Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2019; 25(5): 584-599
Published online Feb 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i5.584
Published online Feb 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i5.584
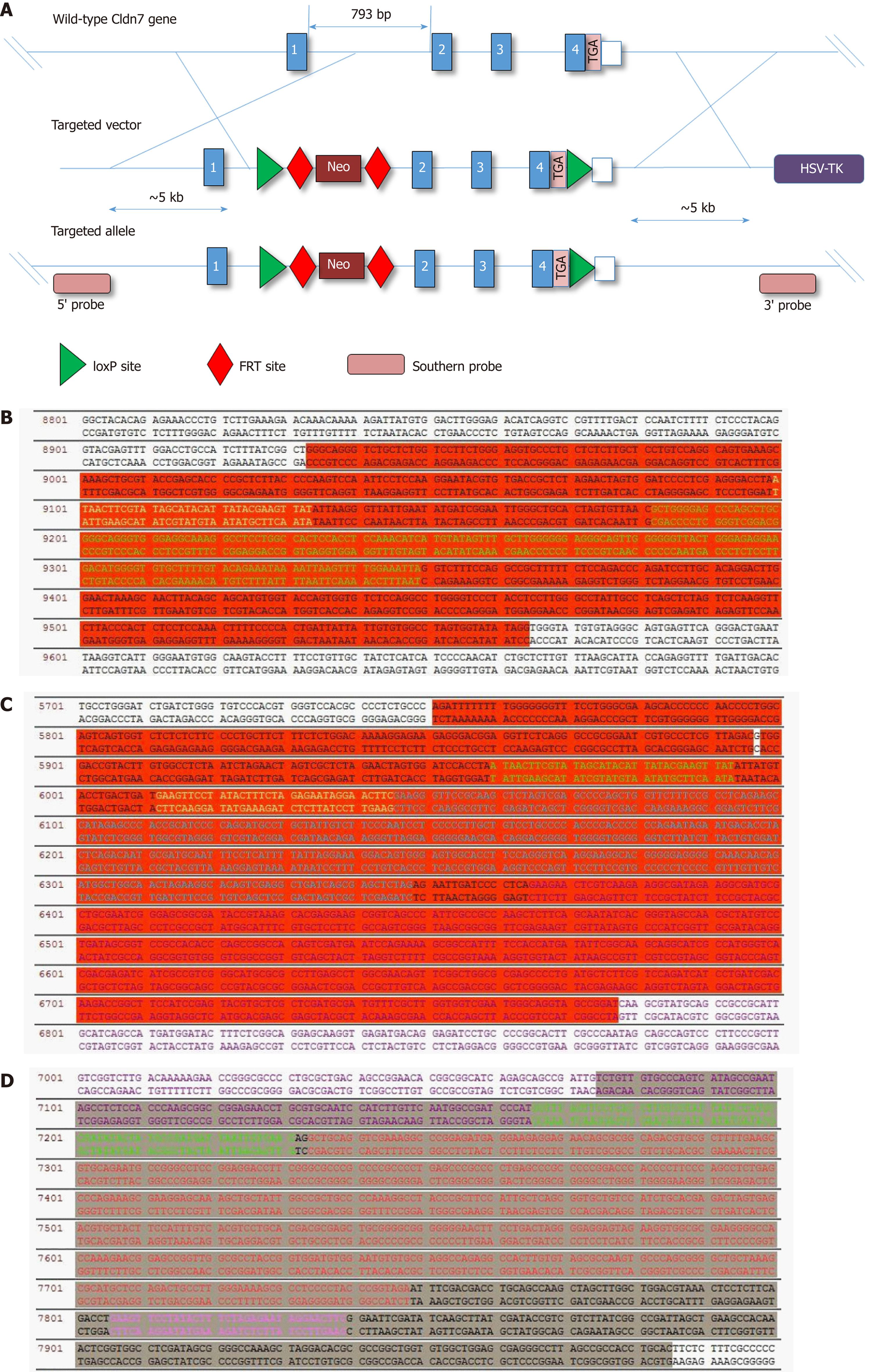
Figure 1 Strategic design and final vector sequencing results.
A: Schematic diagram of the Cldn7 gene knockout targeting vector; B-D: The first and second regions in red show the sequencing results at LoxP and FRT 5’, while the grey region shows the FRT 3’ sequencing results; B-D indicate that the Cldn7 targeting vector was correct. Cldn7: Claudin-7.
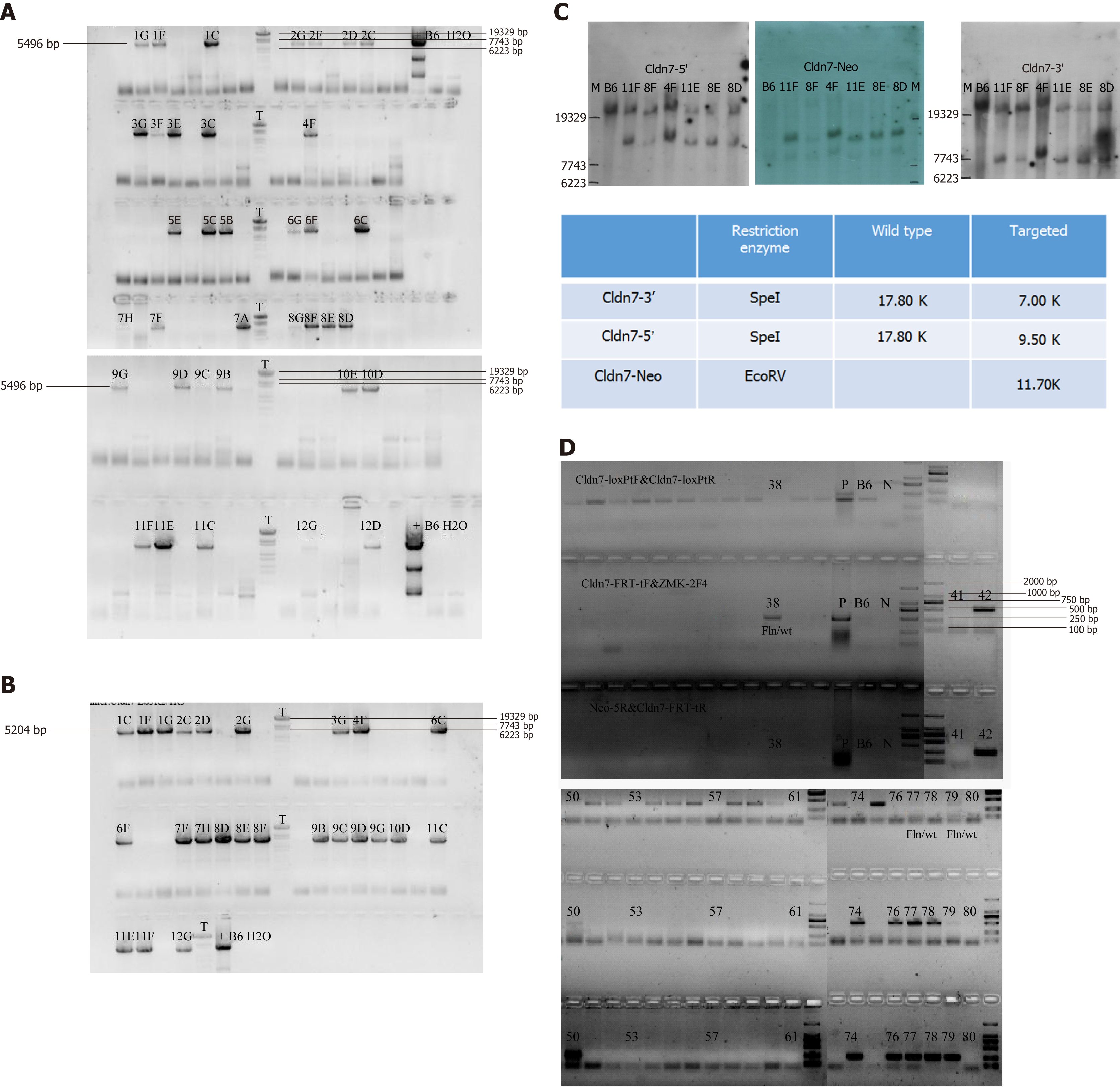
Figure 2 Long range PCR and Southern blot for detecting target clones.
A: The 5’ homologous arm band was first detected, and the product with a length of 5496 bp was a positive clone containing LoxP; B: The 3’ end was then detected, and the product with a length of 5204 bp was a positive clone; C: Southern blot results showing that clones 8D, 8E, 4F, 11E, and 11F were the final targeted clones; D: After blastocyst transfer, newborn mice were genotyped by PCR. The mice numbered 50 and 77 were deemed chimeric mice with the genotype fln/wt.
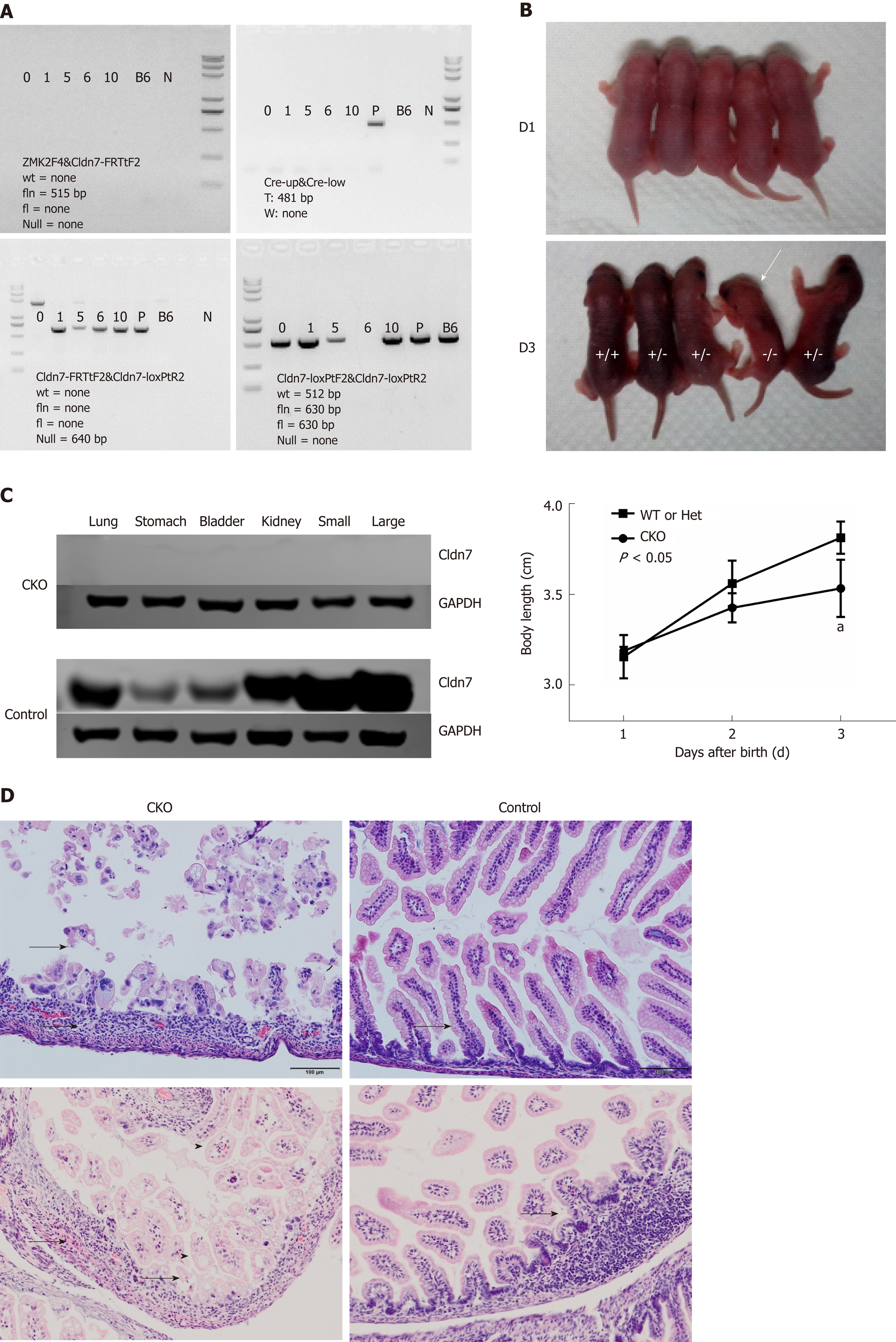
Figure 3 Phenotypic and intestinal pathological changes in Cldn7 CKO mice.
A: Genotype analysis showed that No. 6 mouse was a Cldn7 CKO mouse with the genotype Null/Null CreW. Marker: 8000/5000/3000/2000/1000/750/500/250/100 bp; B: Cldn7 CKO mice were similar to control mice at birth but grew slower than control mice (P < 0.05); from the third day, CKO mice appeared in a dying state; C: CKO mice expressed no Cldn7 in any tissues, while all tissues of control mice expressed Cldn7; D: Intestinal HE staining in Cldn7 CKO mice showed obvious atrophy of intestinal mucosa with inflammatory cell infiltration (as indicated by the arrow), villus shortening, and lymphatic expansion (as indicated by the arrowhead); the control mice showed no obvious histopathological changes (as indicated by the arrow). Cldn7: Claudin-7; CKO: Conventional knockout.
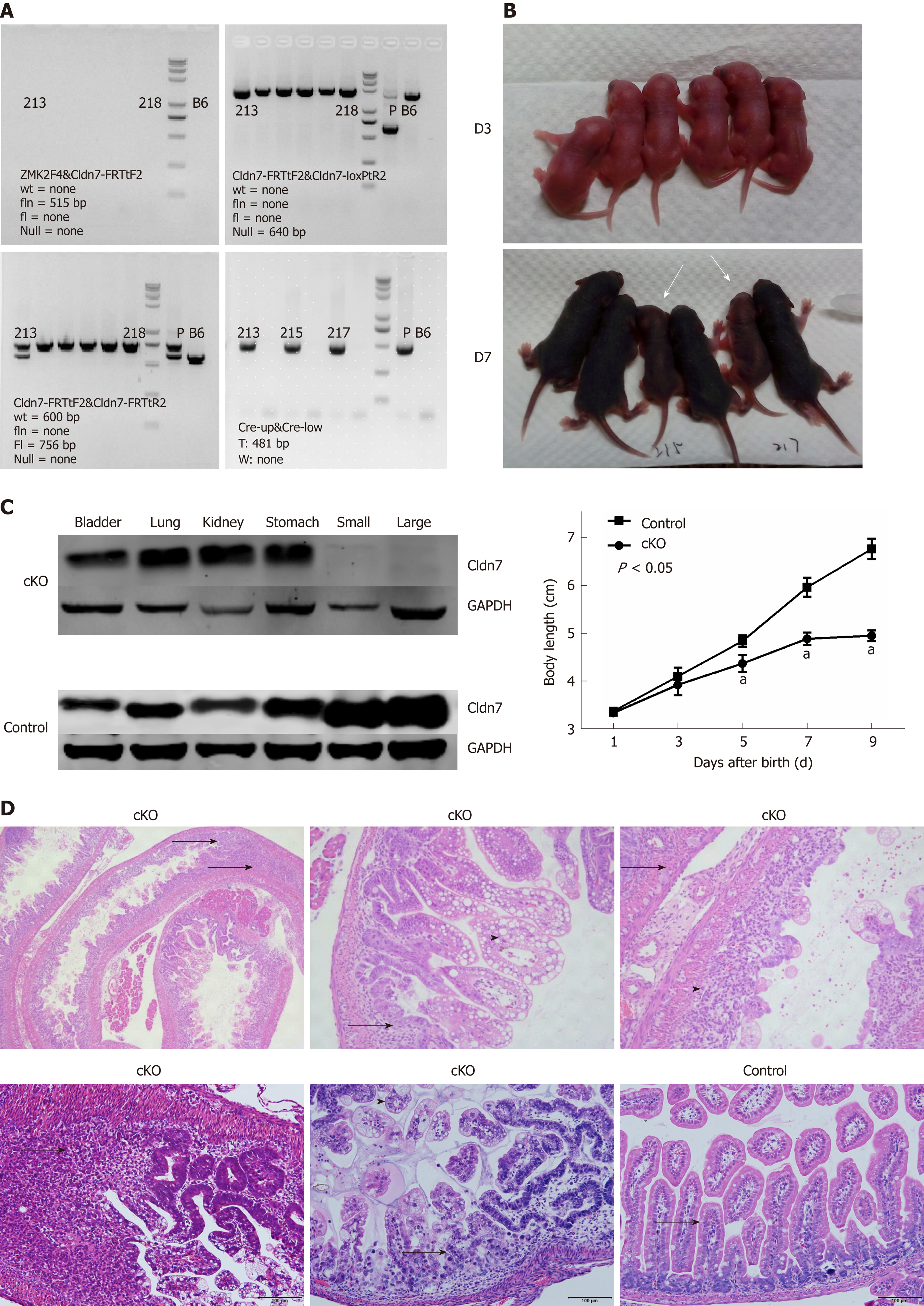
Figure 4 Phenotypic and intestinal pathological changes in Cldn7 cKO mice.
A: Genotype analysis showed the mice numbered 215 and 217 were intestinal specific Cldn7 cKO mice with the genotype Cldn7fl/fl; villin-CreT; B: Cldn7 cKO mice were normal at birth, but their body lengths increased more slowly from the fifth day after birth than those of control mice (P < 0.05); on the 9th day, cKO mice were in poor spirits and died thereafter; C: Cldn7 expression was normal in the lung, stomach, bladder ,and kidney tissues of cKO mice but absent in the small and large intestines; all tissues of the control mice expressed Cldn7; D: Intestinal hematoxylin-eosin staining in Cldn7 cKO mice showed connective tissue hyperplasia with extensive inflammatory cell infiltration in the submucosa (as indicated by the arrow); mucosal epithelial vacuolar degeneration can be observed after magnification (as indicated by the arrowhead); there were no obvious histopathological changes in fl/fl CreW mice. Cldn7: Claudin-7; cKO: Conditional knockout.
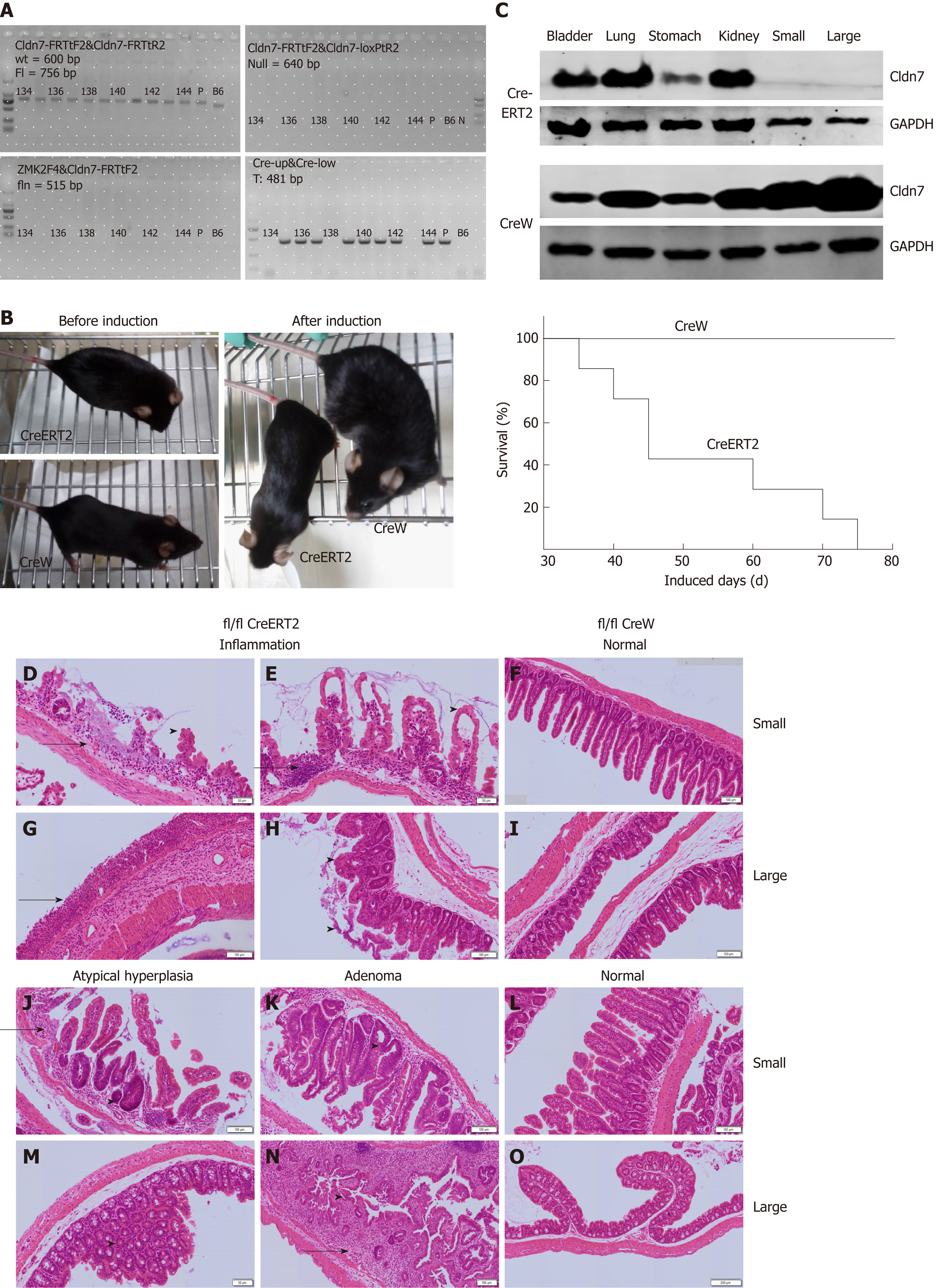
Figure 5 Phenotypic and intestinal pathological changes in Cldn7 ICKO mice.
A: Genotype analysis showed that mice numbered 135-137, 139-142, and 144 were Cldn7 ICKO mice with the genotype Cldn7fl/fl; villin-CreERT2; B: Cldn7 cKO mice were normal at birth and developed smoothly, but beginning at the 7th injection, ICKO mice were in poor health and appeared to be dying; all ICKO mice died within 15 tamoxifen injections; C: Cldn7 was expressed at normal levels in the lung, stomach, bladder, and kidney tissues of ICKO mice but absent in the small and large intestines; all tissues of the control mice expressed Cldn7; D-O: Intestinal hematoxylin-eosin staining in ICKO mice showed obvious inflammatory manifestations; atypical hyperplasia and intestinal adenoma were also observed; the intestinal structure of the control mice was normal. Tamoxifen was dissolved in sunflower oil at a concentration of 10 mg/mL, and each mouse was intraperitoneally injected at 1 mg every 5 days. Cldn7: Claudin-7; cKO: Conditional knockout; ICKO: Inducible conditional knockout.
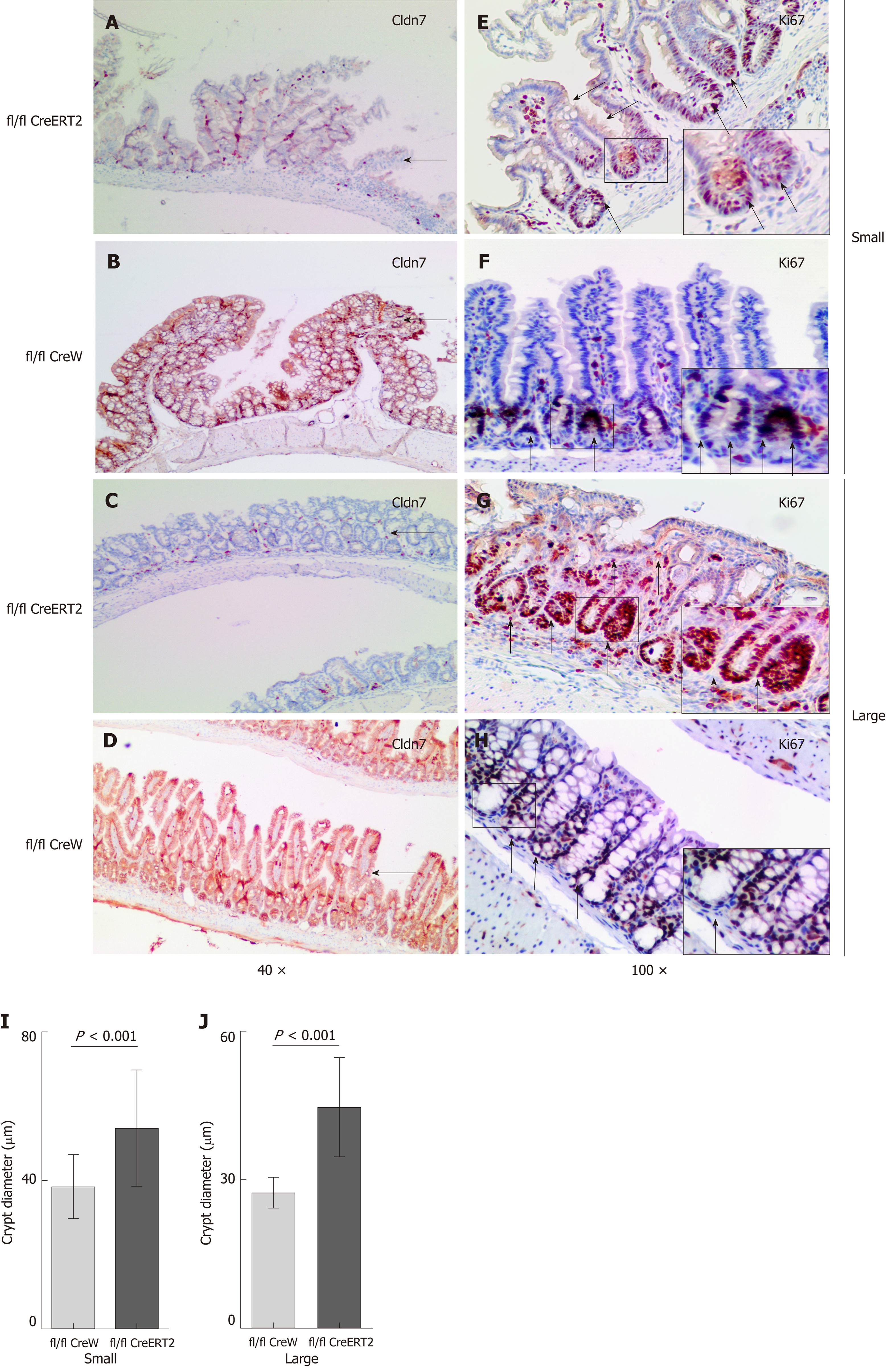
Figure 6 Increased intestinal proliferation in Cldn7 ICKO mice.
A-D: Immunohistochemistry staining showed that Cldn7 was strongly expressed in the intestinal epithelial junctions of control mice but significantly weakened in ICKO mice; E-H: In control mice, Ki67 was mainly distributed in parts of the crypt, while Ki67-positive cells occupied the entire intestinal crypt and could be observed throughout the intestinal villi in ICKO mice; I-J: The size of the intestinal crypt in ICKO mice was increased compared with that in control mice (P < 0.001). Cldn7: Claudin-7; ICKO: Inducible conditional knockout.
- Citation: Xu C, Wang K, Ding YH, Li WJ, Ding L. Claudin-7 gene knockout causes destruction of intestinal structure and animal death in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(5): 584-599
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i5/584.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i5.584