Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2017; 23(48): 8512-8525
Published online Dec 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i48.8512
Published online Dec 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i48.8512
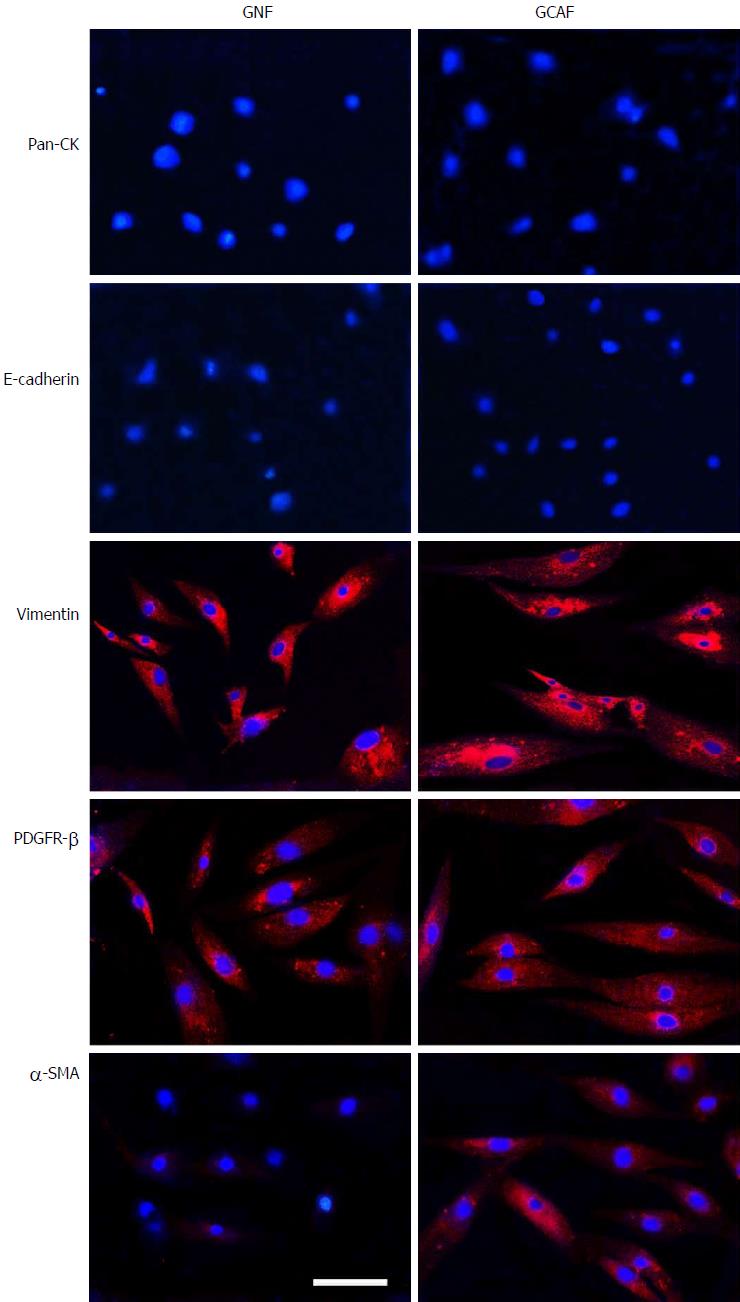
Figure 1 Identification of gastric normal fibroblast and gastric cancer-associated fibroblast.
Fibroblasts were isolated from the tumor and adjacent normal tissues of a gastric adenocarcinoma patient. The expression of Pan-CK, E-cadherin, vimentin, PDGFR-β and α-SMA in the cultured fibroblast cells was detected by immunofluorescence. Scale bar: 100 μm.
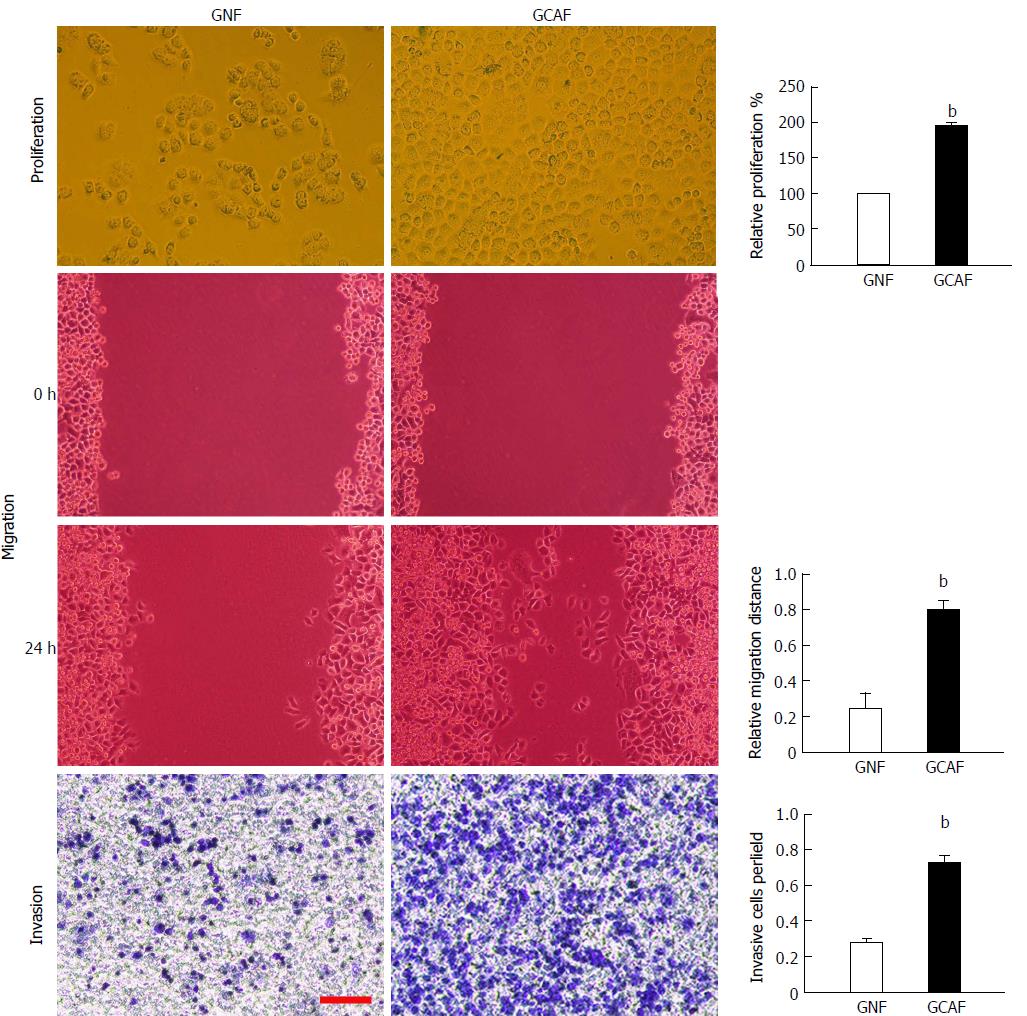
Figure 2 Gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts promote the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells.
BGC-823 cells were cultured with GNF- or GCAF-conditioned medium for 48 h; then, proliferation, migration and invasion capacities were measured. Scale bar: 100 μm. Data are plotted as mean ± SD of three separate experiments. bP < 0.01 vs the BGC-823 cells cultured with GNF-conditioned medium.
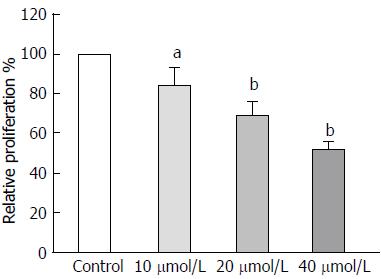
Figure 3 Astragaloside IV inhibited the proliferation-promoting capacity of gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts.
Conditioned media were prepared from the GCAFs treated by vehicle control, 10 μmol/L astragaloside IV, 20 μmol/L astragaloside IV or 40 μmol/L astragaloside IV, and used to culture BGC-823 cells. After culture for 48 h, the proliferation capacity of the BGC-823 cells was measured. Data are plotted as mean ± SD of three separate experiments. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs the BGC-823 cells cultured with the conditioned medium from control-treated GCAFs.
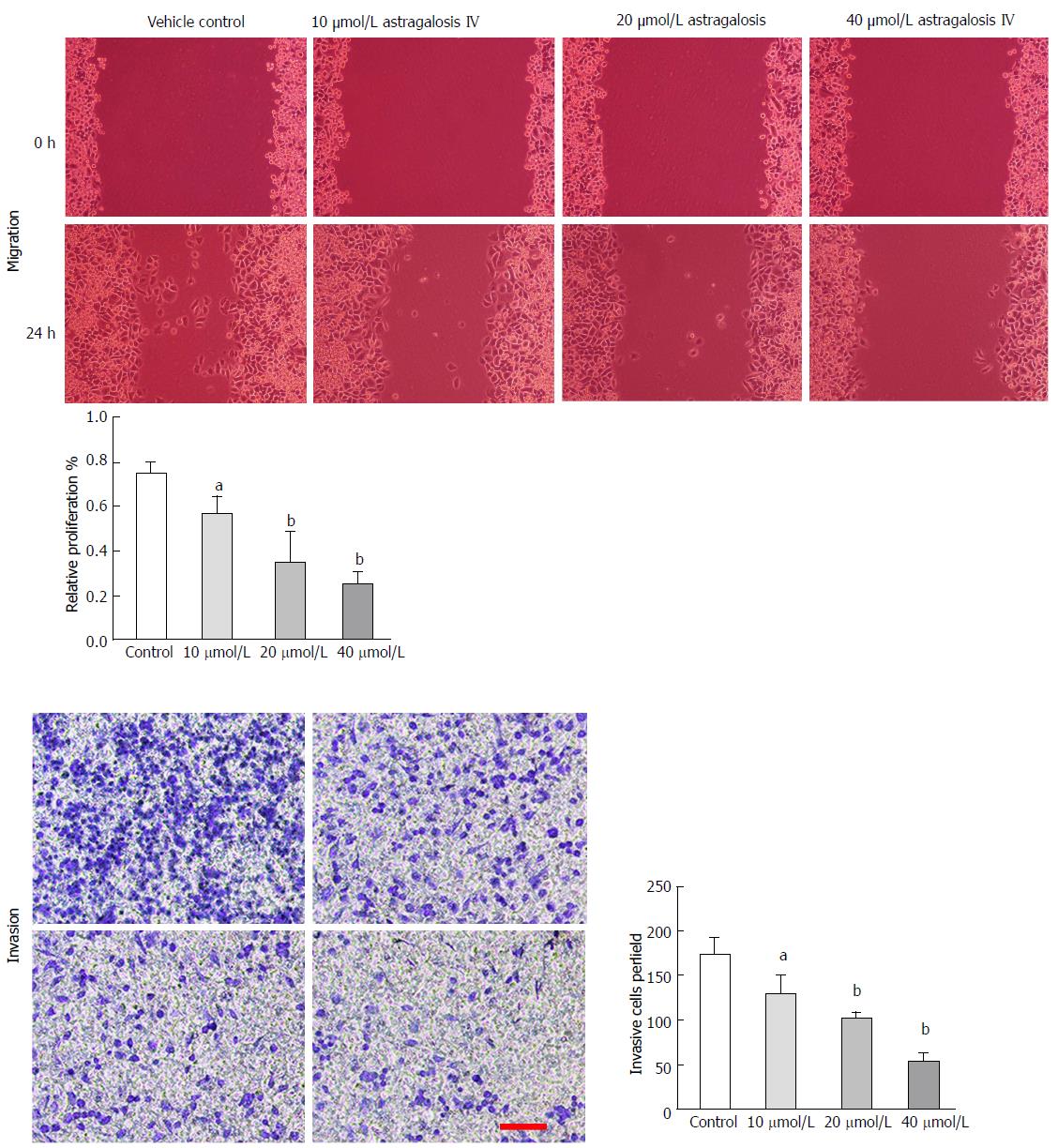
Figure 4 Astragaloside IV inhibited the migration- and invasion-promoting capacities of gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts.
Conditioned media were prepared from the GCAFs treated by vehicle control, 10 μmol/L astragaloside IV, 20 μmol/L astragaloside IV or 40 μmol/L astragaloside IV, and used to culture BGC-823 cells. After culture for 48 h, the migration and invasion capacities of the BGC-823 cells were measured. Scale bar: 100 μm. Data are plotted as mean ± SD of three separate experiments. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs the BGC-823 cells cultured with the conditioned medium from control-treated GCAFs.
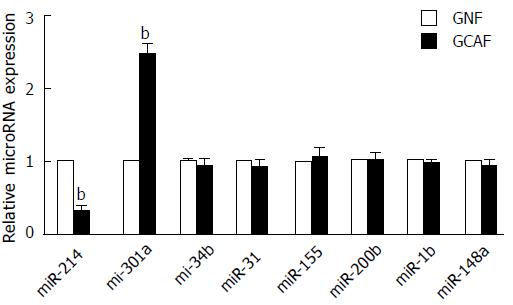
Figure 5 The expression of miR-214 and miR-301a was abnormally decreased and increased in the gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts, respectively.
bP < 0.01 vs the GNFs.
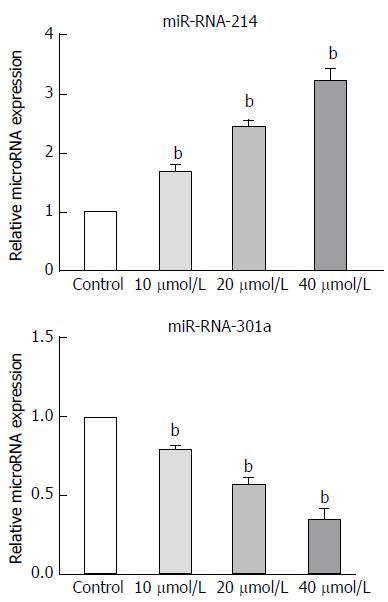
Figure 6 Astragaloside IV treatment up-regulated miR-214 and down-regulated miR-301a expression in the gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts.
Data are plotted as mean ± SD of three separate experiments; bP < 0.01 vs control-treated GCAFs.
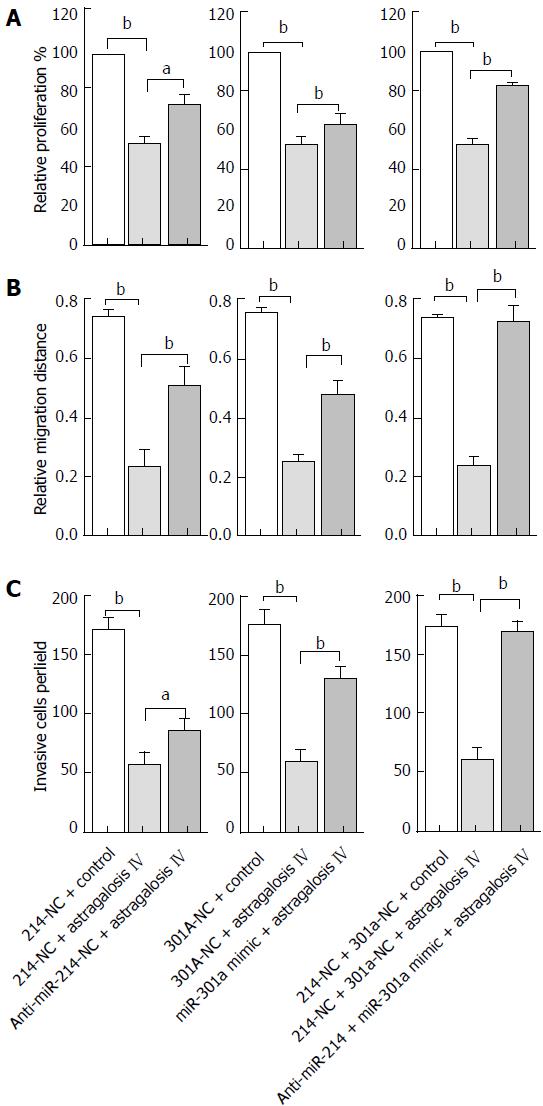
Figure 7 Effects of anti-miR-214 and miR-301a mimic on the astragaloside IV-induced inhibition of proliferation-, migration- and invasion-promoting capacities of the gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts.
The GCAFs were transfected with 50 nmol/L 214-NC, anti-miR-214, 301a-NC or miR-301a mimic, or co-transfected with 50 nmol/L 214-NC and 50 nmol/L 301a-NC or 50 nmol/L anti-miR-214 and 50 nmol/L miR-301a mimic. After 48 h of transfection, the cells were treated with vehicle control or 40 μmol/L astragaloside IV; conditioned media were prepared to culture BGC-823 cells, whose proliferation (A), migration (B) and invasion (C) capacities were then measured. Data are plotted as mean ± SD of three separate experiments. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01.
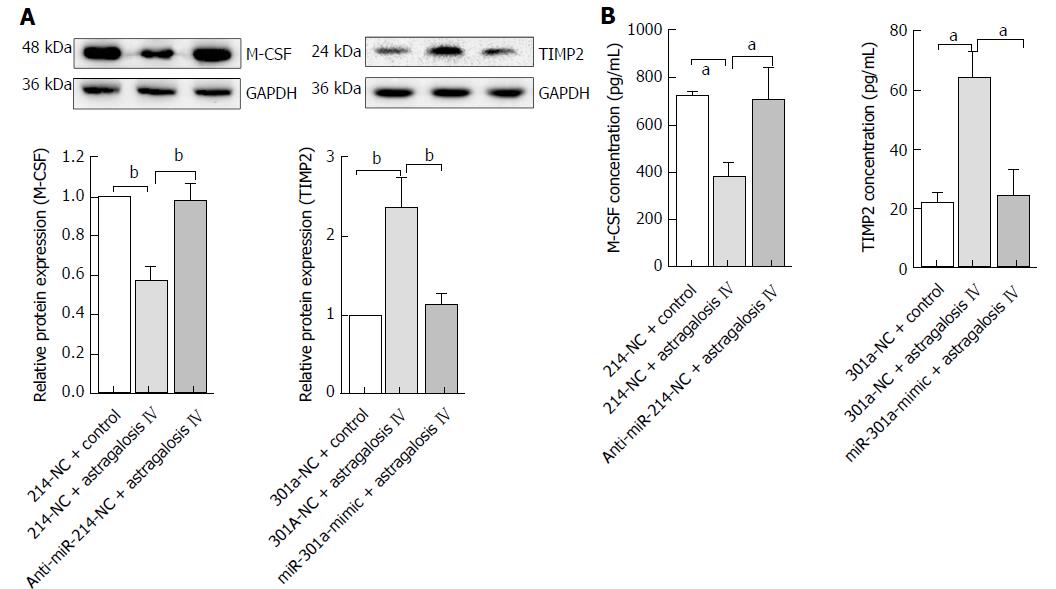
Figure 8 Astragaloside IV suppressed M-CSF and elevated TIMP2 protein expression (A) and secretion (B) in the gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts.
Data are plotted as mean ± SD of three separate experiments. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01.
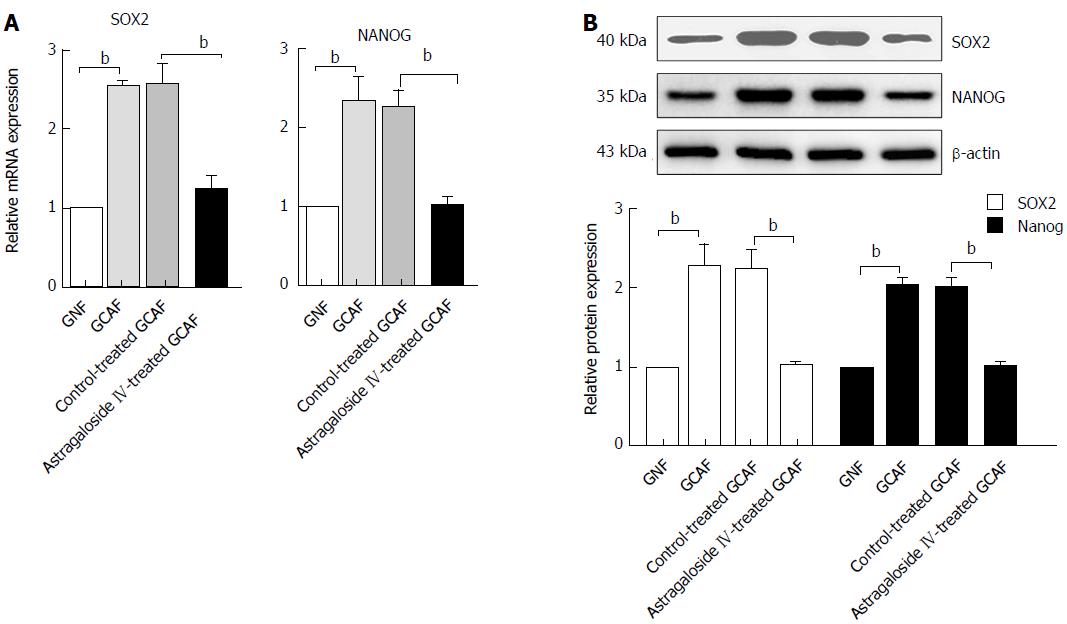
Figure 9 Astragaloside IV abolished the GCAF-induced up-regulation of SOX2 and NANOG in BGC-823 cells.
BGC-823 cells were cultured with conditioned media from the GNFs, GCAFs, control-treated GCAFs or 40 μmol/L astragaloside IV-treated GCAFs. Then, the mRNA (A) and protein (B) expression of SOX2 and NANOG were determined. Data are plotted as mean ± SD of three separate experiments. bP < 0.01.
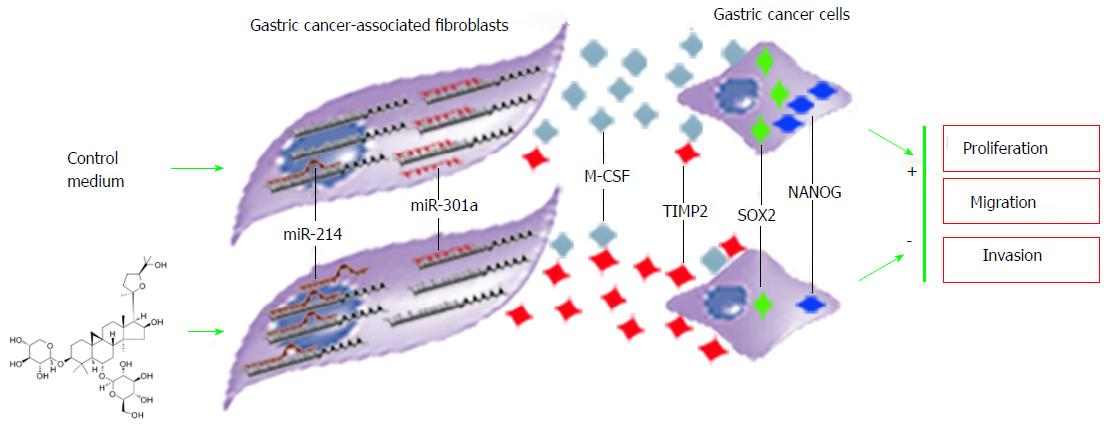
Figure 10 Schematic of the mechanism for astragaloside IV-induced inhibition on the proliferation-, migration- and invasion-promoting capacities of gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts.
- Citation: Wang ZF, Ma DG, Zhu Z, Mu YP, Yang YY, Feng L, Yang H, Liang JQ, Liu YY, Liu L, Lu HW. Astragaloside IV inhibits pathological functions of gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(48): 8512-8525
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i48/8512.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i48.8512