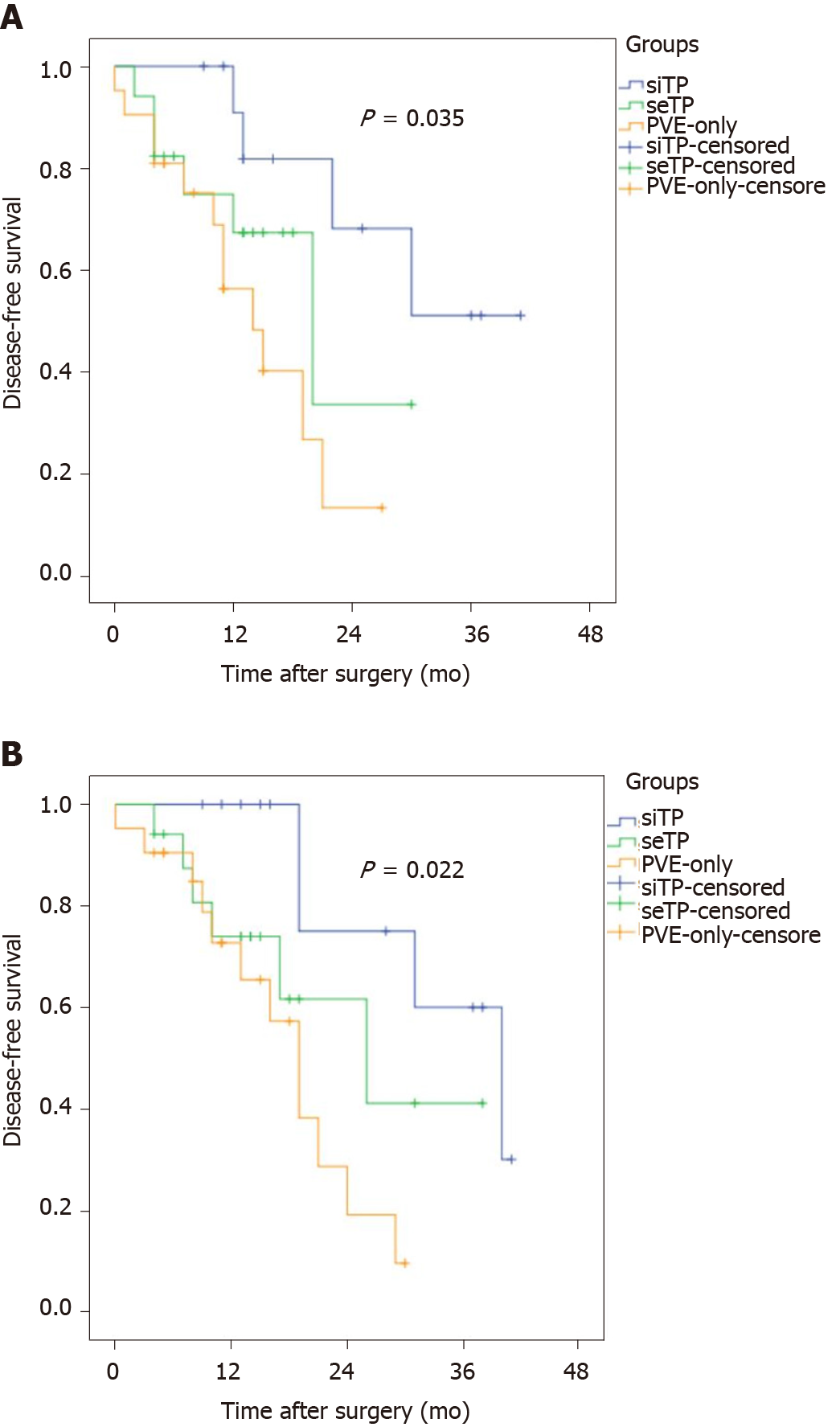
Figure 4 Disease-free survival (A) and overall survival (B) after major hepatectomy in patients with large hepatocellular carcinoma who underwent simultaneous transarterial chemoembolization + portal vein embolization, sequential transarterial chemoembolization + portal vein embolization, or portal vein embolization only.
TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization; PVE: Portal vein embolization.
- Citation: Zhang CW, Dou CW, Zhang XL, Liu XQ, Huang DS, Hu ZM, Liu J. Simultaneous transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and portal vein embolization for patients with large hepatocellular carcinoma before major hepatectomy. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(30): 4489-4500
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i30/4489.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i30.4489