Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2017; 23(36): 6726-6732
Published online Sep 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6726
Published online Sep 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6726
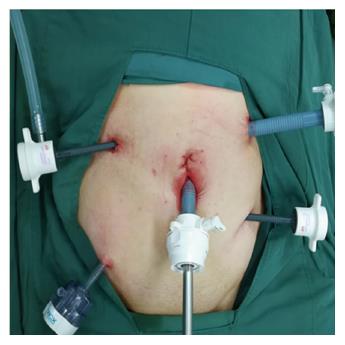
Figure 1 Five-port technique.
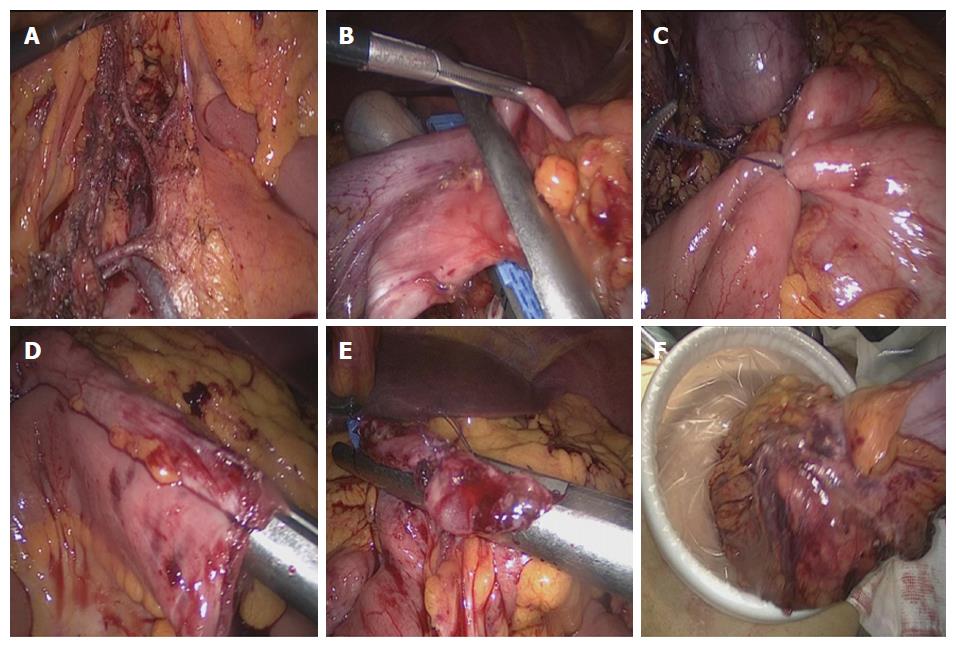
Figure 2 Surgical procedure.
A: The ileocolic vessels, ascending colon vessels, and the right branch of the transverse colon vessels were exposed; B: The right half of the transverse colon was transected using endoscopic linear cutter staplers; C: The proximal ileum and the distal transverse colon were fixed in an overlapped fashion using a piece of absorbable suture to facilitate anastomosis; D: After imbedding the lumens with an endoscopic linear cutter stapler, intestinal walls with no mesentery were got through; E: The common opening was then closed using an endoscopic linear cutter stapler; F: Finally, the specimen was removed from the abdominal cavity using a transverse incision above the symphysis pubis.
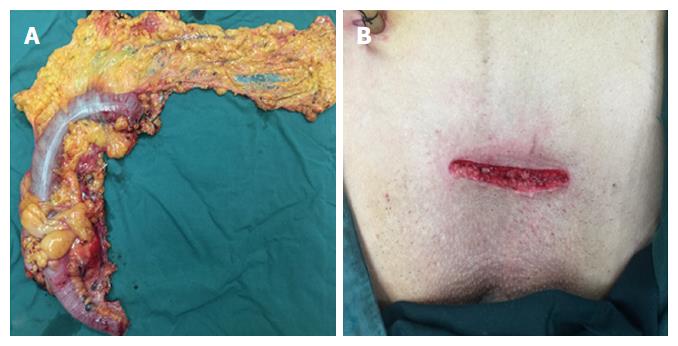
Figure 3 Typical specimen (A) and a transverse incision above the symphysis pubis (B).
- Citation: Zhou HT, Wang P, Liang JW, Su H, Zhou ZX. Short-term outcomes of overlapped delta-shaped anastomosis, an innovative intracorporeal anastomosis technique, in totally laparoscopic colectomy for colon cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(36): 6726-6732
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i36/6726.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6726