Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2016; 22(42): 9300-9313
Published online Nov 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9300
Published online Nov 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9300
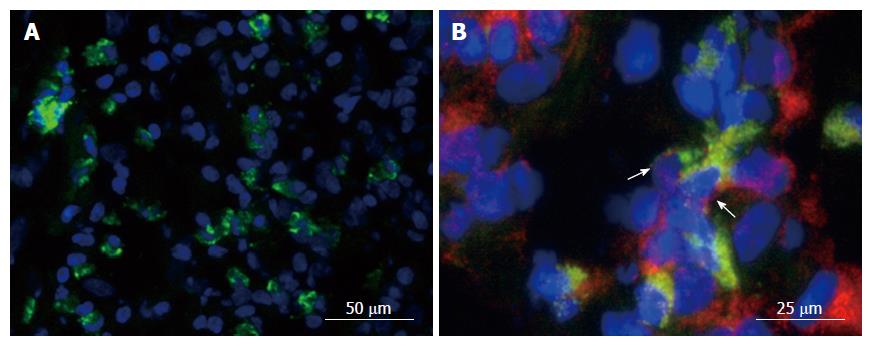
Figure 1 Expression of membrane-bound tumor necrosis factor in the gut.
Gut tissue of patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) was cryo-frozen and stained for cell markers by immunofluorescence. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. A: Staining for mTNF (green). B: Staining for mTNF (green) and CD14 (red). Co-expressing cells are labeled with an arrow.
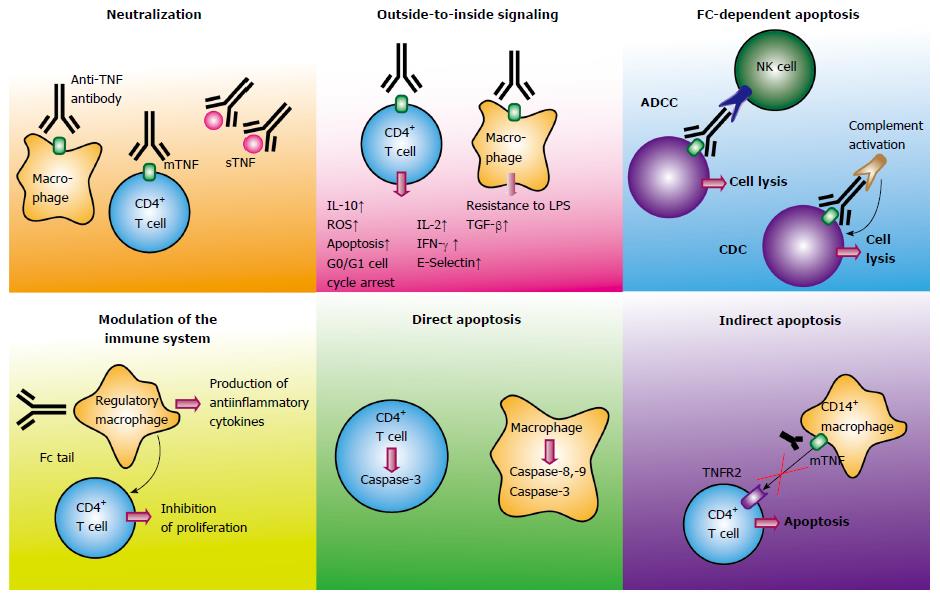
Figure 2 Mechanism of action of anti-tumor necrosis factor antibodies in inflammatory bowel disease.
Schematic illustration of different modes of action of anti-TNF antibodies in inflammatory bowel diseases. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; mTNF: Membrane-bound TNF; sTNF: Soluble TNF; TNFR: TNF receptor; NK cell: Natural killer cell; ADCC: Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; CD: Crohn’s disease; CDC: Complement-dependent cytotoxicity; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.
- Citation: Billmeier U, Dieterich W, Neurath MF, Atreya R. Molecular mechanism of action of anti-tumor necrosis factor antibodies in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(42): 9300-9313
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i42/9300.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9300