Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2017; 23(30): 5610-5618
Published online Aug 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5610
Published online Aug 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5610
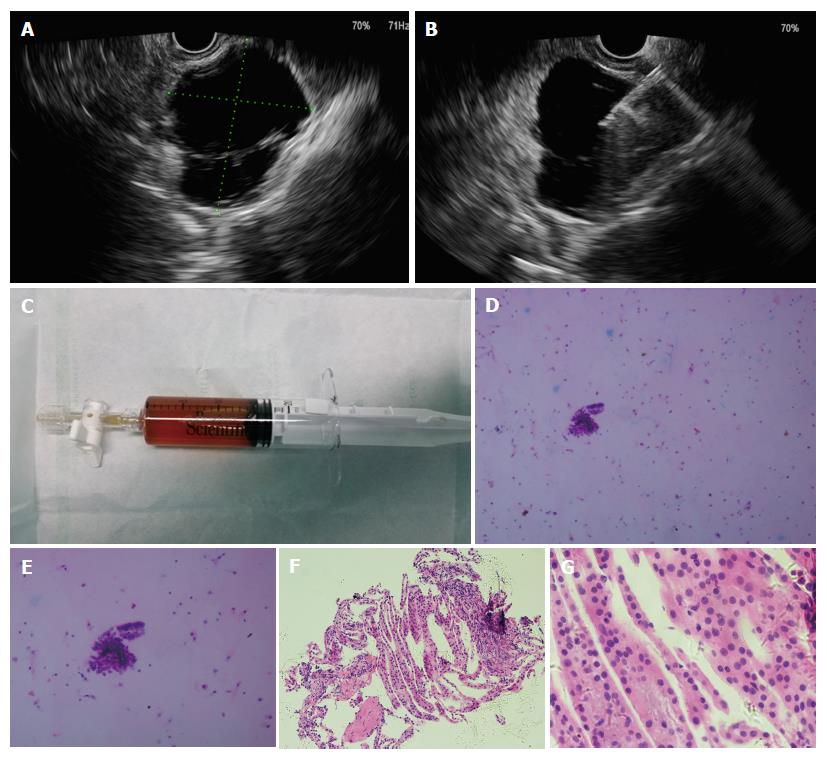
Figure 1 The procedures of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration.
A: Endoscopic ultrasound view of the cyst, showing a 46.0 mm2 × 39.0 mm2 cyst in pancreatic neck; B: Puncture of the cyst with a 19-guage needle and aspiration of the cystic fluid; C: Specimen of cystic fluid, sent for cytology and biochemical analysis; D: Histopathological image of cystic fluid cytology, diagnosed with serous cystic neoplasm (H and E, × 100); E: Histopathological image of cystic fluid cytology (H and E, × 200); F: Histopathological image of biopsy of the cystic wall of the same cyst (H and E, × 10); G: Histopathological image of biopsy of the cystic wall of the same cyst (H and E, × 40).
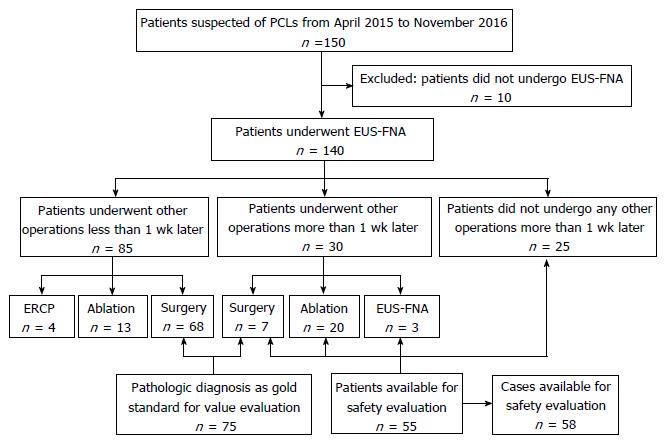
Figure 2 Study flowchart.
ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; EUS-FNA: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration; PCLs: Pancreatic cystic lesions.
- Citation: Du C, Chai NL, Linghu EQ, Li HK, Sun YF, Xu W, Wang XD, Tang P, Yang J. Incidents and adverse events of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for pancreatic cystic lesions. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(30): 5610-5618
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i30/5610.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5610