Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2016; 22(6): 1966-1974
Published online Feb 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.1966
Published online Feb 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.1966
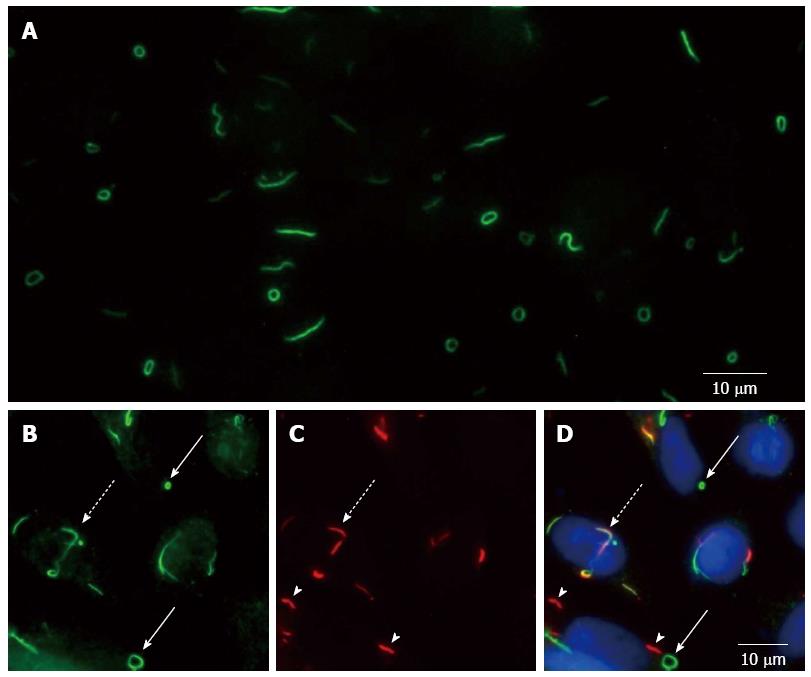
Figure 1 Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase 2 and cytidine triphosphate synthetase enzymes can aggregate into rods and rings structures.
A: Representative image of the RR pattern observed in a Euroimmun HEp-2 slide; B-D: HEp-2 cells were cultivated with DON treatment and labeled by indirect immunofluorescence with anti-RR-positive HCV serum (B) and rabbit anti-CTPS1 antibody (C). Merged image of panel B and C plus DAPI (D). IMPDH2-based (solid arrows), CTPS-based (arrowheads), and mixed RR structures (dotted arrows) can be observed. (A-D) All data and images were obtained in our own laboratory from assays performed by Keppeke GD. RR: Rods and rings; DON: 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; IMPDH2: Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase 2; CTPS: Cytidine triphosphate synthetase.
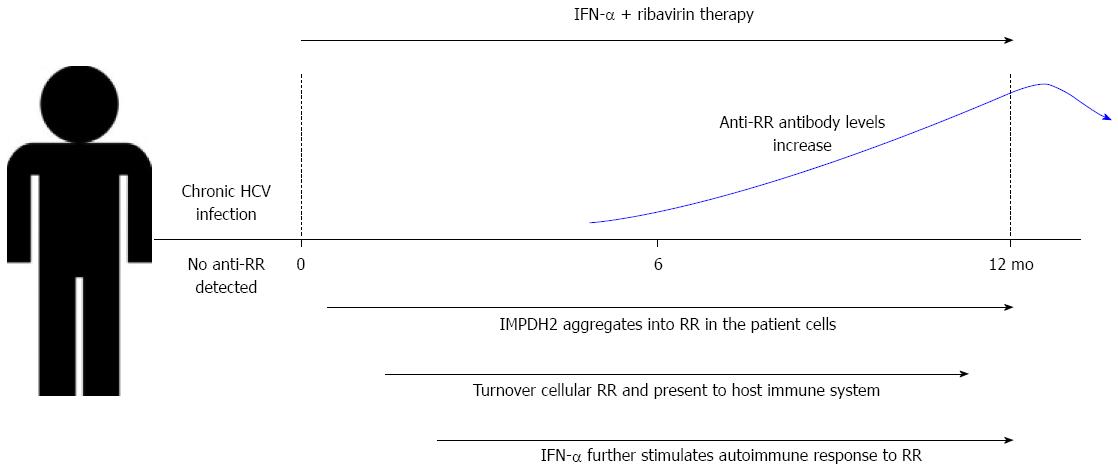
Figure 2 Anti-rods and rings autoantibody production in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection.
Ribavirin therapy leads cells to present RR structures, while interferon-α stimulates the host immune system. These factors, plus others yet to be confirmed, could contribute to the tolerance breakdown with autoantibody production against RR structures, whose levels increase during treatment. RR: Rods and rings; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; IFN: Interferon.
- Citation: Keppeke GD, Calise SJ, Chan EK, Andrade LEC. Anti-rods/rings autoantibody generation in hepatitis C patients during interferon-α/ribavirin therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(6): 1966-1974
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i6/1966.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.1966