Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2017; 23(14): 2511-2518
Published online Apr 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i14.2511
Published online Apr 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i14.2511
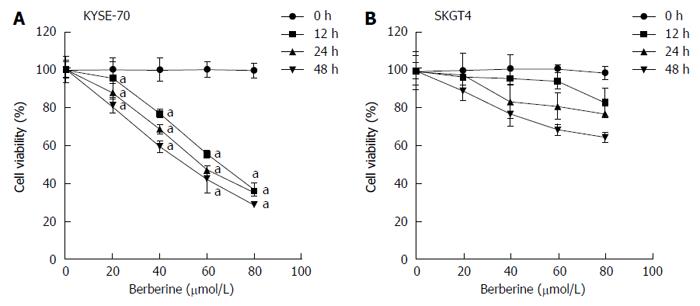
Figure 1 Effects of berberine on viability of esophageal cancer cells.
A, B: KYSE-70 (A) and SKG4 (B) cells were treated with berberine (0, 20, 40, 60 and 80 μmol/L) for 12, 24 and 48 h and the number of viable cells was measured by MTT assay. Data are expressed as mean ± SD of three experiments. aP < 0.05 vs controls.
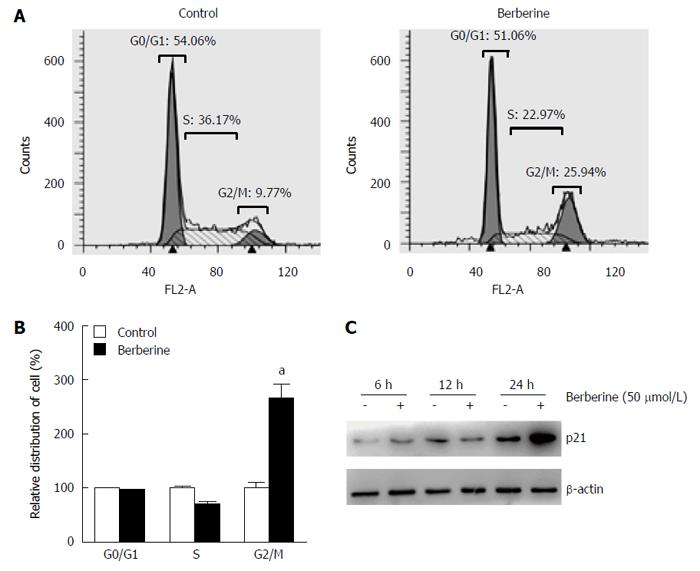
Figure 2 Berberine treatment induced cell cycle arrest in G2/M phase.
A: Flow cytometry analysis of proliferating KYSE-70 cells at 48 h after administration of 50 μmol/L berberine; B: Relative percentages of berberine-treated cells to control cells in different cell cycle phases are shown as the mean ± SE of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05 vs controls; C: Protein expression level of p21 in KYSE-70 cells was examined after berberine administration at 6, 12 and 24 h.
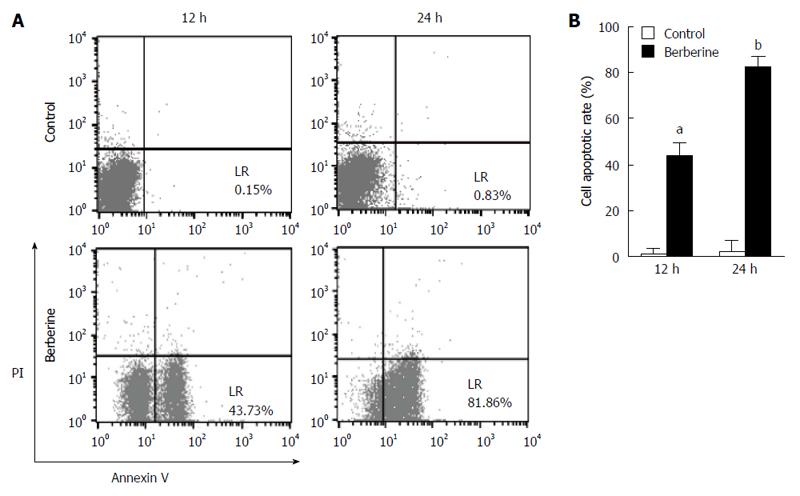
Figure 3 Berberine promotes apoptosis in KYSE-70 cells.
A: KYSE-70 cells were treated with 50 μmol/L berberine for 12 and 24 h. Apoptotic rates were measured using flow cytometry; B: Apoptotic cell values are expressed as mean ± SE of three experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs controls.
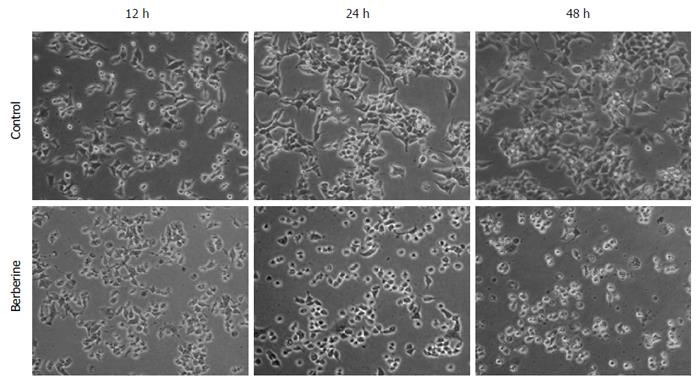
Figure 4 Berberine treatment induced morphological changes of KYSE-70 cells.
Control cells and 50 μmol/L berberine-treated cells were observed under a phase contrast microscope at 12, 24 and 48 h after treatment. Bar represents all images equal to 200 μmol/L.
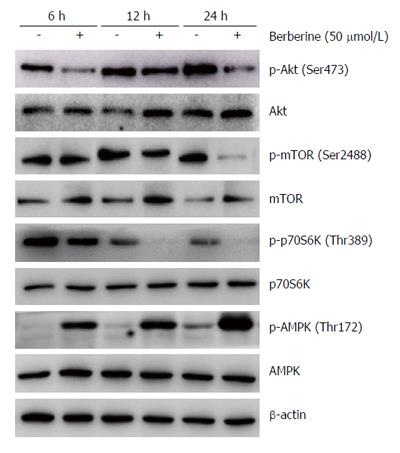
Figure 5 Effects of berberine on AMPK and AKT/mTOR/p70S6K activities.
KYSE-70 cells were treated with 50 μmol/L berberine for 6, 12 and 24 h, and protein expressions of p-AKT, AKT, p-mTOR, mTOR, p-p70S6K, p70S6K, p-AMPK and AMPK were analyzed by western blotting.
- Citation: Jiang SX, Qi B, Yao WJ, Gu CW, Wei XF, Zhao Y, Liu YZ, Zhao BS. Berberine displays antitumor activity in esophageal cancer cells in vitro. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(14): 2511-2518
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i14/2511.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i14.2511