Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2018; 24(21): 2279-2290
Published online Jun 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i21.2279
Published online Jun 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i21.2279
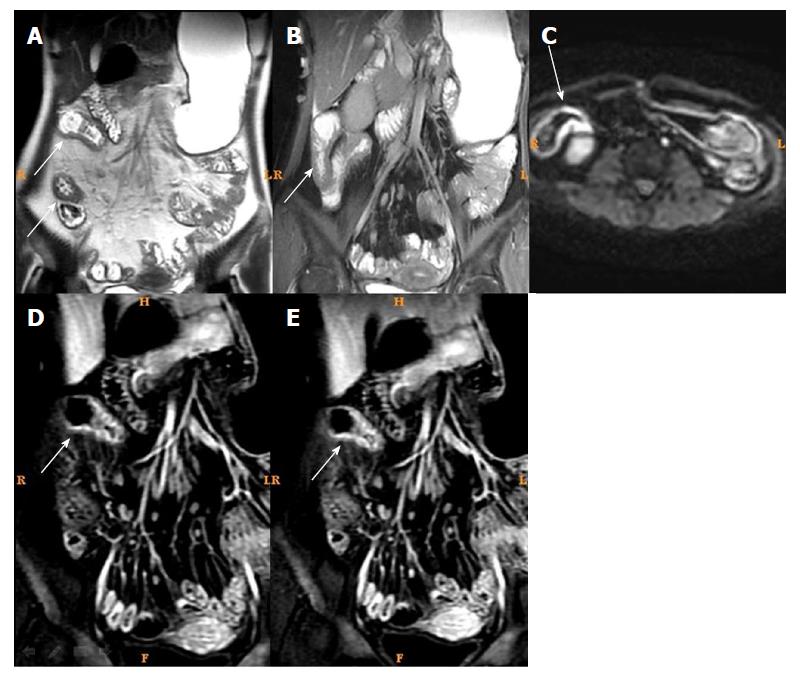
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging of a typical case of active Crohn’s disease before treatment.
Female, 32 years of age, active Crohn’s disease. A: T2WI showed intestinal wall thickening and submucosal edema in the distal ileum; B: Fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition showed intestinal wall thickening and submucosal edema in the distal ileum; C: Diffusion weight imaging showed marked high intensity; D and E: Dynamic enhancement showed obvious layer stratified enhancement.
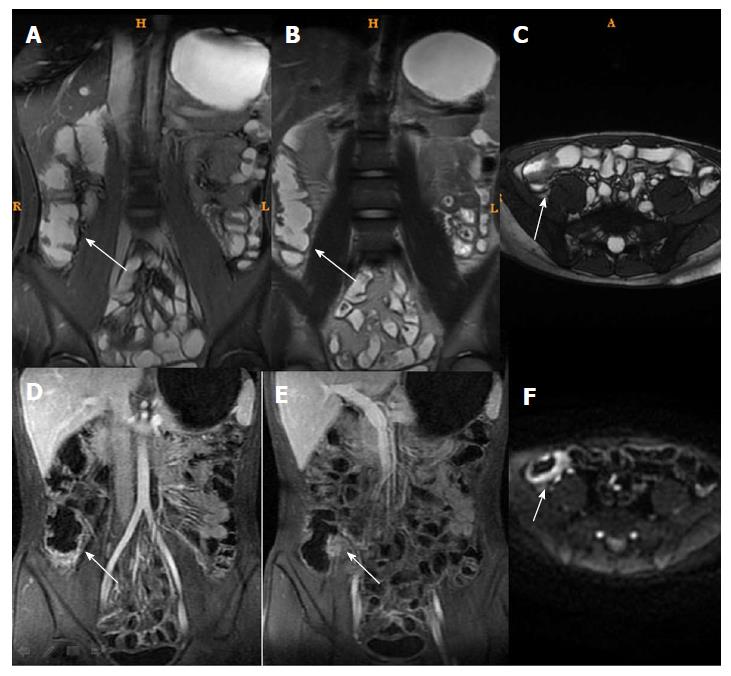
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging of a typical case of active Crohn’s disease after treatment (same patient as in Figure 1).
She remained in the active Crohn’s disease group after treatment. A: T2WI showed intestinal wall thickened and submucosal edema decrease in the distal ileum; B: Fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition showed intestinal wall thickened and submucosal edema decrease in the distal ileum; C: Diffusion weight imaging showed less high intensity; D and E: Dynamic enhancement showed layer stratified enhancement.
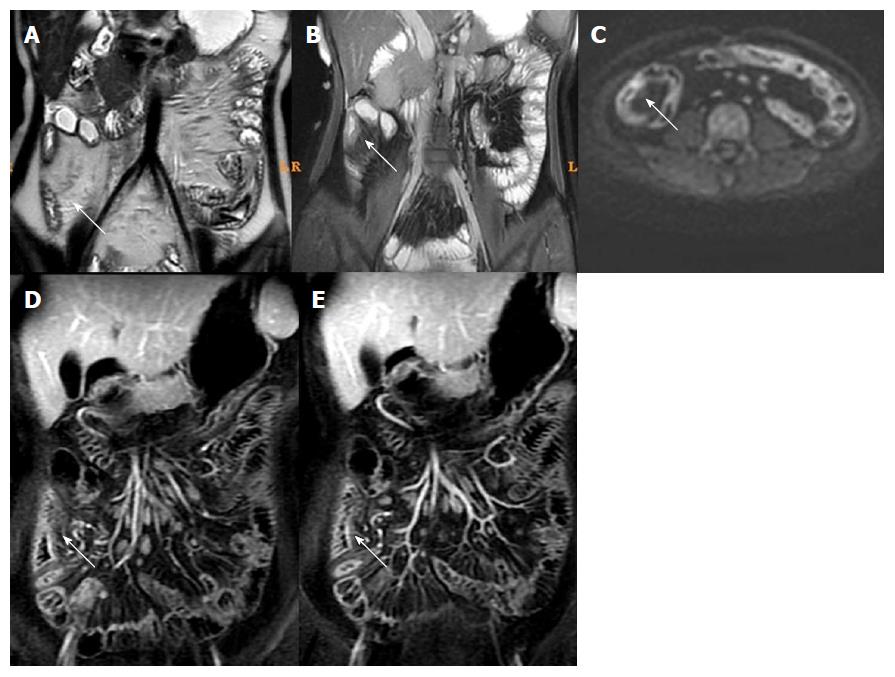
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance imaging of a typical case of active Crohn’s disease before treatment.
Male, 25 years of age, active Crohn’s disease. A: Fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition showed intestinal wall thickening and submucosal edema in the ascending colon; B and C: T2WI showed intestinal wall thickening and submucosal edema in the ascending colon; D and E: Dynamic enhancement showed obvious enhancement; F: Diffusion weight imaging showed marked high intensity.
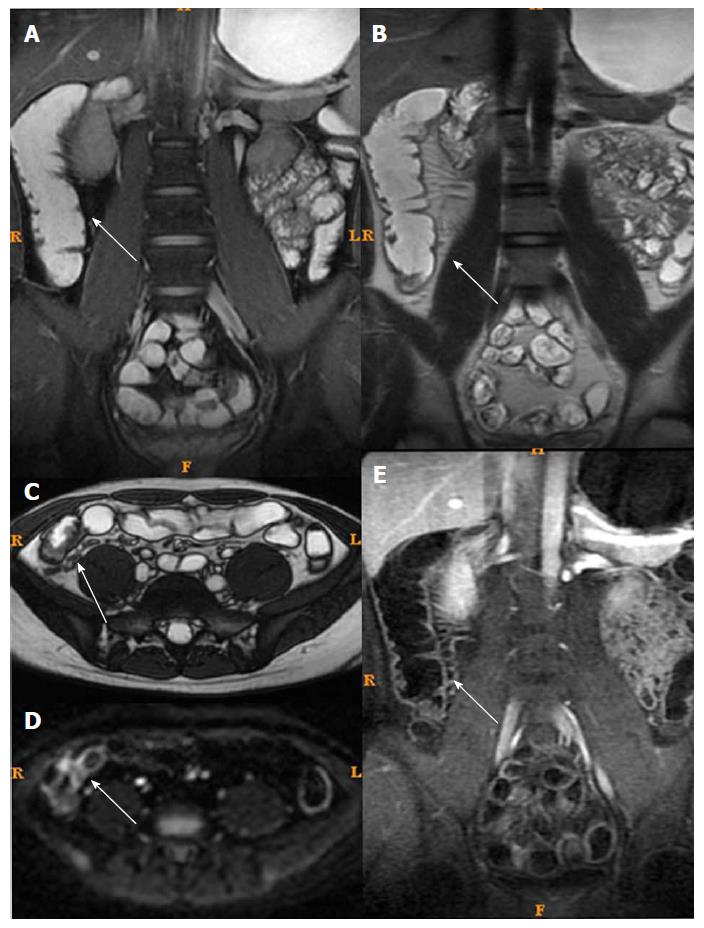
Figure 4 Magnetic resonance imaging of a typical case of active Crohn’s disease after treatment (same patient as in Figure 3).
The patient was in remission (inactive Crohn’s disease) after treatment. A: Fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition showed decreased intestinal wall thickening and no submucosal edema; B and C: T2WI showed decreased intestinal wall thickening and no submucosal edema; D: Diffusion weight imaging showed less high intensity; E: Enhancement showed less enhancement.
- Citation: Zhu NY, Zhao XS, Miao F. Magnetic resonance imaging and Crohn’s disease endoscopic index of severity: Correlations and concordance. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(21): 2279-2290
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i21/2279.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i21.2279