Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2018; 24(35): 4000-4013
Published online Sep 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i35.4000
Published online Sep 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i35.4000
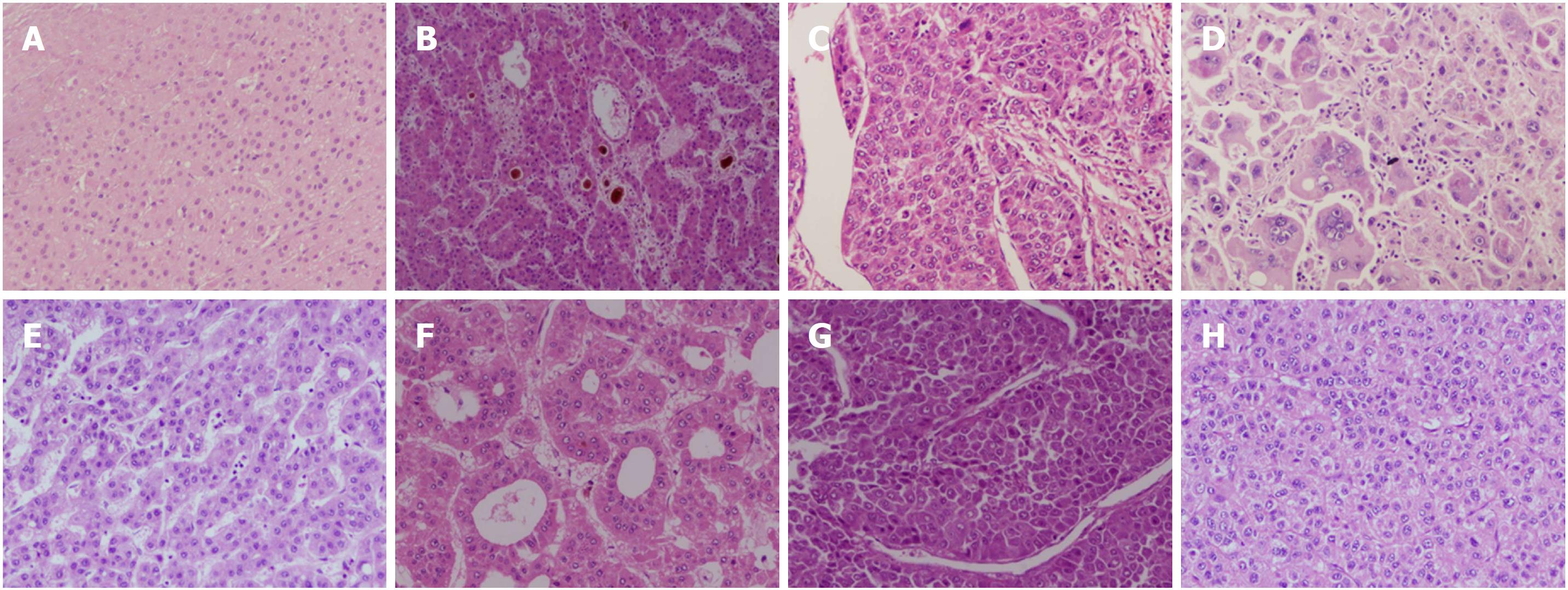
Figure 1 Hepatocellular carcinoma Edmondson and Steiner grading.
Grade 1 (A); grade 2 (B); grade 3 (C); and grade 4 (D). Most common patterns in histopathology of hepatocellular carcinoma: Microtrabecular (E); pseudoglandular (F); macrotrabecular (G); and compact (H). (HE stain).
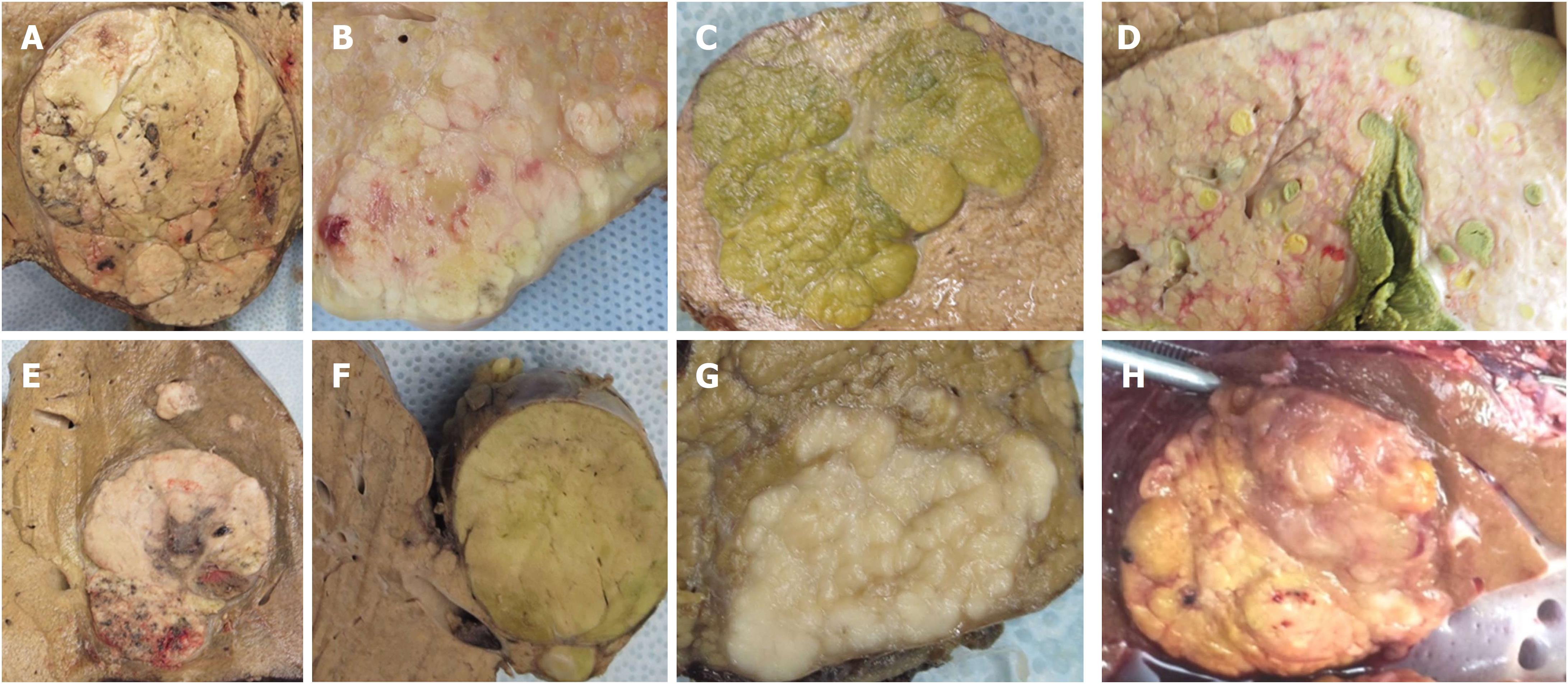
Figure 2 Gross morphology of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Single expanding nodular hepatocellular carcinoma (A); vaguely nodular with perinodular extension (B); Multinodular (C); multicentric with cirrhotomimetic appearance (D); nodular with satellite nodules (E); pedunculated (F); infiltrative (G); and hepatocellular carcinoma in non-cirrhotic background (H).
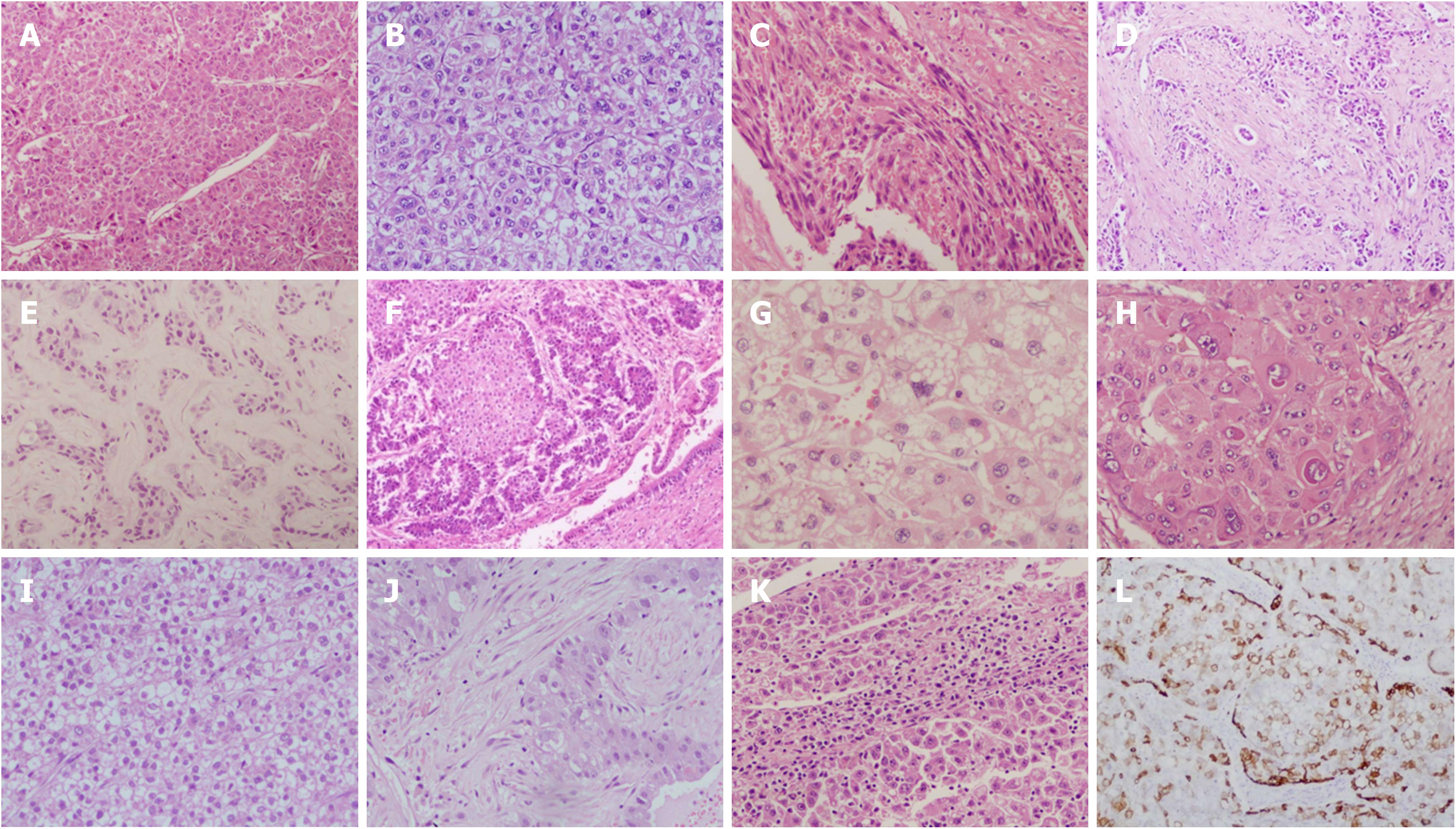
Figure 3 Hepatocellular carcinoma variants, subtypes and histological features.
Macrotrabecular (A); steatohepatitic (B); sarcomatoid (C); cholangiocellular (D); sclerosing (E); combined HCC-CC (F); HCC with foam cells (G); HCC with giant cells and hyaline bodies (H); clear cell (I); fibrolamellar (J); HCC with immune cells (K); CK19 positive stem cells (L). HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
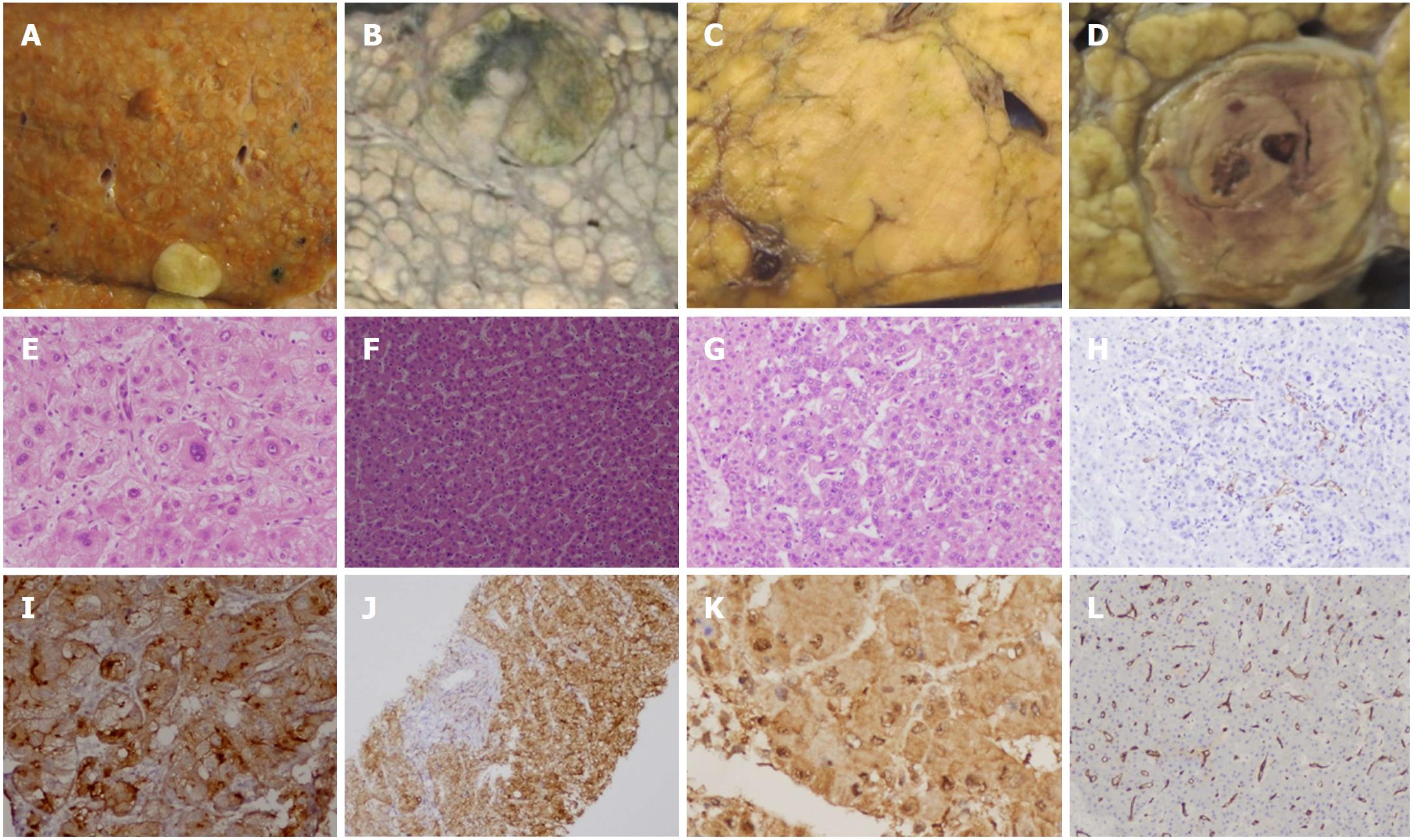
Figure 4 Dysplastic lesions and early hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gross morphology of small distinctly nodular HCC (A); small vaguely nodular HCC (B, C); HCC with nodule in nodule appearance (D). Microphotographs of large cell change (E) and small cell change (F) in dysplastic nodules. Nodule in nodule with low grade dysplasia surrounding central high grade dysplastic nodule (G) on HE stain and focal CD34 positive (H) on immunohistochemistry. Glypican-3 (I), glutamine synthetase (J), HSP-70 (K) and diffuse CD34 (L) immunostaining in well-differentiated HCC. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Rastogi A. Changing role of histopathology in the diagnosis and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(35): 4000-4013
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i35/4000.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i35.4000