Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2019; 25(13): 1566-1579
Published online Apr 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i13.1566
Published online Apr 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i13.1566
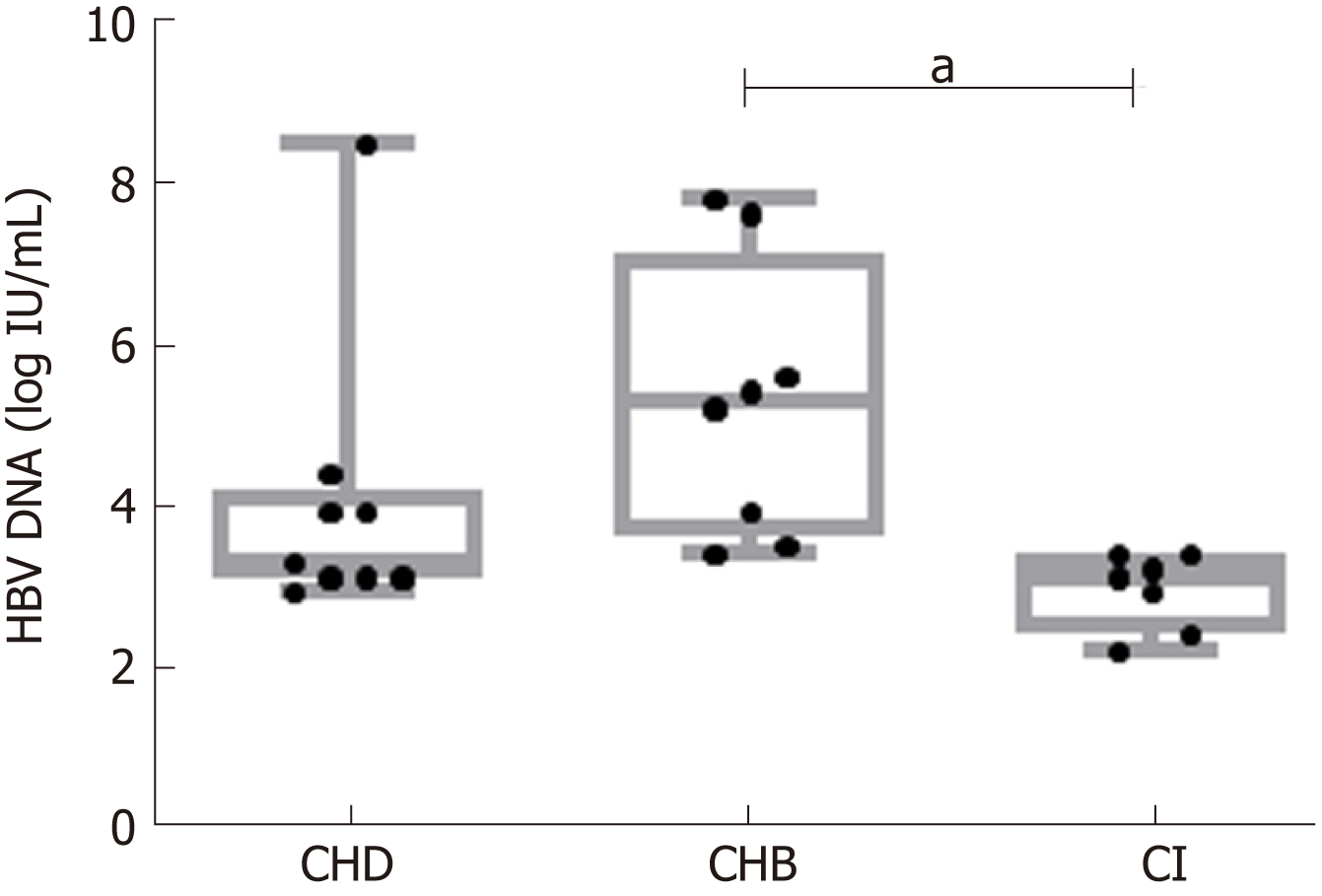
Figure 1 Comparison between hepatitis B virus-DNA serum levels in the three groups.
aP < 0.01. CHD: Chronic hepatitis delta; CHB: Chronic hepatitis B; CI: Hepatitis B virus chronic infection; HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
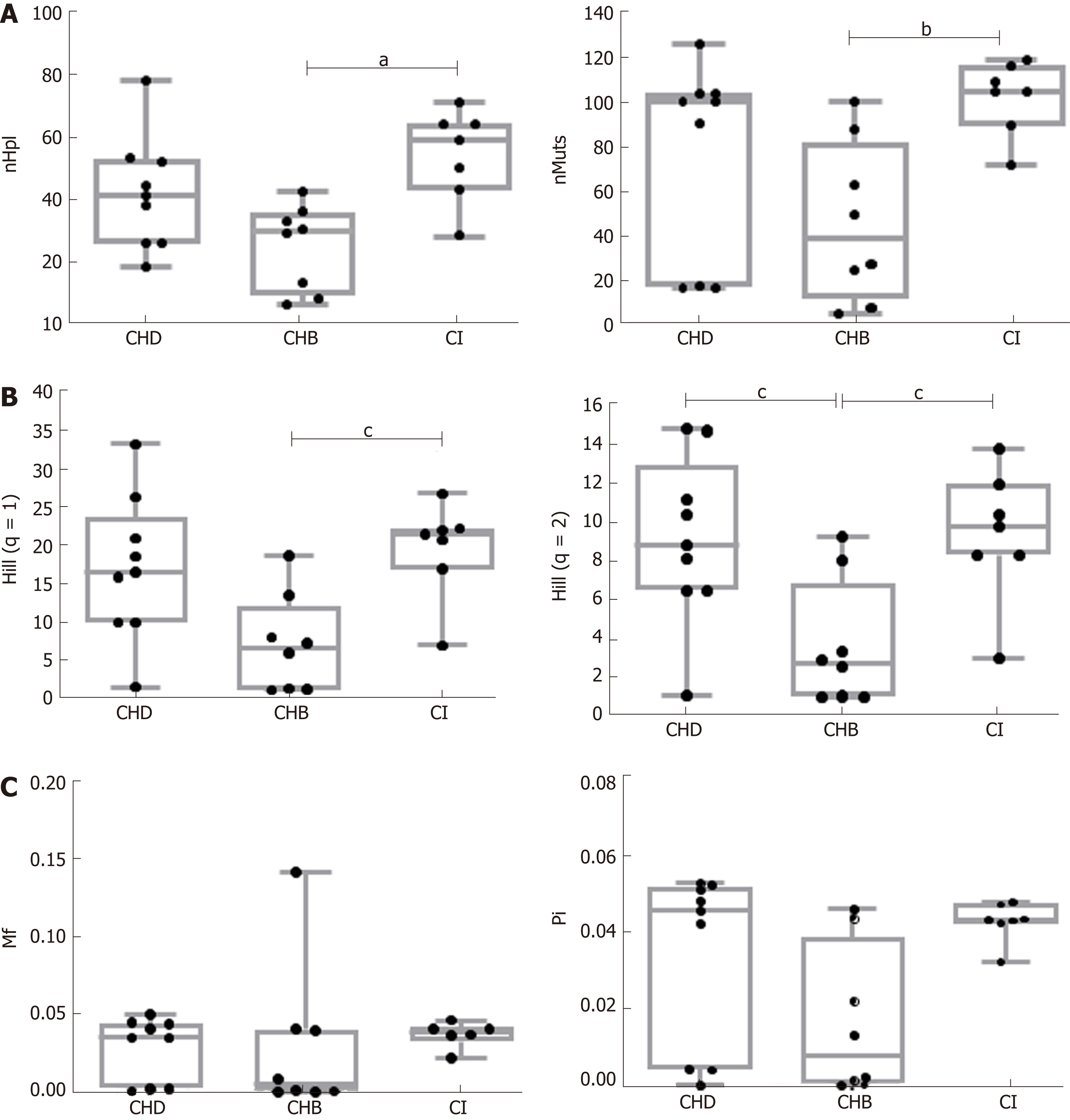
Figure 2 Comparison of the indices of hepatitis B virus quasispecies complexity between the three groups.
A: Incidence-based indices: Number of haplotypes (nHpl), number of mutations (nMuts) (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01); B: Abundance-based indices: Hill numbers (Hill q = 1 and Hill q = 2) (cP < 0.05); C: Functional-based indices: Mutation frequency (Mf) and nucleotide diversity (Pi). One outlier value in the CI group was eliminated in the representation of Mf results, but this value was included in the statistical comparisons. nHpl: Number of haplotypes; nMuts: Number of mutations; Mf: Mutation frequency; Pi: Nucleotide diversity; CHD: Chronic hepatitis delta; CHB: Chronic hepatitis B; CI: Hepatitis B virus chronic infection.
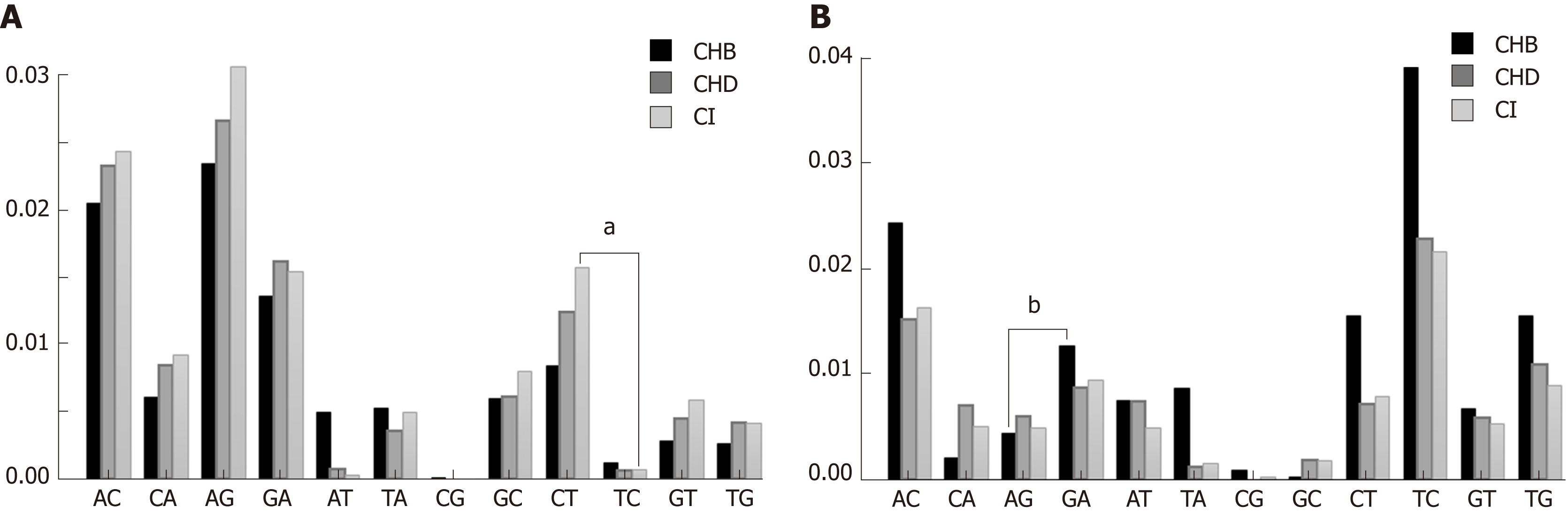
Figure 3 Nucleotide change patterns.
A: Genotype A substitution rates by group; B: Genotype D substitution rates by group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. CHD: Chronic hepatitis delta; CHB: Chronic hepatitis B; CI: Hepatitis B virus chronic infection.
- Citation: Godoy C, Tabernero D, Sopena S, Gregori J, Cortese MF, González C, Casillas R, Yll M, Rando A, López-Martínez R, Quer J, González-Aseguinolaza G, Esteban R, Riveiro-Barciela M, Buti M, Rodríguez-Frías F. Characterization of hepatitis B virus X gene quasispecies complexity in mono-infection and hepatitis delta virus superinfection. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(13): 1566-1579
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i13/1566.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i13.1566