Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2019; 25(25): 3123-3135
Published online Jul 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3123
Published online Jul 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3123
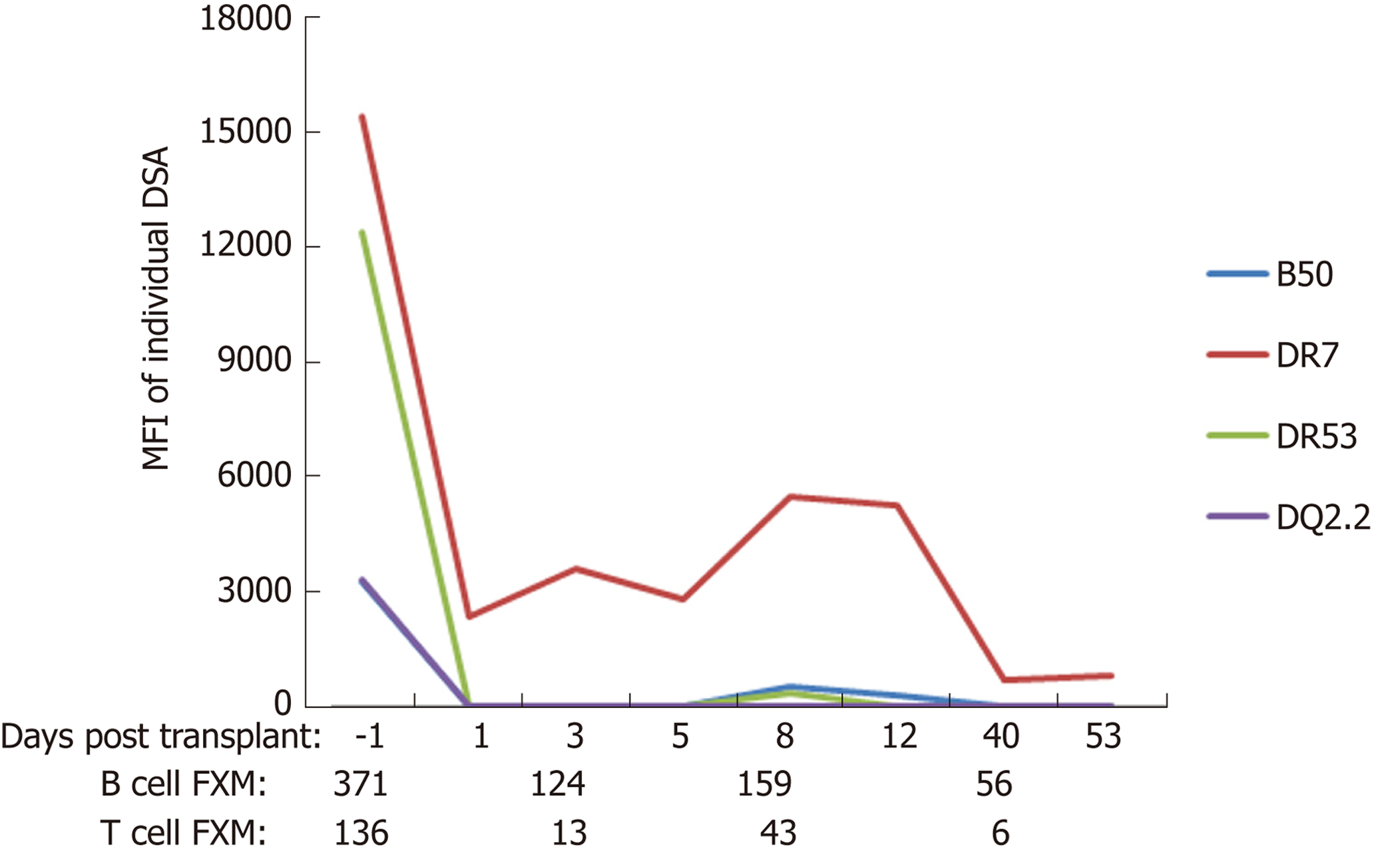
Figure 1 Typical course of donor-specific antibodies and flow cytometric cross match after liver transplant in a patient with fully functional liver allograft who is maintained on triple regimen immunosuppression (tacrolimus, mycophenolate, and prednisone).
DSA: Donor specific antibodies; FXM: Flow cytometric cross match.
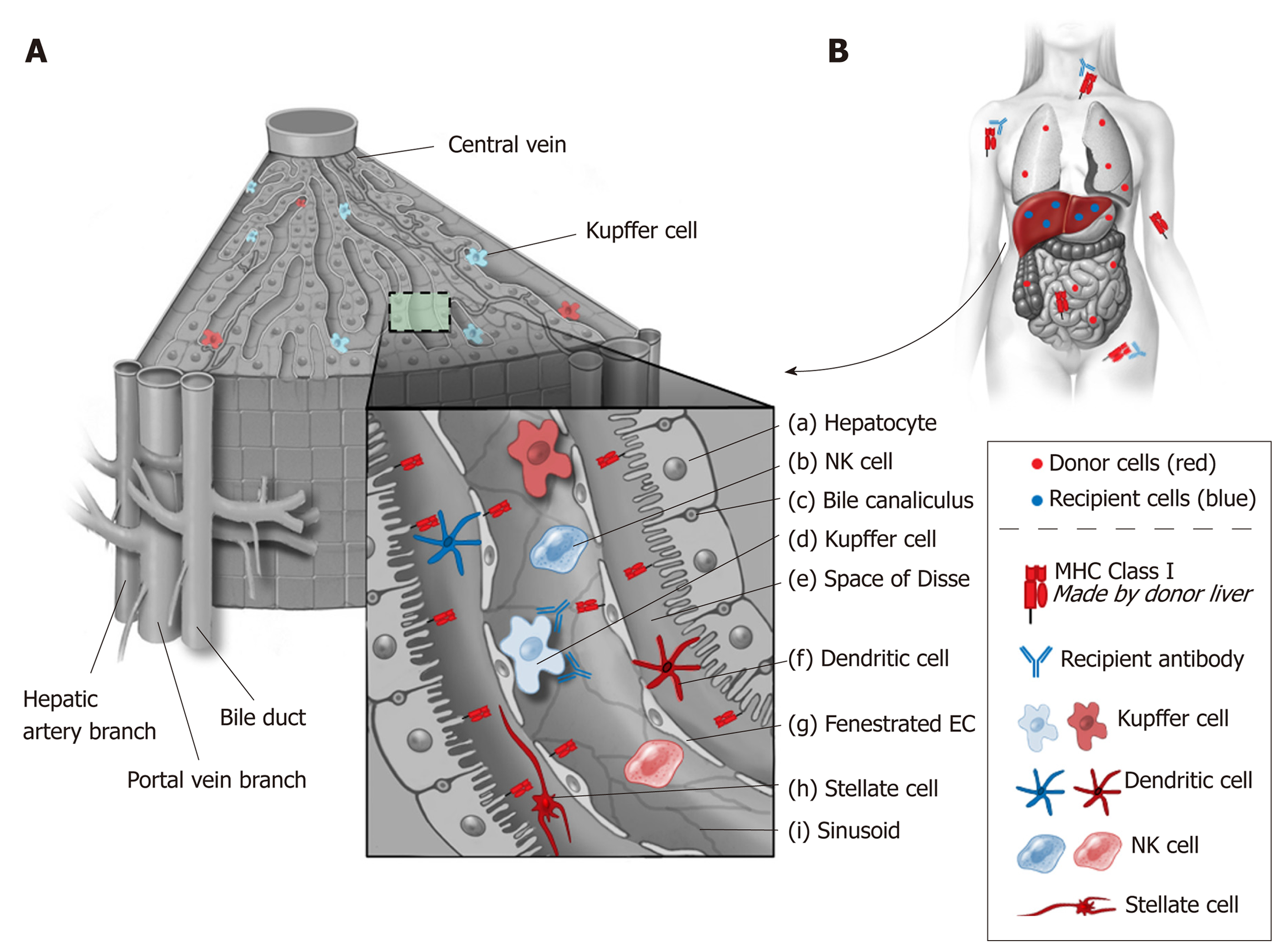
Figure 2 Liver architecture and resident immune cells.
A: The liver’s unique architecture and the large number of passenger immune cells that accompany it during transplant likely play a role in its immunologic activity. Class I major histocompatibility (MHC) antigens are strongly expressed on bile ducts (c) and to a lesser extent on sinusoidal and endothelial cells (g). By contrast, Class II MHC antigens are primarily expressed on capillary endothelium, sinusoidal cells and dendritic cells (f). It is also recognized that cell surface MHC antigens are not static and can change in response to host and allograft dynamics such as infection and rejection; B: Liver transplants secrete soluble class I MHC antigens that bind and neutralize systemically circulating antibodies. Kupffer cells (d) also are involved in neutralization of antibodies. As such, liver allografts are thought to function as sinks for circulating immune complexes. EC: Endothelial cell; NK: Natural killer; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex.
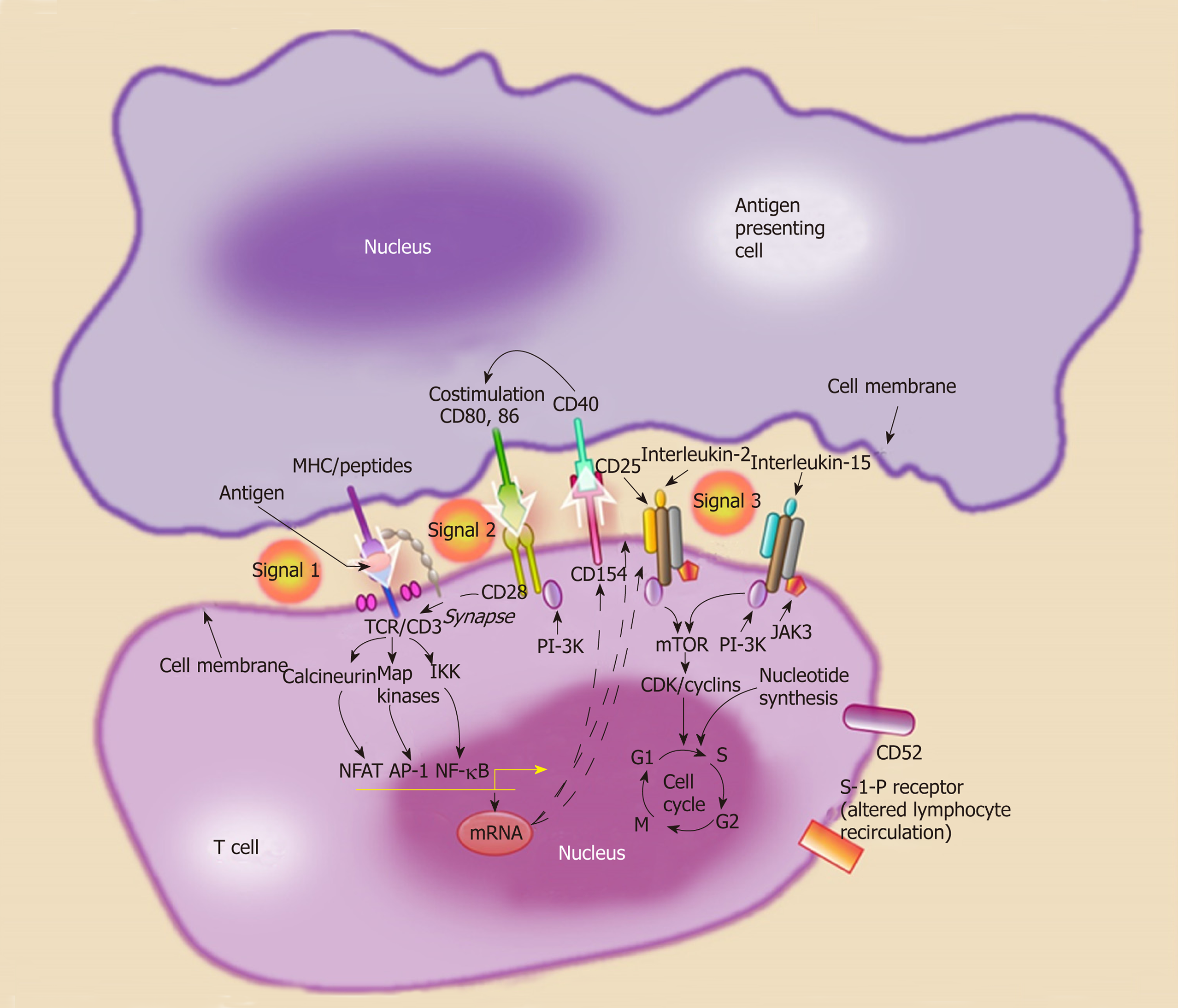
Figure 3 Activation of naïve helper T cells is thought to occur through a three signal pathway.
Signal 1, antigen recognition by the T cell receptor complex. Antigens are presented by major histocompatibility complex II cells [antigen presenting cells (APC) such dendritic cells]. Signal 2, co-stimulation, the interaction between the APC (CD80 and CD86) and the T cell (CD28). Signal 3, cellular proliferation and T cell differentiation into effector phenotypes (Th1, Th2), through cytokine stimulation. MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; APC: Antigen presenting cells.
- Citation: Abrol N, Jadlowiec CC, Taner T. Revisiting the liver’s role in transplant alloimmunity. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(25): 3123-3135
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i25/3123.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3123