Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2020; 26(29): 4327-4342
Published online Aug 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i29.4327
Published online Aug 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i29.4327
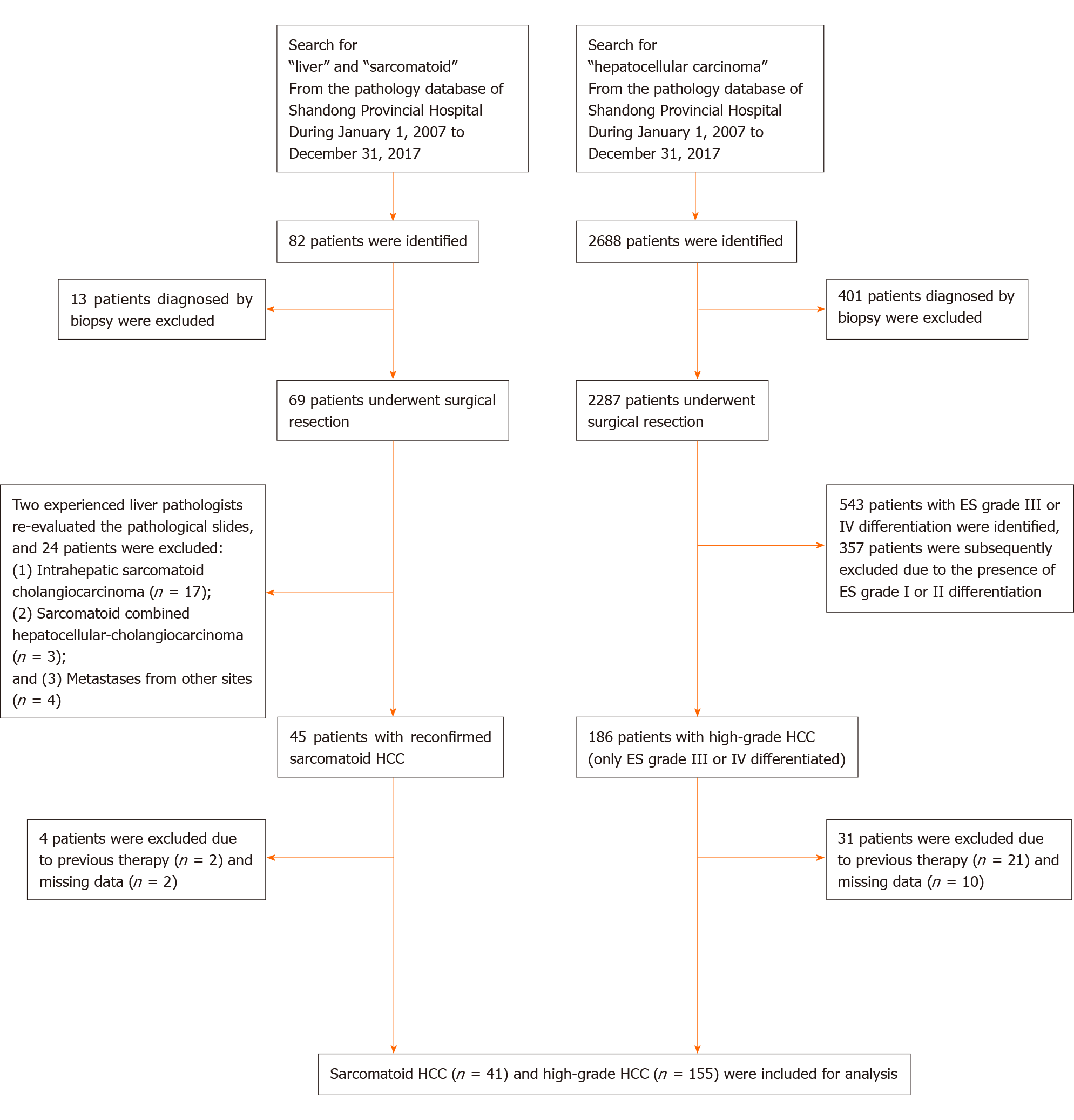
Figure 1 Flowchart of patient selection.
ES: Edmondson-Steiner; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
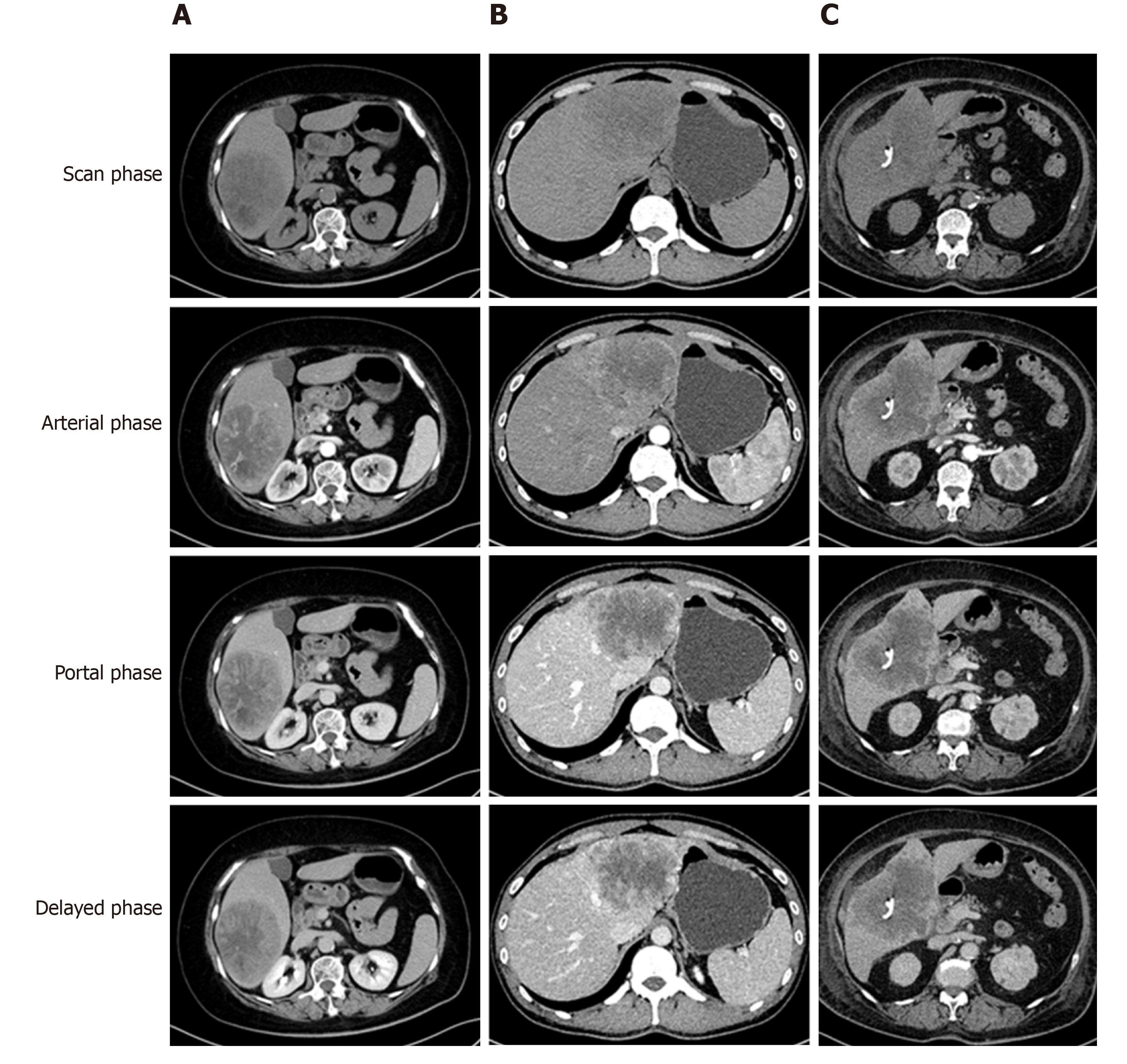
Figure 2 Imaging findings of sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with various initial diagnoses based on radiologic findings.
A: Hepatocellular carcinoma; B: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; C: Hepatic abscess.
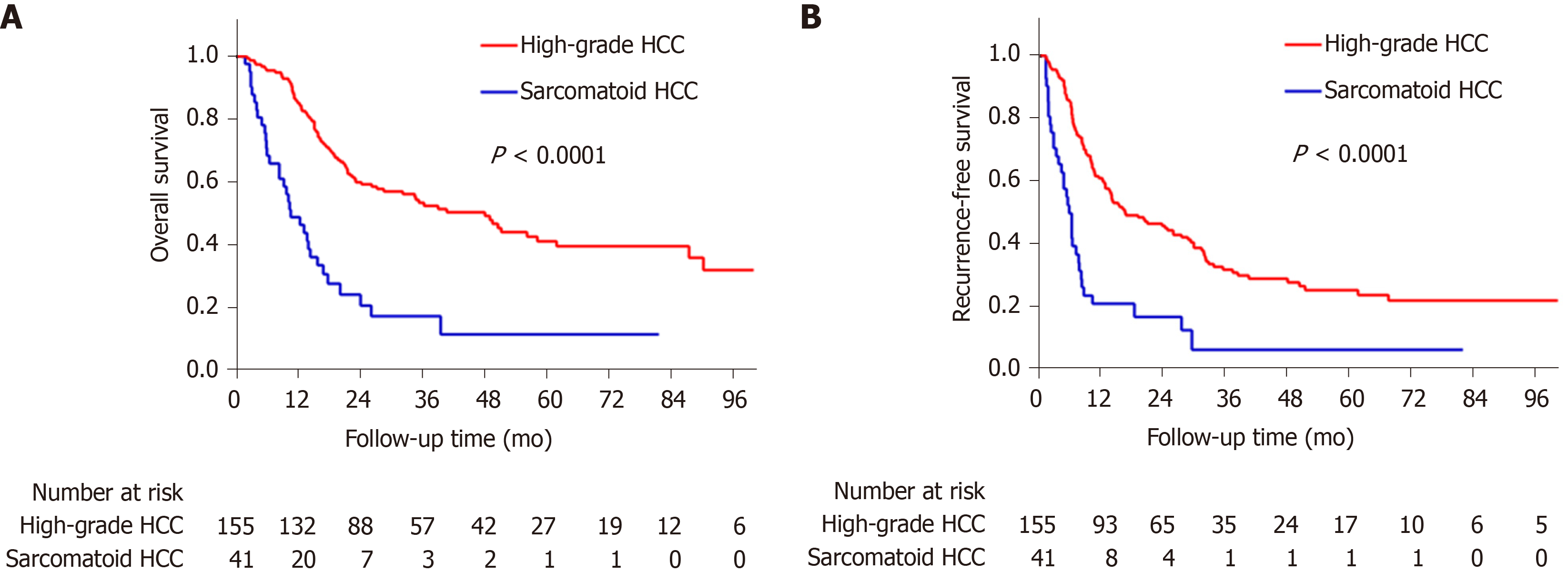
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier estimated overall and recurrence-free survival curves.
A: Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is associated with worse overall survival (log-rank P < 0.0001); B: Sarcomatoid HCC is associated with worse recurrence-free survival (log-rank P < 0.0001).
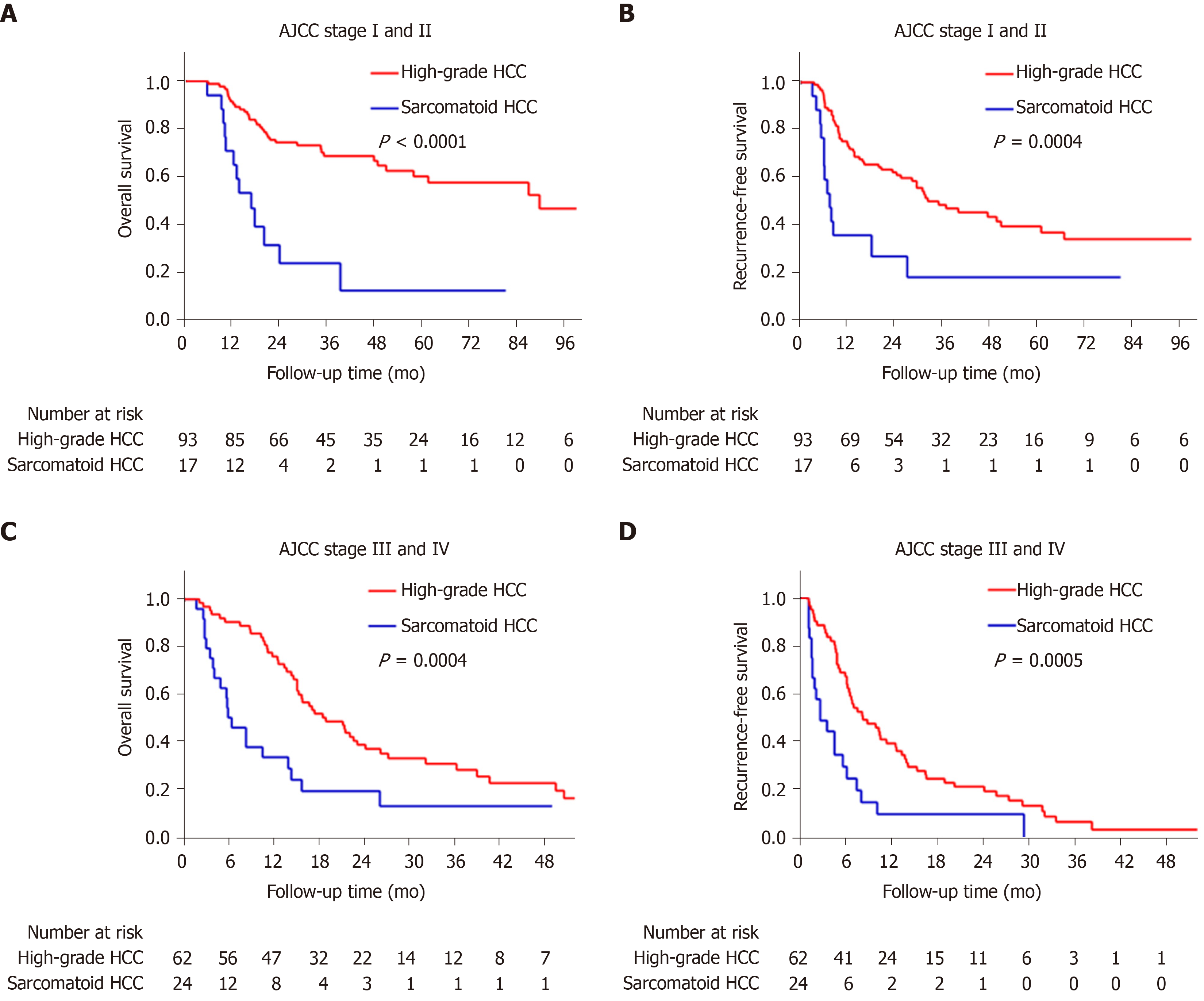
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier curves of the estimated overall survival and recurrence-free survival of patients with sarcomatoid or high-grade hepatocellular carcinoma stratified by American Joint Committee on Cancer stage.
A: Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is associated with worse overall survival (OS) in patients with American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage I-II disease (log-rank P < 0.0001); B: Sarcomatoid HCC is associated with worse recurrence-free survival (RFS) in patients with AJCC stage I-II disease (log-rank P = 0.0004); C: Sarcomatoid HCC is associated with worse OS in patients with AJCC stage III-IV disease (log-rank P = 0.0004); D: Sarcomatoid HCC is associated with worse RFS in patients with AJCC stage III-IV disease (log-rank P = 0.0004).
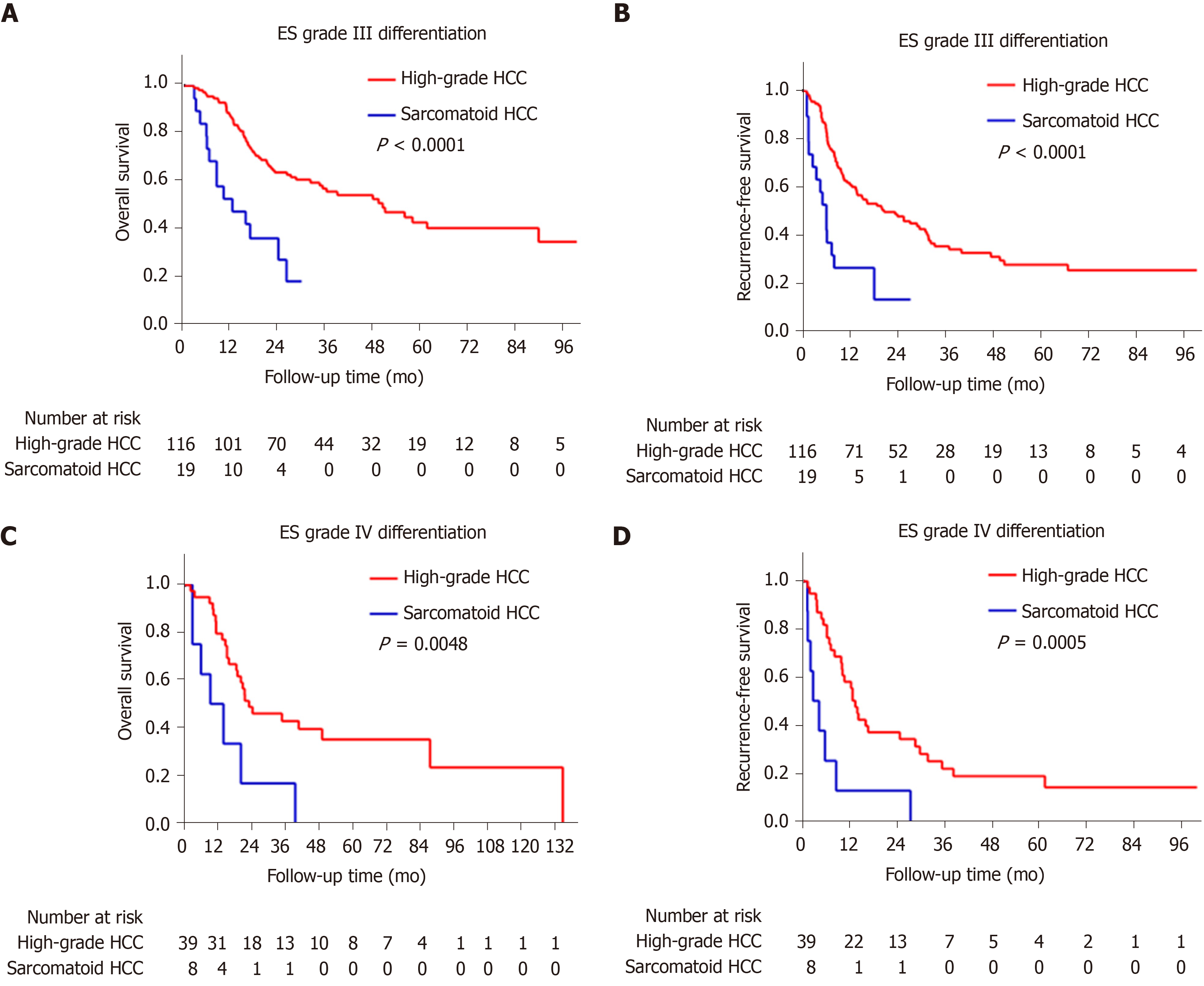
Figure 5 Kaplan-Meier curves of the estimated overall survival and recurrence-free survival of patients with sarcomatoid or high-grade hepatocellular carcinoma stratified by differentiation grade of the carcinomatous component.
A: Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is associated with worse overall survival (OS) in patients with Edmondson-Steiner (ES) grade III differentiation (log-rank P < 0.0001); B: Sarcomatoid HCC is associated with worse recurrence-free survival (RFS) in patients with ES grade III differentiation (log-rank P < 0.0001); C: Sarcomatoid HCC is associated with worse OS in patients with ES grade IV differentiation (log-rank P = 0.0048); D: Sarcomatoid HCC is associated with worse RFS in patients with ES grade IV differentiation (log-rank P = 0.0005).
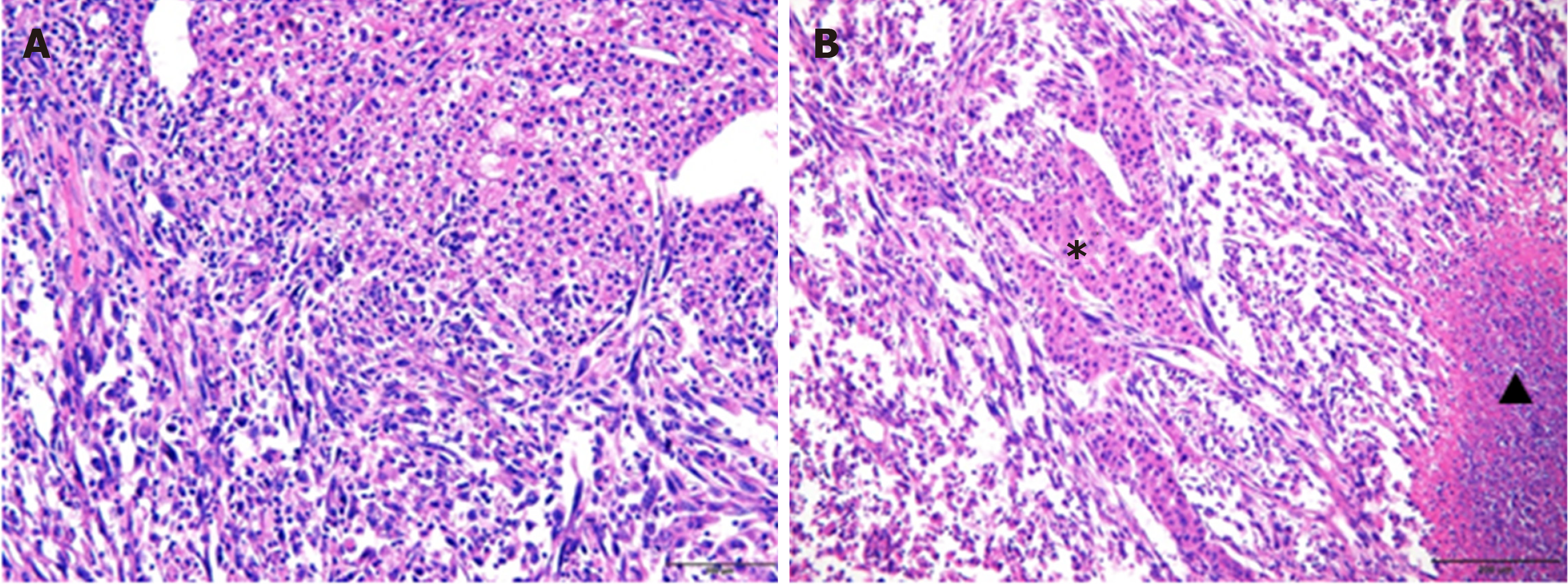
Figure 6 Pathological findings of sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: The lower left area of the image shows the sarcomatous change, with spindle-shaped cells forming interlacing bundles. The upper right region represents conventional hepatocellular carcinoma, with tumor cells at Edmondson-Steiner (ES) grade II differentiation (hematoxylin & eosin staining, × 200 magnification). (B) Scattered patchy carcinomatous components with ES grade III differentiation in sarcomatous regions (Hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 100 magnification). Star: Carcinomatous components, Triangle: Tumor necrosis.
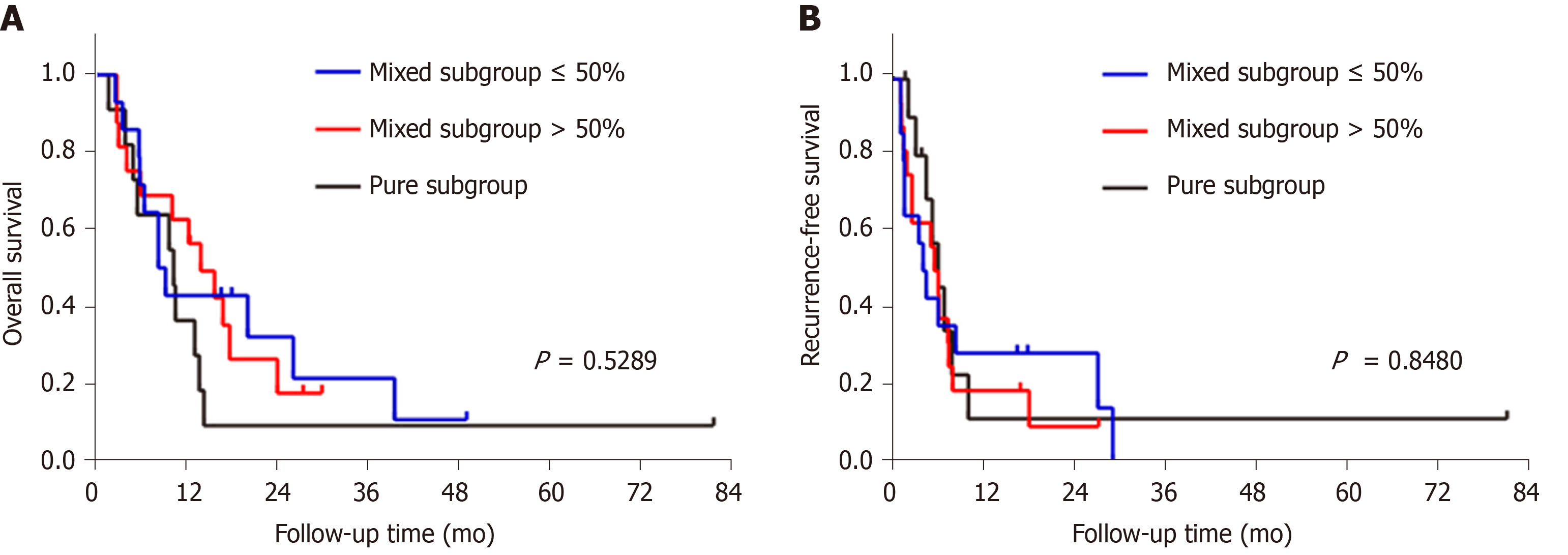
Figure 7 Kaplan-Meier curves of the estimated overall survival and recurrence-free survival of patients with sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma stratified by the proportion of the sarcomatous component in the tumor.
Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma patients were divided into three subgroups based on the proportion of the sarcomatous component in the tumor: (1) mixed subgroup ≤ 50% (n = 14); (2) mixed subgroup > 50% (n = 16); and (3) pure subgroup (n = 11). Kaplan-Meier analyses of (A) overall survival and (B) recurrence-free survival showed no differences among the three subgroups.
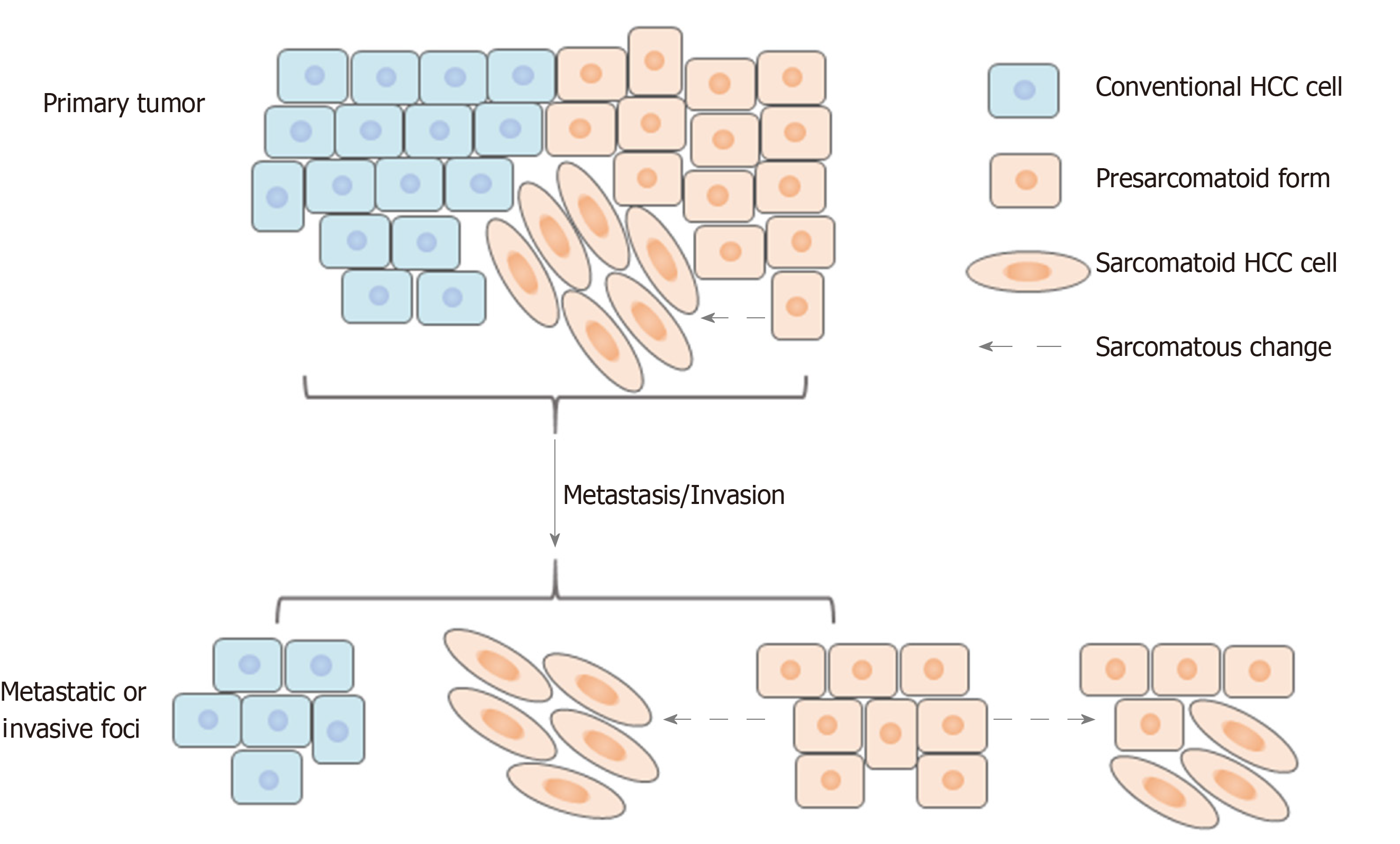
Figure 8 Schematic of the hypothesis.
HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Wang JP, Yao ZG, Sun YW, Liu XH, Sun FK, Lin CH, Ren FX, Lv BB, Zhang SJ, Wang Y, Meng FY, Zheng SZ, Gong W, Liu J. Clinicopathological characteristics and surgical outcomes of sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(29): 4327-4342
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i29/4327.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i29.4327