Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2016; 22(9): 2736-2748
Published online Mar 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i9.2736
Published online Mar 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i9.2736
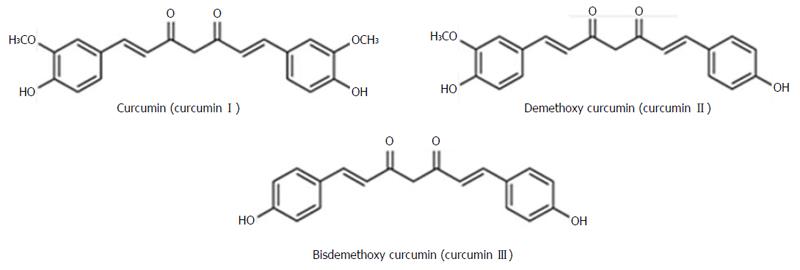
Figure 1 Structure of curcuminoids: Curcumin I, II and III.
Adapted from Park et al[75]. New perspectives of curcumin in cancer prevention.
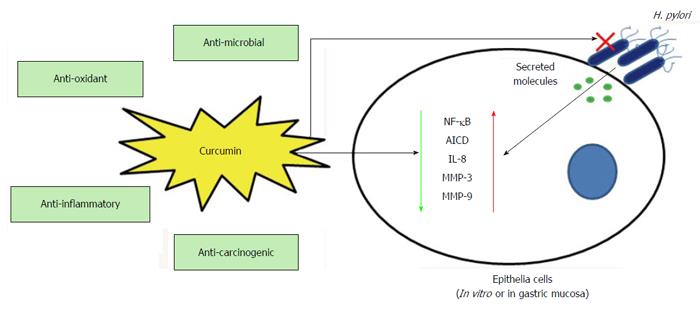
Figure 2 Role of curcumin in Helicobacter pylori infection.
Important properties of curcumin which probably helps host cells in H. pylori infection are anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-carcinogenic. Other than its direct anti-H. pylori effect (anti-microbial) curcumin inhibits H. pylori induced NF-κB, AICD, IL-8, MMP-3 and MMP-9 in host epithelial cells and thereby protects from inflammatory response (may sometime leads to host cell apoptosis). MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinases; IL: Interleukin; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; AICD: Activation induced cytidine deaminase.
- Citation: Sarkar A, De R, Mukhopadhyay AK. Curcumin as a potential therapeutic candidate for Helicobacter pylori associated diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(9): 2736-2748
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i9/2736.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i9.2736