Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2018; 24(5): 549-572
Published online Feb 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i5.549
Published online Feb 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i5.549
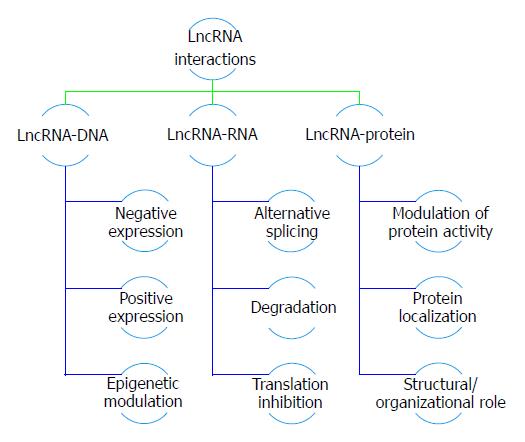
Figure 1 Long non-coding RNAs actions and interaction in cancer development; a schematic representation to the role of deregulated long non-coding RNAs in various types of cancers.
lncRNAs: Long non-coding RNAs.
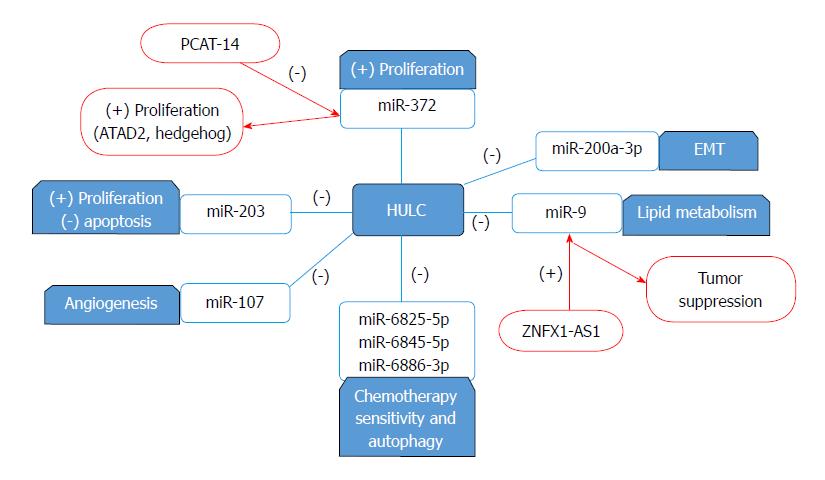
Figure 2 Highly up-regulated in liver cancer interactions with miRNA.
Highly up-regulated in liver cancer (HULC) inhibits the actions of miR-6825-5p, miR 6845-5p and miR 6886-3p which modulates the cell sensitivity to chemotherapy and autophagy. Moreover, it inhibits the function of miR-200a-3p hence inducing EMT and metastasis. HULC downregulates miR-107 promoting angiogenesis and tumor proliferation. Overexpression of HULC diminishes miR-203 antitumor effect. While HULC contributes to lipid deregulation and tumor progression through the downregulation of miR-9, ZNFX1-AS1 upregulates miR-9 resulting in tumor suppression HULC and PCAT-14 promote proliferation through the inhibition of miR-372 however through different mechanisms. (-): Inhibits/Downregulates (+): Upregulates. EMT: Epithelia-mesenchymal transition; PCAT: Prostate cancer-associated transcript.
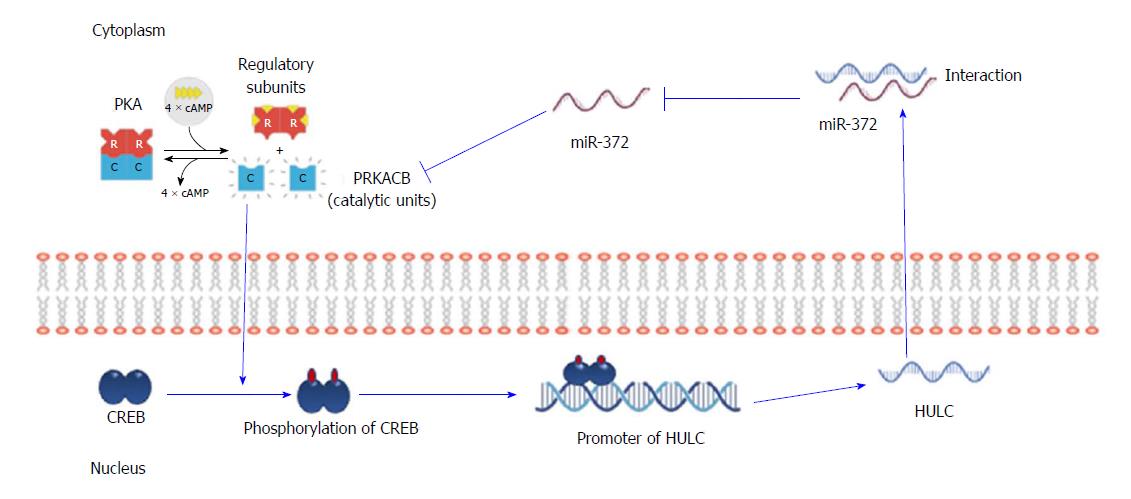
Figure 3 The auto-regulatory loop of highly up-regulated in liver cancer through inhibition miRNA-372 in hepatocellular carcinoma.
miR-372 binding to HULC can repress the expression and activity of miR-372. Inhibition of miR-372 leads to a reduction in translational repression of its target gene PRKACB, which in turn induces phosphorylation of CREB, thereby increasing the amount of CREB that can bind to the proximal promoter of HULC to induce HULC expression. HULC: Highly up-regulated in liver cancer.
- Citation: El Khodiry A, Afify M, El Tayebi HM. Behind the curtain of non-coding RNAs; long non-coding RNAs regulating hepatocarcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(5): 549-572
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i5/549.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i5.549